|
Domain Name System Security Extensions(DNSSEC) is a combination of protocols and cryptographic technology(digital signature) for Domain Name System (DNS) and developed for integrity and security enhancement. Cyberattacks and DNS manipulation are the key concerns for Domain Name System Security Extensions(DNSSEC) as to tackle and prevent phishing, data theft, and similar suspicious kinds of attempts and activities.
DNSSEC is developed and built for DNS to add an extra layer of security and to ensure that the users are getting connected to the desired website and not getting redirected to fake and malicious websites It also maintains a safe and secured online browsing and surfing environment on the internet.
In this article, we will learn all about DNSSEC like its definition, DNSSEC set-up, difference between DNSSEC and TLS, primary technologies, key terms, DNS Spoofing, Practical examples, Scenarios, advantages, and disadvantages, etc.
What are Domain Name System Security Extensions?
Domain Name System Security Extensions(DNSSEC) is a DNS extension protocol and are used for securing DNS records by employing digital signatures and cryptographic keys(public and private) for encryption and decryption.
Domain Name System Security Extensions Setup
DNSSEC protocol can be set as follows,
- Cryptographic key generation and DNS server configuration need to be carried out for incorporation of DNSSEC by respective domain owners and DNS records signing with the cryptographic keys.
- DNS resolvers and browsers are to be setup for validation of DNSSEC signatures and to ensure end-to-end security as well.
Difference Between DNSSEC and TLS
|
Aspect
|
DNSSEC
|
TLS
|
|
Security and Encryption
|
DNSSEC are used for encrypting DNS data and to ensure authenticity and integrity.
|
Transport Layer Security (TLS) are used to secure the web browser and web server communications.
|
|
Functionality and Scope
|
DNSSEC does not provide or encrypt data or safeguard network connection instead prevent malicious tempering and modifications of DNS response.
|
TLS provide communication channel security and includes application based protocol along with email, file transfer.
|
|
Application
|
DNS-related threats like pharming and cache poisoning are handled by DNSSEC.
|
TLS deals with connections security for websites by enabling HTTPS encryption.
|
Primary Technology associated with DNSSEC
DNSSEC is follows public key cryptography and uses a pair of keys for data encryption and decryption.
DNSSEC adds the digital signatures to DNS records by signing using the private key and for verification or when someone tries use the domain then uses the public key to check the digital signature and prevents unauthorized access by individuals or organizations and disallows the DNS data alterations during the transmission.
Key Terms
- Domain Name System(DNS): A DNS is conventional naming system and are used on the internet or related resources connected to the internet or on a private network
- Public Key Cryptography: The Public key cryptography uses a public and private key for data encryption and decryption to maintain the authenticity and integrity.
- Digital Signature: The Digital Signature is applied on a digital message or document and uses a mathematical formulation to ensure authentication and integrity.
- Zone Signing Key (ZSK): Zone signing key is a DNSSEC key and are used for creating the digital signature on a particular area or zone and are valid for shorter period (few months and so on)
- Chain of Trust: Chain of Trust is the parent and child zones hierarchical trust and relationship along with the different DNSSEC keys .
- Resource Record (RR): Resource Record (RR) is a DNS database data record and contains the specific resources information.
- Zone: Zone is a DNS namespace portion where a DNS server is authoritative.
- Key Tag: Key Tag is an unique identifier and are assigned and used for distinguishing between the different types of DNSSEC keys for respective domains.
- Key Signing Key (KSK): Key Signing Key (KSK) is a DNSSEC key and are used for signing DNS records, secure management of DNSSEC keys, zone key signing and resides at the root of DNSSEC chain of trust.
- Delegation Signer (DS) Record: Delegation Signer or DS Record is a DNS record and are used for DNSSEC key authenticity verification and to secure the DNSSEC delegation as well.
- Resolver: Resolver is a software component and provides services related to DNS lookup to the respective applications or devices.
