|
In this article, we will learn how to find the maximum sum of a contiguous subarray for a given array that contains both positive and negative integers in C language.
Example:
Input:
arr = {-2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3}
Output:
7
Explanation: The subarray {4,-1, -2, 1, 5} has the largest sum 7. 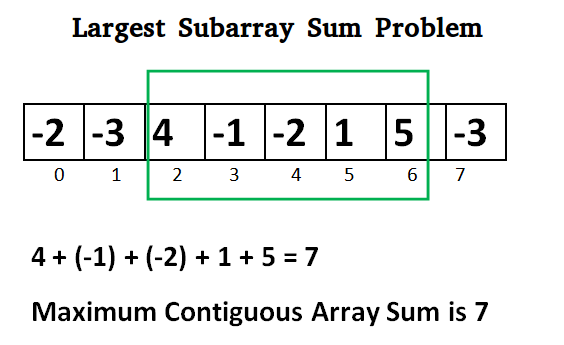 Maximum subarray Sum Method 1: Traversing Over Every SubarrayIn this method, we traverse over every contiguous subarray, calculate the sum of each subarray, and return the maximum sum among them.
Approach:- Run a nested loop to generate every subarray.
- Calculate the sum of elements in the current subarray.
- Return the maximum sum from these subarrays.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C
// C program to find Maximum Subarray Sum
#include <stdio.h>
// Find maximum between two numbers.
int max(int num1, int num2)
{
return (num1 > num2) ? num1 : num2;
}
// Returns the sum of max sum subarray
int maxSubarraySum(int arr[], int n)
{
// Initializing result
int result = arr[0];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int sum = arr[i];
// traversing in current subarray
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
// updating result every time
// to keep an eye over the maximum sum
result = max(result, sum);
sum += arr[j];
}
// updating the result for (n-1)th index.
result = max(result, sum);
}
return result;
}
int main()
{
// initialize an array
int arr[] = { -2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4 };
// calculate the size of an array
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// print the maximum sum of subarray
printf("Maximum Subarray Sum is %d\n",
maxSubarraySum(arr, n));
return 0;
}
OutputMaximum Subarray Sum is 6
Time Complexity: O(N^2)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Kadane’s Algorithm is an efficient way to find the maximum subarray sum with a linear time complexity.
-(2).jpg) Illustration of Kadane’s Algorithm Approach:- Initialize two variables: max_so_far and max_ending_here.
- Iterate through the array and update these variables as follows:
- max_ending_here = max(arr[i], max_ending_here + arr[i])
- max_so_far = max(max_so_far, max_ending_here)
- Return max_so_far as the result.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C
// C program to solve maximum subarray sum problem using
// Kadane’s Algorithm
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to return maximum of two integers
int max(int a, int b) { return (a > b) ? a : b; }
// Function to find the maximum sum subarray
int maxSubarraySum(int arr[], int n)
{
int max_so_far = arr[0];
int max_ending_here = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
max_ending_here
= max(arr[i], max_ending_here + arr[i]);
max_so_far = max(max_so_far, max_ending_here);
}
return max_so_far;
}
int main()
{
// Initialize the array
int arr[] = { -2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4 };
// Calculate the number of elements in the array
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Print the maximum sum of any subarray
printf("Maximum Subarray Sum is %d\n",
maxSubarraySum(arr, n));
return 0;
}
OutputMaximum Subarray Sum is 6
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
We can use the dynamic programming approach to solve this problem by using an auxiliary array to store the maximum subarray sum ending at each position.
Approach:- Create an auxiliary array dp of the same size as the input array.
- Initialize dp[0] with arr[0].
- Iterate through the array starting from the second element:
- dp[i] = max(arr[i], dp[i – 1] + arr[i])
- The maximum value in the dp array will be the maximum subarray sum.
Below is the implementation of the Dynamic Programming approach in C:
C
// C program to solve maximum subarray sum problem using
// Dynamic Programming
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to return maximum of two integers
int max(int a, int b) { return (a > b) ? a : b; }
// Function to find the maximum sum subarray using Dynamic
// Programming
int maxSubarraySumDP(int arr[], int n)
{
int dp[n];
dp[0] = arr[0];
int max_so_far = dp[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
dp[i] = max(arr[i], dp[i - 1] + arr[i]);
max_so_far = max(max_so_far, dp[i]);
}
return max_so_far;
}
int main()
{
// Initialize the array
int arr[] = { -2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4 };
// Calculate the number of elements in the array
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Print the maximum sum of any subarray
printf("Maximum Subarray Sum is %d\n",
maxSubarraySumDP(arr, n));
return 0;
}
OutputMaximum Subarray Sum is 6
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
Both Kadane’s Algorithm and the Dynamic Programming approach provide efficient solutions to the Maximum Subarray Sum problem. Kadane’s Algorithm is generally preferred due to its lower auxiliary space complexity.
|


-(2).jpg)