|
|
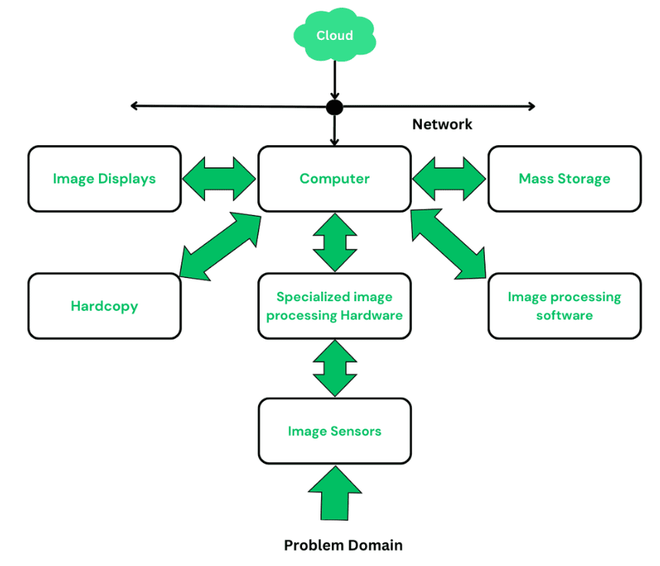
Digital Image Processing is an on-demand technique and plays a crucial role in this evolving era. Digital Image Processing is a process that involves analyzing and manipulating images digitally via computer to make them more informative for human interpretation and picture information for tasks such as maintaining storage, fast transmission, and extraction of pictorial data. This is used in various domains such as automation, medicine, remote sensing, and more. What are Digital images?An image is a two-dimensional rectilinear of pixels that gives a pictorial representation of something. An image can also be defined as a two-dimensional function f(x,y) where X and Y are spatial coordinates, and f at any pair of coordinates (x,y) is called the intensity. When the x, y, and f are all finite then the image is called a digital image. What is Digital Image Processing?Digital Image Processing is a process of analysis and manipulation of images via digital computer to get some information. In a broader sense, one can say it is a processing of two-dimensional data. Digital Image Processing focuses on two major tasks: improvement of pictorial representation for human interpretation and Processing of image data for storage, transmission, and representation for autonomous machine perception. Origin of Digital Image ProcessingDigital Image Processing was first used in the newspaper industry. At that time images were sent by submarine cable between London and New York. In the early 1920s, the Bartlane cable picture transmission system was introduced which reduced the time requirement to transport a picture across the Atlantic from more than a week to less than three hours. The pictures are coded in specialized printing equipment, and after reaching the end they are reconstructed. Initial problems found in improving the visual quality of early digital pictures were related to the selection of printing procedures and the distribution of intensity levels. The history of digital image processing is coupled with the development of digital computers. John von Neumann introduced the modern digital computer in the year of 1940. The birth of the Digital Image Processing was in 1960. The first picture of the moon was taken by U.S. spacecraft Ranger 7 to Jet Propulsion Laboratory in 1964 which serves as the basis of future image processing. In the year 1970 image processing was used in medical imaging, astronomy, and remote sensing. From 1960 to today’s date image processing has seen tremendous growth. Components of Digital Image Processing Block Diagram of Digital Image Processing Components Image Sensors/sensing: To get digital images two subsystems are required: The first is a physical sensor that responds to the energy radiated by the object and the second is a device used for converting the physical sensing device into a digital form called a digitizer. A digitizer converts result outputs to digital data. Specialized image processing hardware:To perform arithmetic and logical operations on the entire image a digitizer and hardware are used. This hardware is also called a front-end subsystem, and its speed is the most distinguishing characteristic. Because of the requirement of fast data throughput the typical main computer cannot handle it. Computer:The computer in an image processing system is a general-purpose computer that can range from a PC to a supercomputer. A well-equipped PC is beneficial for offline image processing tasks in image processing systems. Image Processing Software:It consists of some specialized modules that perform some specific task. A well-designed package allows users to write minimum code and utilizes the specialized module. Highly developed software packages allow the integration of those modules and software commands from at least one computer language. MATLAB is a well-known image processing toolbox that is common in image processing systems. Mass Storage:Mass storage is crucial in image processing applications when dealing with large sizes of images. An image of size 1024 × 1024 pixels requires one-megabyte storage if it is not compressed. Image processing systems face the challenge of storing thousands, or even millions, of images. Digital storage follows three principles :
Storages are measured in bytes(eight bits), Kbytes(one thousand bytes), Mbytes(one million bytes), Gbytes(Giga or one billion bytes), and Tbytes(Tera or one trillion bytes). Image Displays:Image displays are mainly color, flat-screen monitors. Monitors are driven by the outputs of image and graphics display cards which play an integral part of the computer system. Hardcopy:Hardcopy devices are used for recording images which include laser printers, film cameras, heatsensitive devices, ink-jet units, and digital units, such as optical and CD-ROM disks. The film is responsible for providing the highest resolution, but paper is the obvious medium for written material. Images are in a digital medium if image projection equipment is used. The final approach is to gain acceptance as the standard for image presentations. Networking and Cloud:Networking and cloud communication are mostly used functions in today’s era. Because of the large amount of data built-in in image processing applications, the key consideration in image transmission is bandwidth. When communicating with remote sites via the internet is not always as efficient, so to tackle this situation optical fiber and other broadband technologies are used. Image data compression plays a major role in the transmission of large amounts of image data. Blind Deconvolution in Image ProcessingImage deconvolution is a process used frequently to signify linear image restoration. Similarly, a filter is used in the restoration process called deconvolution filters. For estimating the degradation function three principles were used-
To restore an image by using a degradation function that has been estimated by any of these approaches is sometimes called blind deconvolution. It is an iterative process. Importance of Phase in Image ProcessingThe phase contains fifty percent of the image information. The phase is used to detect edge and segmentation in an image. It also contains liberal symmetrical information rather than magnitude if phase components are swapping in frequency which leads to changes in their general appearance. Ringing Effect in Image ProcessingAn image having uneven sharp edges is called a ringing effect image. It is also known as the overshoot effect. The ringing or overshoot effect is produced by the edge enhancement filter. The solution to the ringing effect depends upon the parameter of the problem: if the cause is a low-pass filter, we can choose a different filter design. Where we can not replace the filter in case of a band-limited signal which results in difficulties in fixing the ringing artifacts. Applications of Digital Image ProcessingDigital Image Processing techniques are now used for various tasks in various areas:
ConclusionIn conclusion, Digital Image Processing helps to enhance, sharpen, restore and makes images more informative. Digital Image Processing also helps in fast transmission, and storage and reduces memory consumption. For such techniques, Digital Image Processing is used in various industries. Digital Image Processing has limitless scope and increment in modern computing leads to fast development in computing and imaging in the future. Frequently Asked Questions on Image Processing – FAQ’sWhy image compression is important?
What is Image Segmentation?
What is the difference between image processing and computer vision?
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Electronics Engineering |
| Related |
|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 16 |