|
|
The MongoDB aggregation framework in Node.js performs data aggregation operations such as filtering, grouping and transforming documents within a collection. This is achieved using aggregation pipelines. An aggregation pipeline consists of multiple stages, with an output of using stage being passed to the next stage as input. This allows to processing of the data and returns computed results. An Aggregation pipeline can have one or more stages, each processing using expression operators. Key Stages in Aggregation PipelineThe MongoDB aggregation framework provides several stages that can be used to perform various data processing activities. Some of the key stages include: 1. $matchThe `$match` stage filters documents based on a specified condition. It is similar to the find operation. Syntax: { $match: { <field>: <value> } }Example: { $match: { age: { $gte: 18 } } }This will output only the documents where the age field is greater than or equal to 18. 2. $groupThe $group stage groups documents by a specified identifier and applies accumulator expressions to each group. Syntax: { $group: { _id: <expression>, <field>: { <accumulator>: <expression> } } }Example: { $group: { _id: "$city", totalPopulation: { $sum: "$population" } } }This will group documents by the city field and calculate the total population for each city. 3. $projectThe `$project` stage reshapes each document by including, excluding, or adding new fields. Syntax: { $project: { <field>: <1 or 0> } }Example: { $project: { name: 1, age: 1, _id: 0 } }This will include only the name and age fields in the output documents. 4. $sortThe `$sort` stage sorts input documents using a given field in either ascending (1) or descending (-1) order. Syntax: { $sort: { <field>: 1 or -1 } }Example: { $sort: { age: -1 } }This will sort the documents by the age field in descending order. 5. $limitThe `$limit` stage limits the number of documents passed as output to the next stage. Syntax: { $limit: <number> }Example: { $limit: 5 }This will output the first 5 documents to the next stage. 6. $skipThe $skip stage skips the first N documents and passes the remaining documents. Syntax: { $skip: <number> }Example { $skip: 10 }This will skip the first 10 documents and output the rest. Steps to Implement MongoDB Aggregation FrameworkStep 1: Create a node.js project and Install Required ModulesTo utilize the MongoDB aggregation framework in a Node.js application, Create a node.js project and install the mongodb package using: npm init
npm install mongodbStep 2: Create an index.js File and modify index.js fileCreate a file named index.js and add the following code: Step 3: Update package.jsonModify the package.json to include all your required dependencies and define the start command. "scripts": {
"start": "node index.js",
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"dependencies": {
"mongodb": "^6.8.0"
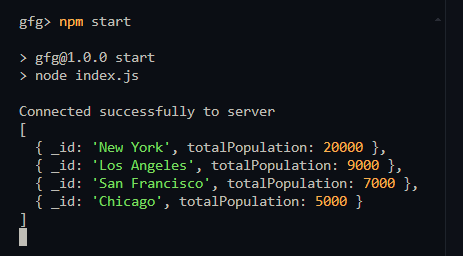
}Step 4: Run the applicationInsert some placeholder data into your MongoDB collection and run the application using ‘npm start’. Example data [ Run the application using below command: npm startOutput:  aggregation pipeline output MongoDB Aggregation Framework – FAQsWhat is the difference between the $match stage and the find method in MongoDB?
Can we use multiple stages in a single aggregation pipeline?
How to use the MongoDB aggregation framework with other Node.js frameworks like Express.js?
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| MongoDB |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 15 |