|
|
The North Star Framework is a strategic approach used by product development teams to align their efforts with overarching business goals and customer-centric outcomes. At its core, the framework revolves around identifying a “North Star Metric” a single key performance indicator (KPI) that encapsulates the ultimate measure of success for a product or service.  North Star Product Framework In this article, we are going to learn, the North Star Product framework in detail. Table of Content
What is the North Star Product Framework?The North Star Product Framework is a strategic tool that a product team uses to assemble the major efforts under a unified metric, possibly behind the growth and success of a product. The model is specifically geared toward defining the most critical measure referred to as the “North Star Metric” (NSM), which relates to the core value the product creates for its customers. These specifications become guiding standards, preventing any tasks the team provides from being irrelevant and tense situations from happening. Key Components of the North Star FrameworkHere are the following key Components of the North Star Framework: 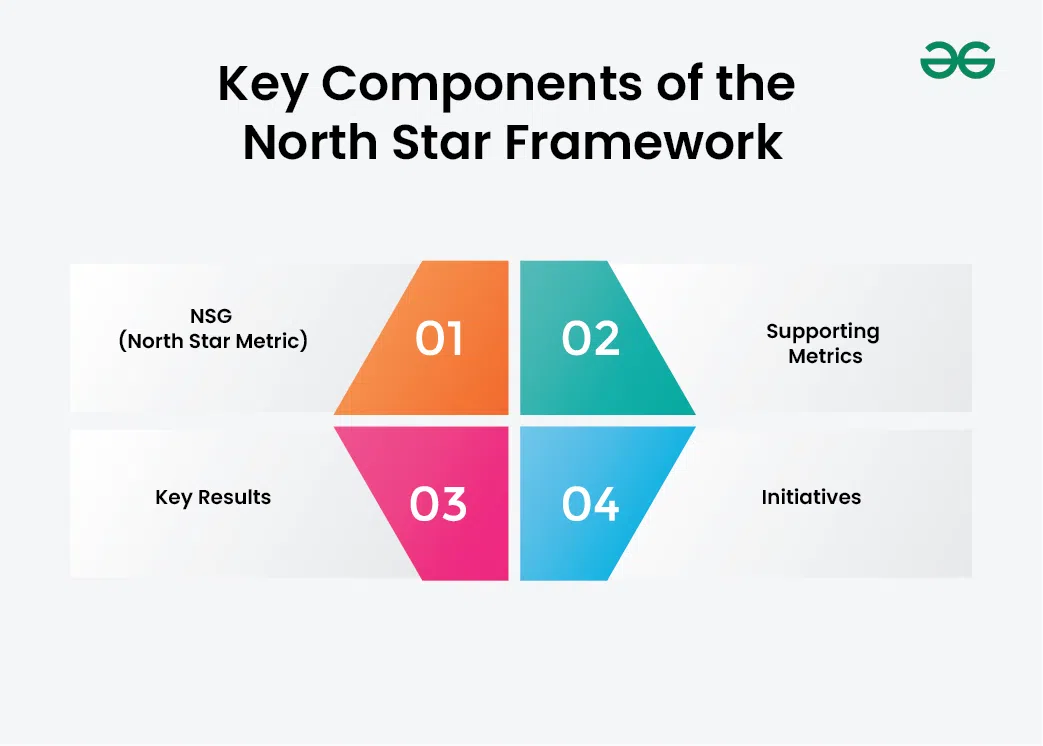 Key Components of the North Star Framework 1. NSG (North Star Metric)The NSM is a thing like a main metric that shows all the market benefits and asserts the core value of your product as well as your customers. It is proof that the product team has achieved all its objectives and accomplished extraordinary feats. It is not only an indicator of sustainable growth but also a process by which customers’ value is ensured continuously and retained while at the same time, the company is supported in the achievement of its set objective; last but not least every team member would understand it.
2. Supporting MetricsThese are the metrics that were paramount for the performance of the NSM while the other statistics give it a context and allow defining the stages of its implementation. They break down a complex NSM into processes by which consequences can be measured. Investors, comparable to factors of NSM, help in better understanding how circumstances affect the scheme as well as identifying the areas that require improvement.
3. Key ResultsCrucial Indicators, (KPIs) or specific and measurable outcomes that show that NSM is accomplished, are the NSM. They have the nature of the goals which are frequently the short to the mid-term goals and can be tracked and reviewed as frequently as possible. KPIs provide the tool to translate the overall NSM into specific milestones and deadlines needing periodical control and responsibility throughout.
4. InitiativesEfforts are the particular activities, initiatives or innovations aimed at the Key Results. That`s what`s called the tactical; the set of attempts driven by the product and development teams. Initiatives create the extra part of what is required to impact the performance and the baseline metrics consequently.
