|
|
SQL (Structured Query Language) is a powerful language used for managing and manipulating relational databases. It provides a standardized language for querying the databases which are found to be structured, allowing users to define, manipulate, and control the data retrieval with ease. SQL operates through a variety of commands and operators that facilitate some of the most important tasks that are listed below:
To perform these operations, learning about the operators that are used in them is crucial. Having an in-depth knowledge of the operators and their syntax allows us to write much more efficient queries. MySQL NOT EQUAL OperatorIn MySQL, the NOT EQUAL operator is used to compare two expressions to determine if they are not equal. This operator is primarily used for filtering results in queries to exclude specific values or find records that differ from a given value. Efficient use of the NOT EQUAL operator can significantly enhance your ability to manipulate and retrieve data from a MySQL database. In MySQL, there are two ways to express the NOT EQUAL operator:
Both operators function identically and can be used interchangeably. Syntax:SELECT column_name(s) Parameters:
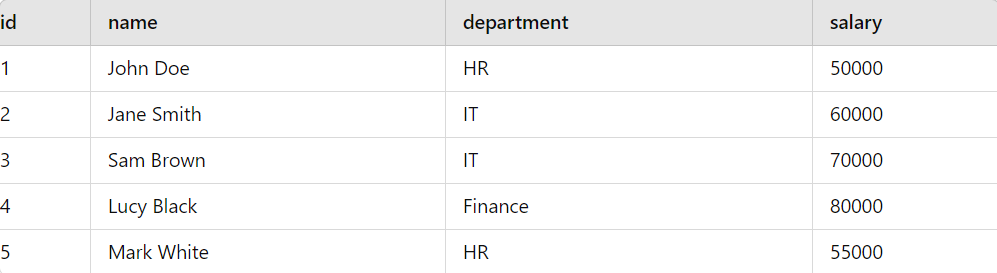
Let’s understand the working of a NOT EQUAL operator by working with a live example. Example of MySQL NOT EQUAL OperatorCreatin the employees table: -- Create the employees table Output:  Employees Table 1. Using != OperatorTo find all employees who do not work in the IT department, you can use the following query: SELECT name, department Output:
Explanation: This query retrieves the names and departments of all employees who do not work in the IT department from the employees table. It filters out employees in the IT department, returning only those in other departments. 2. Using the <> operatorSuppose you want to find all employees who do not have a salary of 60000. You can use the following query SELECT name, salary Output:
Explanation: This query retrieves the names and salaries of all employees who do not have a salary of 60,000 from the employees table. It filters out employees with a salary of 60,000, returning only those with different salaries. ConclusionThe MySQL NOT EQUAL operator (!= or <>) is a powerful and flexible tool for filtering data that doesn’t match a specific value. By learning how to use this operator effectively, you can make your SQL queries more precise and efficient. Whether you’re excluding certain records or searching for values that are different from a given criterion, the NOT EQUAL operator can help you get the results you need. Adding this operator to your SQL skill set will enhance your ability to work with databases and retrieve the exact data you want. FAQs on MySQL NOT EQUAL OperatorWhat is the difference between
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Databases |
| Related |
|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 19 |