|
|
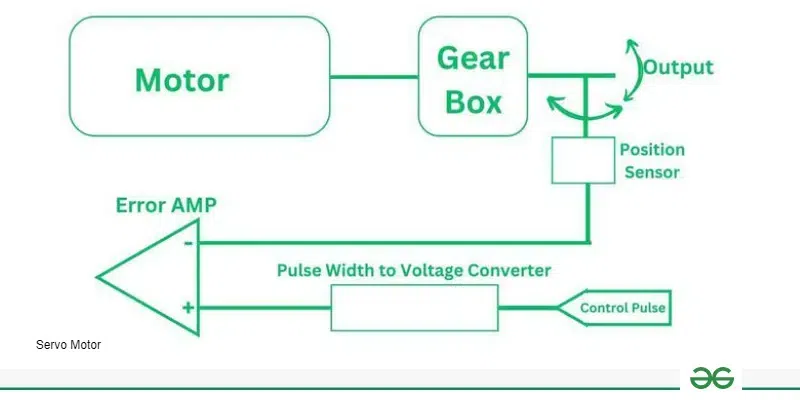
One of the types of actuators is the servo motor. It provides accurate control over angular or linear position, velocity, and acceleration. It finds application in places where the use of proper positioning is necessary such as robotics, CNC machinery, and automation systems. The servo motor system consists of a motor plus feedback sensors and a controller. The accuracy of the feedback sensors is continually monitored by the feedback system to ensure that it adjusts to any requirements needed by the task at hand for successful completion. Table of Content What is a Servo Motor?The Servo motor is a field actuator that provides position control at a certain angle. It includes motors, feedback systems and controllers. Continuous feedback monitors the engine’s accuracy and adjusts to the needs of the job. The controller interprets the difference between the actual position and the desired position and sends a signal to the motor to correct the change. Here is the diagram of Servo Motor for the better understanding :  Servo Motor Working Principle of Servo MotorThe Working Principle of the Servo Motor are :
Controlling a Servo MotorServo motors are controlled by controlling their position using pulse width modulation techniques. The pulses used by the motor vary in width and are delivered at set times. The Pulse width finds the positioning of the servo motor.
Applications of Servo MotorServo Motor are used is vast variety for fields. Few of the applications of Servo Motor are as follows:
RoboticsServo motors are used in robot arms, legs, joints, fasteners, etc. to provide important instructions and force for the robot to perform tasks such as picking, placing, welding and assembly. Servo motors plays a very important role in the field of robots. They are used in robotic arms, to perform tasks, such as picking and placing object, welding, painting, and even surgery. Good control ensures easy movement and high precision, which is very important in difficult tasks. Industrial AutomationServo motors are used to control the movement and position of various parts and equipment in production. Servo motors are in conveyors, feeders, loaders, unloaders, etc. to automate the system to deliver better quality and increase the productivity of manufacturing. In industrial automation, servo motors drive robotic arms and other automated systems. These motors allow controlled movement required for operations such as assembly, welding and painting. The precision and repeatability of servo motors increases the efficiency and quality of the production process. Printing And ScanningServo motors are used in printing machines to managing the printing panel up and down for heat press the ink on the material. Scanners and printers use servo motors to control the movement of the print head or scanner head. This precise control ensures that text and images are printed or printed accurately and maintains high resolution and clarity. Servo motors help ensure consistency in printing and printing output. CNC MachinesServo motors are used to control the axes of CNC machine tools. CNC Machine tools includes lathe, milling machine, etc. uses Servo Motors. CNC machines uses Servo Motor to complete sensitive and difficult tasks such as: Cutting, drilling, engraving, etc. Servo motors provide precisely control the position and speed of the tool used in CNC machine, which is essential for tasks such as milling, turning and 3D printing, where even small deviations can affect the quality of the product. Servo motors make the same thing repeatable, which is important for the production of good products. AerospaceDevices used in spaces needs electronic controller, servo motors are used to provide angular controller for motion control and other required features as well. In aviation, servo motors control the control functions of aircraft components such as flaps, ailerons, and rudders. This precise control is required for stable and effective management. Servo motors on aircraft help position solar panels and antennas for proper operation and communication. Medical DevicesServo Motors are also used in the fields of health and care devices. Servo motors are used in various medical devices and equipments. Some of the major uses cases are in: surgical robots, scanners, pumps, ventilators, etc. Servo motors are used to provide precise and controllable movement in medical equipment. For example, in robotic surgery, servo motors are used to perform delicate operations with high precision. Diagnostic equipment such as MRI or CT scanners use these to produce clear and precise images. Conveyor BeltsServo motors in conveyor systems provide the speed and position control necessary to ensure synchronized operation of production lines. For example, on a packaging or sorting line, the product must move at a similar speed and be positioned correctly for the next process, such as labeling or routing. Camera and Surveillance SystemsIn surveillance systems, servo motors control the digital camera’s pan and tilt feature, allowing for accurate adjustments. This option is essential for tracking gadget movement, covering large areas, and focusing the camera on specific points of interest. Antenna PositioningIn communications, especially in satellite and radar systems, servo motors adjust the position of antennas to ensure the antennas are aligned to send and receive signals. This precise control is necessary to manage the communication network, especially when tracking the movement of objects or paying attention to the environment. Advantages and Disadvantages of Servo MotorGiven below is the list of Advantages and Disadvantages of Servo Motor : AdvantagesServo Motors has many advantages:
DisadvantagesServo Motor has few drawbacks as well:
ConclusionServo Motors is one of the most used motor in the real world. Its major benefit is its 360 degree turning capacity. Servo Motor has a variety of utilities and hence it is used in various fields. Servo Motors can also clubbed with other motors to create a unique motion architecture depending upon the needs. Frequently Asked Questions on Applications of Servo Motor – FAQsWhat are the types of Servo Motor?
Can it work with Node MCU?
How Servo Motors are different from stepper motors?
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Electrical Engineering |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 20 |