|
|
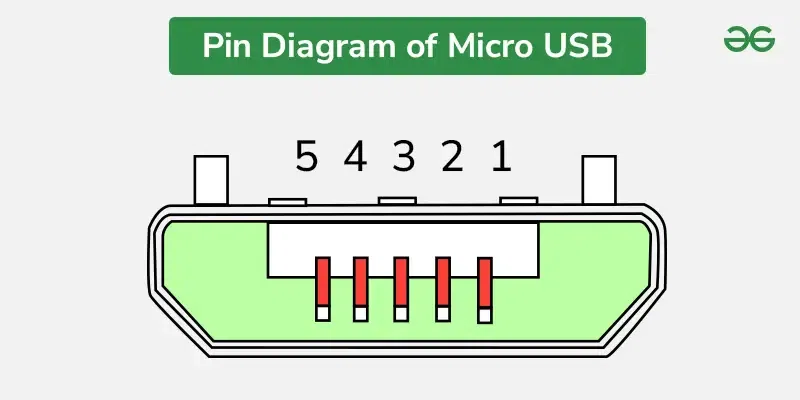
USB means Universal Serial Bus. It was introduced in 1990 to make easier the procedure by which so many devices connect to computers. It worked across operational systems and platforms, it was inexpensive, and it was end-user friendly. Now, most of the existing computers have different USB ports, even including MiniUSB and MicroUSB. What is a Micro USB?The smaller version of USB is referred to as Micro USB. It serves as a connector for portable, small gadgets such as photo printers, MP3 players, smartphones, GPS units, and digital cameras. Micro-USB comes in three varieties: MicroA, B, and USB3. The USB3 is akin to MicroB but features an additional pin on its face, doubling the number of wires, which enables USB 3. Like standard USB, the micro versions are designed to be plug-and-play. The creation of USB accessories was a collaborative effort among companies like IBM, Compaq, DEC, Northern Telecom, Microsoft, NEC, Intel, etc. This technology is freely available for all devices and computers. The USB standards are established and updated by an organization called the USB-IF (USB Implementers Forum). In its basic definition, USB recognizes only two types of connectors: A & B. However, changes to the specifications and instructions for manufacturers have broadened the connector widths used in USB devices, although the majority of USB-based products still use the A & B connector interfaces. Pin Configuration of Micro USBA common connector, such as Micro-USB, is often employed for recharging portable gadgets using a micro-USB charging cable, or by linking mobile devices to a computer. The setup of the Micro-USB pins is outlined below:  Pin Diagram of micro USB
The Micro-USB cable features four shielded cables, with two cables carrying power signals such as +5 VDC and ground, and the other two cables carrying data signals such as D+ and D-. Non-Return to Zero Invert or NRZI is a method primarily used to transmit data across a sync field, which helps in aligning the clocks of both the receiver and the host. In the USB data cable, signals like Data+ and Data- are sent over a twisted pair cable. SpecificationsHere are the details of MicroUSB:
History of the Micro USBThe universal standard interface bus was developed by business collaboration from Compaq, IBM, Digital Equipment Corp., Intel, Microsoft, NEC, and Northern Telecom. It is licensed without fees to those who produce computers and devices. The Micro-USB was developed to allow the production of the smaller size devices that were more portable. It was introduced in 2007, which brought massive popularity due to the flexibility and user-friendly nature of the device. Due to minute size, micro USBs can easily be connected to very small devices like smartphones, tablets, digital cameras, smart watches, etc. Working of Micro-USBMicro-USB, while much compatible for charging ever more devices, include smartphones, tablets, cameras, and others. However, when the USB is connected to a power source, it allows the current to run through the micro-USB cable, hence recharging the smartphone. This feature is also present on laptops, PCs, connecting your device to a computer, so that it executes many things on your device from the computer. That can be used not only to charge but also for accessing files, photos, etc. Types of Micro USBMicro USBs are primarily utilized for connecting various electronic gadgets such as smartphones, GPS units, and digital cameras. These USBs enable manufacturers to create compact devices. Their primary role is to function like standard USBs. MicroUSBs come in several varieties, including Micro-A USB, Micro-B USB, and Micro-B USB 3.0. Micro-A USBMicro-A USB is compatible with modern devices like smartphones, GPS units, and digital cameras. It is smaller than Mini-B USB but offers high-speed data transfer at 480 Mbps. The design features a white casing and a five-pin structure, with a female connector that is only available in this design. It is shaped like a rectangle. Micro-B USBMicro-B USB is similar to its Micro-A counterpart, suitable for use in current gadgets and small electronic devices. It is smaller than Micro-A USB but provides similar functionalities. Devices such as USB 1.1 & 2.0 support Micro-B ports that appear identical. This USB type has both male and female connectors, allowing for compatibility with various devices through either connection type. It is housed in a black container and features a five-pin design. Micro-B USB 3.0Micro-B USB 3.0 is designed for use in devices that support USB 3.0 technology. It is primarily used for high-speed data and power transfer. This type of micro USB is also compatible with devices that use USB 1.1 & 2.0. Like its Micro-B counterpart, Micro-B USB 3.0 is similar in design. However, it stands out by incorporating an additional group of pins on its face, which doubles the number of wires. This enhancement allows for USB 3.0 to operate at its optimal speed. How to Use Micro USB?
ApplicationsThe Applications of Micro USB are as follows.
How to Choose a Micro USB Cable
ConclusionTherefore, this provides a summary of MicroUSB and its functionality. A USB cable is crucial for linking devices to a computer for data exchange and file sharing, as well as for charging mobile phones and tablets by connecting them to a laptop or computer. There are various types of USB interfaces, with Micro-USB being one of them; it was primarily created to replace older interfaces such as Mini USB. Frequently Asked Questions on Micro USB – FAQsIs Micro USB the same as C?
What are the components of a micro USB?
Which is faster Type-C or micro USB?
What is the difference between Type-C charging connectors and micro-USB connectors?
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Computer Subject |
| Related |
|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 13 |