|
Spring Cloud Config Server is a powerful tool and it provides server-side as well as client-side support for externalized configuration in a distributed system. It allows us to manage the configurations of multiple applications in a centralized way. By using Git as a backend, you can version the configuration files and manage them more effectively.
Prerequisites:- Java 11 or higher version
- Maven dependency for project management
- Git installed in your local system
- Basic understanding of the Spring Boot and Spring Cloud
Spring Cloud Config Server can read the configuration properties from the Git repository and it provides them to the client applications. This setup ensures that the configuration changes are instantly available to all the client applications.
How Spring Cloud Config Works?The Spring Cloud Config Server fetches the configuration properties from the variety of the sources, such as the Git repository, the file system, or even the database. These configuration properties are then the served to the client applications at the runtime. The clients refresh their configurations dynamically without requiring the restart.
Advantages of Using Git as a Backend for Config Server:- Version Control: Git inherently supports the versioning, so every change in the configuration is tracked and can be reverted if necessary of the application.
- Collaboration: Multiple developers can work on the configuration files simultaneously, it can leveraging the Git’s branching and merging the capabilities.
- Auditing: Git can provides the history of the changes, making it easy to see who made what change and when.
- Security: Git repositories can be secured using the SSH or HTTPS, it can ensuring that only authorized the users have access to the configurations.
Config Server Architecture- Config Server: It acts as the central hub that can be provides the configuration properties to the client applications. It fetches the configuration from the Git repository.
- Git Repository: It stores the configuration files. Each application can have its own set of the properties and environments can have different configurations of the application.
- Config Client: It fetch their configuration properties from the Config Server. They can use the Spring Cloud Config dependency to the communicate with the Config Server.
Step-by-Step Flow:- Setting Up the Git Repository: We can create the Git repository that contains the configuration files for the different applications and environments.
- Config Server Fetches Configurations: The Config Server can be configured to the point to Git repository. It fetches the configuration properties from this repository.
- Client Applications Retrieve Configurations: Client applications are configured to use the Config Server URL. On the startup, they can fetch their configuration properties from the Config Server.
- Dynamic Updates: If the configuration property changes in the Git repository, the Config Server can be notify the clients or the clients can periodically check for the updates and refresh their properties without the restarting.
Implementation of Using Git as a Backend for Spring Cloud Config ServerBelow is the implementation for using Git as a Backend for Spring Cloud Config Server.
Create the Config-ServerStep 1: Create the Spring ProjectCreate the new Spring Boot project using Spring Initializr on creating the project add the following dependencies into the project.
Dependencies:
- Spring Web
- Spring Cloud Config Server
- Lombok
- Spring DevTools
Once create the project then the file structure looks like the below image.
 Step 2: Application Propertiesspring.application.name=config-server
spring.cloud.config.server.git.uri=https://github.com/yourusername/config-repo
server.port=8888 Step 3: Main ClassNo changes are required in the main class.
Java
package org.example.configserver;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.config.server.EnableConfigServer;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigServer
public class ConfigServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConfigServerApplication.class, args);
}
}
pom.xml:
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.2.6</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>config-server</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>config-server</name>
<description>config-server</description>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>2023.0.1</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Step 4: Run the applicationThe application will start at port 8888.
Create the Config-ClientStep 1: Create the Spring ProjectCreate the new Spring Boot project using Spring Initializr on creating the project add the following dependencies into the project.
Dependencies:
- Spring Web
- Spring Cloud Config Server
- Lombok
- Spring DevTools
Once create the project then the file structure looks like the below image.
 Step 2: Application Propertiesspring.application.name=config-client
spring.cloud.config.uri=http://localhost:8888 Step 3: Create the MessageControllerWe will now create the simple REST endpoint of the application.
Java
package org.example.configclient;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class MessageController {
@Value("${message}")
private String message;
@GetMapping("/message")
public String getMessage() {
return this.message;
}
}
Step 4: Main ClassNo changes are required in the main class.
Java
package org.example.configclient;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class ConfigClientApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConfigClientApplication.class, args);
}
}
pom.xml:
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.2.6</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>config-client</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>config-client</name>
<description>config-client</description>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>2023.0.1</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Step 5: Run the applicationThe application will start at port 8080.
Step 6: Testing the EndpointGET http://localhost:8080/message Output: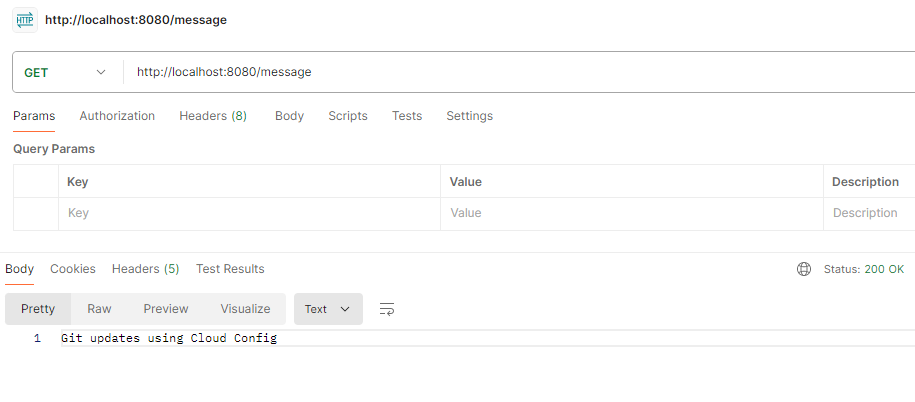 Once update the git configuration file then it will updated the endpoint results also.
This Example project demonstrates using the Git as Backend for the Spring Cloud Config server of the Spring Boot project.
|