DNS Spoofing
Let us take an example, where an attacker issues false DNS entry to the DNS and changes the IP address for real and legitimate website and redirect the users to a fake web site and may steal the sensitive and touchy information.
.webp) DNS Spoofing Practical Example
Example 1: Let’s consider a sample e-commerce company named ABC. ABC want to secure and maintain the online shopping portal by using the DNSSEC as follows,
- Key Generation: ABCs the network administrator needs to generate the DNSSEC keys(KSK and ZSK) whereas KSK is used for zone key signing and in turn the ZSK signing. ZSK is responsible for DNS record signing for the ABCs online portal.
- Updating the DNS records: ABCs DNS records are updated to include the signed zone key and the ZSK with the help of registrar or DNS hosting provider respectively.
- DNSSEC Validation: Whenever a user raise an response to use the ABCs shopping portal then the respective resolver checks and validate the DNS for the corresponding DNSSEC signatures. If the resolver detects that the signatures are valid and redirect the user to the portal with the correct IP address.If the resolver found that the signatures are invalid or missing, then the resolver will not provide any response and neither any IP address, of the online shopping portal and in turn raise an request to indicate security and potential data breaches.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: However, DNSSEC keys need to be regularly updated and monitored along with the ZSK and related services time to time.
Example 2: In the United States DNSSEC are built into the top -level domains (.gov and .Edu) to protect the DNS data integrity and to ensure the users to redirect to the safe and correct governmental or educational organization website upon searching in the internet.
Example Scenario
- DNS query request raise: A user type and search some domain name of a website for example www.google.com and local DNS are checked first by the Internet Service Provider (ISP) and if found then redirect the user to the website and if not found then the request goes to root DNS.
- Root DNS server: Whenever local DNS did not found the IP address then only forwards the request to the root DNS server via the ISP DNS Server and upon receiving the response the root DNS server forwards the issue to TLD DNS servers associated with the user query for example, the .com top-level domain (TLD) and the root DNS servers do not posses any information regarding the domain but just act as communicator between local DNS and TLD DNS.
- TLD DNS server: Local DNS raises a request to the TLD DNS via the ISP DNS Server and upon receiving the request from root DNS the TLD server forwards to the corresponding authoritative name servers for the respective domain.
- Authoritative name server: Authoritative name server provides the required IP address but also employs DNSSEC and signs the DNS response with a cryptographic signature(private key) for ensuring the authenticity and integrity.
- DNS response verification: ISP’s DNS server performs the cross-validation by using the cryptographic signature and public key of the authoritative name server to ensure the DNS response hasn’t been modified or tempered during the transmission and sends to the local DNS e.g. to the user.
- User’s Website Access: User can connect and browse the requested website via local DNS sever and do the needful.
