|
|
Django’s built-in User model is useful, but it may not always meet your requirements. Fortunately, Django provides a way to extend the User model to add additional fields and methods. In this article, we’ll walk through the process of extending the User model by creating a small web project that displays a custom user profile, showcasing the popular site GeeksforGeeks. How to Extend User Model in DjangoWe’ll create a Django project named user_project and an app called user_app. This project will demonstrate how to extend the User model and display user profiles. Step 1: Setting Up the Django ProjectFirst, ensure you have Django installed. If not, install it using pip: pip install djangoCreate a new Django project: django-admin startproject user_project Create a new Django app: python manage.py startapp user_appAdd the app to your project’s settings. Open user_project/settings.py and add ‘user_app’ to INSTALLED_APPS: INSTALLED_APPS = [  Step 2: Extending the User ModelThere are two main ways to extend the User model in Django: using a one-to-one link or subclassing the AbstractUser model. We’ll use the one-to-one link method. Create a new model in user_app/models.py: Run the following commands to create and apply the migrations for the new model: python manage.py makemigrations Step 3: Register same in admin.py fileCreatesuperuser using the below command as much you want to create python manage.py createsuperuser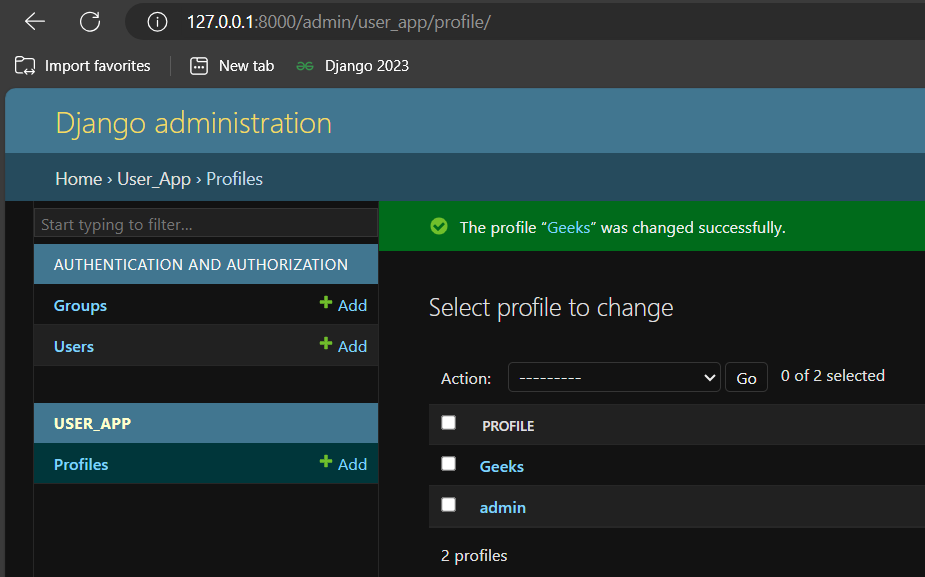 Step 4: Creating and Displaying User ProfilesCreate a signal to automatically create or update the user profile whenever a User instance is created or updated. Add the following to user_app/signals.py: Connect the signals in user_app/apps.py: Update user_app/__init__.py to include the app configuration: Create a view to display user profiles in user_app/views.py: Create a URL configuration in user_app/urls.py: Include this app’s URLs in the project’s URL configuration. Edit user_project/urls.py: Step 5: Creating TemplatesCreate a template to display the user profile in user_app/templates/profile.html: Step 6: Running the ServerRun the development server to test your project: python manage.py runserverVisit http://127.0.0.1:8000/profile/<username>/ in your browser, replacing <username> with the username of a registered user. You should see the user’s profile information. Video Demonstration |
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Python |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 19 |