|
Processing of the digital signals is the most important part in modern electronics, which includes telecommunication, audio processing and others. In this field, filters are essential for shaping or modifying signals to their desired properties. Among all digital filter types, Finite Impulse Response (FIR) and Infinite Impulse Response (IIR) filters stand as unique due to their distinctive traits and usages.
The term FIR is used because these filters have finite impulse response meaning that after some time their output becomes zero eventually. Their linear phase response allows them to preserve the shape of waveforms of filtered signals. Conversely, IIR filter has an impulse response that theoretically extends forever. They also provide steep roll-off characteristics with fewer coefficients thereby being computationally efficient.
Engineers and researchers require knowledge about how FIR and IIR filters differ so as to develop systems suitable for specific applications such as eliminating noise from audio signals or maintaining clear data transmission channels from one point to another. To get insights into these definitions, various types, mechanisms of operation and differences between FIR filters and IIR filters including advantages & disadvantages in addition to practical uses see this article.
What is FIR Filter?
The Finite Impulse Response (FIR) filter is a kind of digital filter whose response to an impulse input lasts for a finite time, and then it becomes zero at some number of samples taken. These filters are simple in nature and also have stability as they do not require the use of feedback. Usually, FIR filters are implemented by using coefficients that determine its behavior and can be linear phase making all the frequency components in the input signal delayed for equal periods of time.
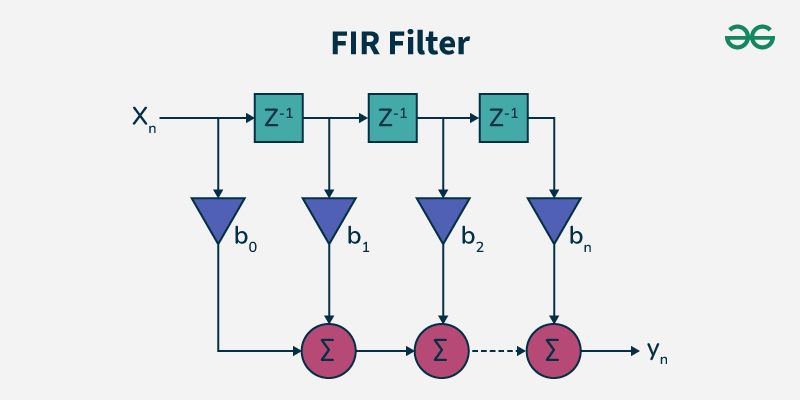 FIR Filter Simplified Diagram Types of FIR Filters
- Low-Pass FIR Filter: It allows frequencies whose cut off frequency is lower than certain value to pass and attenuates those with higher frequencies.
- High-Pass FIR Filter: In contrast, it enables signals having a frequency above a certain cutoff point.
- Band-Pass FIR Filter: This type of filter allows only some frequencies to go through but prevents others from doing so.
- Band-Stop FIR Filter: A filter in this mode lets through all but one narrow range of frequencies.
- Multi-Band FIR Filter: Allow many frequency bands to be passed through while other are rejected.
Advantages of FIR Filters
- Stable: Unstable since it does not have a feedback loop.
- Linear Phase: Can be designed to respond linearly in phase.
- Simple Implementation: Can be implemented easily on digital hardware.
- Flexibility: Design can assume various characters of filters.
- No Feedback: Makes the design process for the filter simpler.
Disadvantages of FIR Filters
- High Order: Requires a higher order for sharp frequency responses.
- More Computations: The computations are more intensive due to many coefficients.
- Memory Usage: More memory is used for storing the coefficients.
- Longer Delay: Longer group delay compared to IIR filters.
- Limited Use: Less efficient in real-time processing that requires speed for efficiency reasons.
Applications of FIR Filters
- Audio Signal Processing: These are employed in equalizers and also noise reduction systems.
- Data Transmission: They are vital when designing modems as well as other communication equipment.
- Image Processing: This applies to edge detection, image enhancement, etc.
- Speech Processing: They are used in echo cancellers and voice recognition systems among others.
- Radar Systems: these become important when filtering and detecting signals are concerned.
What is IIR Filter?
Infinite Impulse Response (IIR) filter is a digital filter whose impulse response goes on forever theoretically. Unlike FIR filters, IIR filters utilize feedback; hence, they can achieve a desired frequency response with low orders than which results to computational efficiency. However, there may be phase distortions or issues relating to stability because of feedback presence. Analog filters imitation is what IIRs are often designed for, which provide sharp cutoff frequencies and good filtering properties.