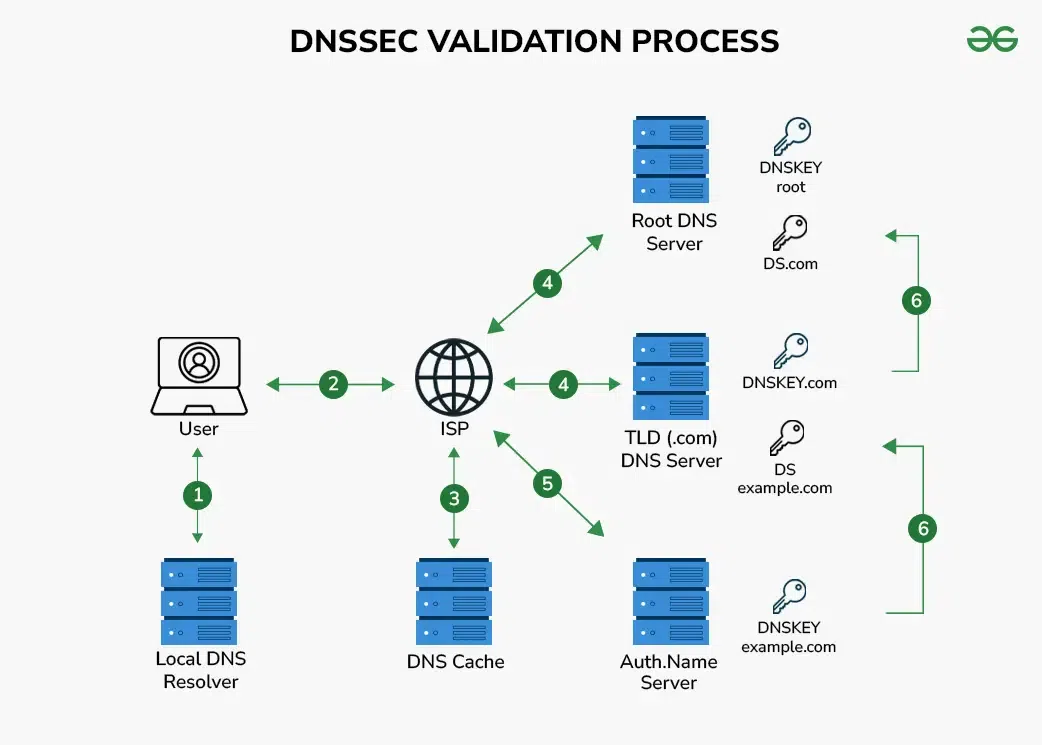 DNSSEC Validation Process Advantages of DNSSEC
- Data Privacy: DNSSEC ensures data integrity and authentication and prevents redirection to malicious and unsecured website or DNS related attacks and safeguard sensitive and touchy information and ensure data privacy.
- Compliance with Law: Some industry and regions made safeguarding and protection mandatory for online and internet browsing and DNSSEC can be useful to comply with the law and governance.
Disadvantages of DNSSEC
- Compatibility: DNSSEC does not fit for certain DNS servers and may cause disruption and interrupted DNS data related services and tasks.
- Complexity and Overhead: DNSSEC uses digital signature and public key cryptography to ensure data integrity but may also increase the DNS response size and often lead to higher bandwidth utilization and slower resolution.
Conclusion
DNSSEC is a vital and essential DNS extension protocol to ensure and provide DNS records authentication and integrity.
DNSSEC follow Public key cryptography and digital signatures for security and ensures that the DNS records are not tampered or modified with during the transmission and can significantly reduces the DNS spoofing and pharming risk.
Frequently Asked Questions on DNSSEC – FAQs
What to do if ZSK or KSK is compromised?
However, if ZSK or KSK is compromised an immediate action is utmost important including the generation of new keys and signing the DNS records with the new keys and updating the DS record.
Can DNSSEC provide completely protection against DNS spoofing and cache poisoning attacks?
Yes, DNSSEC can provide and ensure extra layer of security and safety against the DNS spoofing and cache poisoning attacks but still may prone to be affected by the other kind of attempts by the attackers such as DNS resolver subversion or DNS protocol exploitation.
Is it mandatory to implement DNSSEC?
However, DNSSEC implementation is optional but recommended and must with respect to the security and safety for organization such as e-commerce websites, banks, and government agencies.
How does DNSSEC affect DNS caching?
DNSSEC cause a slight and negligible delay in the DNS resolution as to permit the resolver to carry out the additional DNS records validation check and does not impact much for the DNS caching.
What role DNS play in the internet?
DNS may be referred as the internet phone book and are responsible for domain names translation into IP addresses (e.g. 194.0.2.1) and underlying system use the IP address to do communications with each other.
When DNSSEC came into existence and are used widely on the internet?
DNSSEC was initially proposed in the year 1997 with basic overview and specifications but for commercial and individual use generally several year times were needed. As of 2021 onwards top level domains now follow and employ DNSSEC including .com, .org and . gov as well.
|
.webp)
.webp)
