|
|
Inheritance is a feature or a process in which, new classes are created from the existing classes. The new class created is called “derived class” or “child class” and the existing class is known as the “base class” or “parent class”. The derived class now is said to be inherited from the base class. When we say derived class inherits the base class, it means that the derived class inherits all the properties of the base class, without changing the properties of base class and may add new features to its own. These new features in the derived class will not affect the base class. The derived class is the specialized class for the base class.
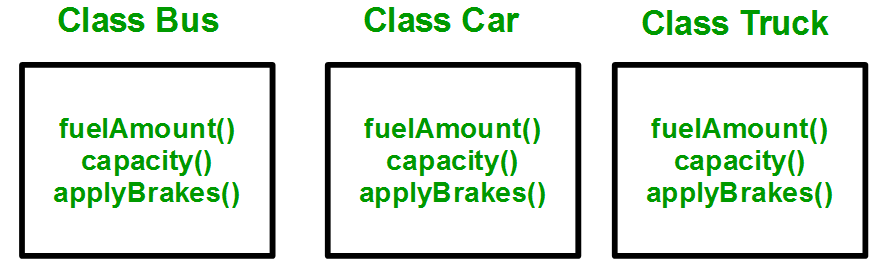
Why and When to Use Inheritance?Let’s understand need of inheritance with the help of an example. Consider a group of vehicles. You need to create classes for Bus, Car, and Truck. The methods fuelAmount(), capacity(), applyBrakes() will be the same for all three classes. If we create these classes without inheritance, then we have to write all of these functions in each of the three classes as shown below figure:
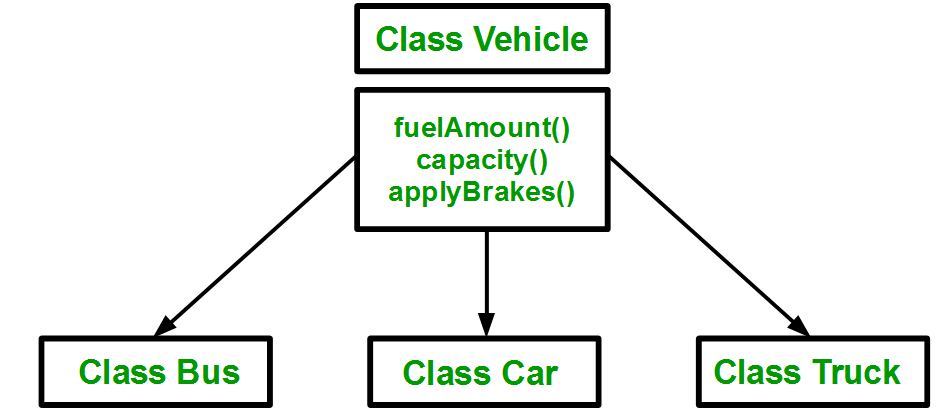
You can clearly see that the above process results in duplication of the same code 3 times. This increases the chances of error and data redundancy. To avoid this type of situation, inheritance is used. If we create a class Vehicle and write these three functions in it and inherit the rest of the classes from the vehicle class, then we can simply avoid the duplication of data and increase re-usability. Look at the below diagram in which the three classes are inherited from vehicle class:
Using inheritance, we have to write the functions only one time instead of three times as we have inherited the rest of the three classes from the base class (Vehicle). |
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Programming |
| Related |
|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 17 |