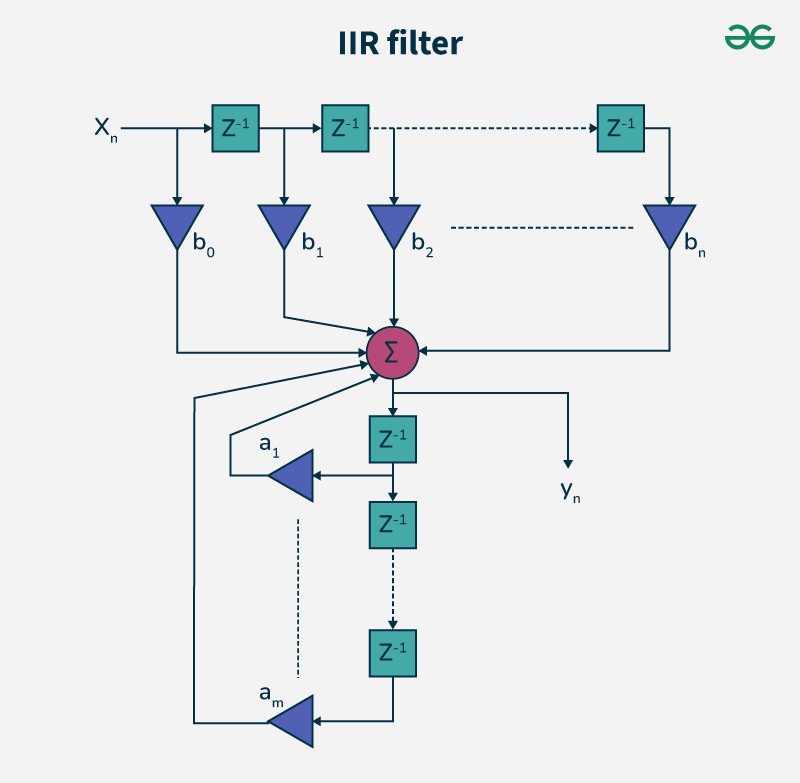 IIR Filter Simplified Diagram Types of IIR Filters
- Butterworth Filter: This has got a flat magnitude response resulting into smooth passband transition region.
- Chebyshev Filter : It has steeper filters than Butter worth filters which have ripple either in the stop or pass band .
- Elliptic Filter : For the given order, it exhibits both pass and stop band ripples thus gives an ultimate cut off rate.
- Bessel Filter : This is used to preserve the shape of waveform as it imparts a linear phase response over its entire bandwidth.
- Notch Filters: They selectively suppresses narrow sections of spectrum.
Advantages of IIR Filters
- Efficiency: It achieves desired characteristics with a lower order.
- Sharp Cutoff: Provides sharper cutoff with fewer coefficients.
- Analog Compatibility: Analog filter designs are closely similar to this type of IIR filters..
- Lower Memory Use: Memory use is less since there are few coefficients involved here..
- Quick Response: It has quicker response suitable for real time applications.
Disadvantages of IIR Filters
- Stability Issues: Stability may not be guaranteed unless the feedback is properly handled.
- Phase Distortion: A nonlinear phase response is introduced.
- Complexity: Design becomes more complex because of feedback components.
- Impulse Response: Infinite impulse response makes analysis very difficult.
- Implementation Difficulty: Impediments to implementation arise from the presence of feedback loops.
Applications of IIR Filters
- Integral in designing controllers for various systems are control systems.
- Used in ECG and EEG analysis is biomedical signal processing.
- Critical for filtering vibration signals in machinery are vibration analysis.
- Applied in geophysics for analyzing seismic waves is seismic data processing.
- Used in designing loudspeakers and microphones is acoustic engineering.
Differences Between FIR and IIR Filters
|
Feature
|
FIR Filter
|
IIR Filter
|
|
Impulse Response
|
Finite
|
Infinite
|
|
Stability
|
Always stable
|
Stability depends on feedback loop
|
|
Phase Response
|
Linear phase achievable
|
Non-linear phase response
|
|
Complexity
|
Higher order required for sharp cutoffs
|
Lower order sufficient for sharp cutoffs
|
|
Computation
|
Generally more computations required
|
Computationally efficient
|
|
Memory Requirements
|
Higher due to more coefficients
|
Lower due to fewer coefficients
|
|
Analog Equivalent
|
No direct analog equivalent
|
Mimics analog filters
|
Conclusion
In digital signal processing, both FIR and IIR filters are very important with each having advantages over the other. FIR filters are stable and have linear phase response but require a lot of computational resources. On the other hand, IIR filters present efficient filtering with lesser requirements but they bring about issues like instability that may result into phase distortion. In deciding between FIR and IIR filters, there are several factors at play which include desired frequency response, computational efficiency, and the importance of phase characteristics among others. Engineers need to know these dissimilarities so as to be able to make informed choices thereby ensuring that their signal processing systems function optimally.
Frequently Asked Questions on Difference Between FIR and IIR Filter-FAQ’S
Can real-time system use FIR filters?
While the usage of FIR filters is possible for real-time applications, they generally have higher demand on computational power because of large coefficients in number thus limiting their use in systems with tight processing requirements.
Why IIR filter Use When They Can Be Unstable For Certain Applications?
IIR filters are commonly preferred in situations where there is a need to sharply cutoff frequencies and ensure low computational burden. These stability issues can be addressed through proper design measures, making them suitable for applications such as real-time processing or control.
What is the effect of FIR and IIR filters on signal phase?
Linear phase response can be achieved by these type of filters which retain the shape of the signal waveform but for IIR types since they do not respond linearly to feedback mechanism they introduce some form of phase distortion that affects the characteristics of signal phases.
|