The Role of the North Star Framework in Product Development1. Shifts Attention to Adding Customers’ ValueNSM which embodies the main benefit a product gives to its clients, is a metric intended for measuring the value of products. Tendering central attention to this indicator will allow product development teams to direct the entire recorded efforts towards improving consumers’ experience as well as providing product/service value. It is the axis of consensus that guides the diagnosis of the necessary features and improvements that the users essentially need. 2. Aligns Cross-Functional TeamsThe framework, therefore, offers a bridge between the various departments like Product, Engineering, Marketing, and Customer Support that are all united revolving around a common goal. An NMS helps teams to consistently operate in the same direction and to no longer be constrained by departments and units, instead having a single orientation and approach to the project or product being developed. 3. Drives Data-Driven Decision MakingThe support of the metrics and the KRs (Key Results) creates a data-driven service, which should be based on. Teams may use these figures to assess the effectiveness of their actions and attempts and make a conclusion on the importance of oil spill prevention to them. With this approach to analysis, it is clear that solutions to the problems are decided upon by the available statistics as opposed to only by intuition and feelings which leads to more effective and measurable outcomes. 4. Enhances Strategic PlanningThe model will allow for comprehensive planning that involves the decomposition of the big picture into more manageable tactical and operational KRs. This decomposition enables organisations to focus on specific and measurable goals that are atomic objectives constituting the overall mission. It aids in setting up roadmaps, deciding on the distribution of resources and the choice of priorities that are beneficial to attain the maximal value. 5. Promotes Accountability and OwnershipWith identifiers of the Key Results and Initiatives, the North Star Framework encourages teammates to have this feeling of accountability and ownership. From this, the TNs can tell clearly what they have to offer and how their jobs are related to the company. An exactness of understanding aids in making progress and taking responsible careers of the individuals who worked together to achieve them. 6. Encourages Continuous ImprovementRegular monitoring of the NSM and KPIs associated with strengthened results in a culture of constant improvement. This gap between private sector platforms and government initiatives will be filled by teamwork, which will help identify the strengths and limitations of strategies so that they can be developed iteratively and refined. It is through this continuous adjustment of activities that an organization can deal with challenges or add new features and subsequently, more customers can be satisfied and business objectives are easily met. 7. Simplifies communication and reporting.The framework greatly facilitates communication with stakeholders through the usage of one, comprehensive metric (NSM) which will distil the whole product’s performance. Such ease in reporting progress and explaining decisions to the board, investors, and various other capital owners, either directly or indirectly, contributes to this concept. It allows you to tell an engaging story of product activities and how they contribute to the overall growth and success of your business. 8. Engages and Fuel Innovation and ExplorationThrough the proposition of NSM as the major objective, teams are forced to be highly imaginative in their realignment of the means to achieve their goals. Such concentration of the HRM practices is the critical bearer of a new culture, where the team members are motivated to apply new approaches to accomplish the organizational goals. When the experiments are successful they can result in important boosts to product improvements, aiding in a continuing rise in sales. 9. Facilitates Long-Term Perspective and Short-Term InitiativeThe strategy sets realistic expectations in a balanced manner by considering both short- and long-term achievements. NMS indicates the final objective while metrics, KRs and Initiatives show the intermediate activities of achieving the final goal. This framework gives the team focus by enabling clarity in their daily tasks which then meets the long-term strategic goals, thus, keeping them in sync and ensuring consistent gains are made. Implementing the North Star Product FrameworkThe North Star Metric determines which metric is your company’s major gauge of success. Getting to know your customers is an important step in not only establishing what the common need is but also identifying how your product meets that need for your target audience. By this, you will be able to select the most illustrative metric that can measure what value your product brings.  Implementing the North Star Product Framework
Steps to Define Your North Star Metric1. Identify the End-Result for Customers:
2. Ensure Applicability to All Customers:
3. Confirm Measurability:
4. Determine the Optimal Measurement Frequency:
5. Minimize External Influences:
6. Tie NSM Growth to Business Growth:
7. Incorporate the Full Pirate Funnel: Incorporate the Full Pirate Funnel:
8. Ensure Stability Over Time:
Through the comprehensive strategy of understanding your burning questions, you will be able to construct a wise North Star Metric which is not just a crucial element of product management but is also the glue that binds your team members around a common target and ensures the growth of your business on a sustainable level. Aligning Your Team with the North Star FrameworkConvey an NSM (North Star Metric).The key to keeping every player in the team updated about NSM(North Star Metric), why it is important, and how it serves as the guide is alignment and focus. Have the inaugural meeting with the aim of the NSM being able to detail reasons it has a lot to do with the company and how. Give a credible, understandable document that states the purpose of the NSM and the reasons for setting this standard. Determine Supporting Metrics and Key Results (KRs).Defining the strategic metrics from the NSM that each department and worker will be able to act on, including Key Results (KRs), creates the route for achieving the overall purpose. Connect with the team leaders and do community mapping to identify particularly effective supporting indicators for the NSM. Consider having particular results be met, and produce measurable, realizable, relevant, and within a specific time (SMART). To Define the Goals and DetailsIt is indispensable in a strategic planning process to focus on and put first the initiatives and projects that will be the means to achieve targets set by the KRs and NSMs. Indicate possible ways that we might increase the effectiveness of the targets and KRs. Assess the efficiency and feasibility of each initiative concerning what impact they can have on the targeted problem. Create a Culture of Ownership and Be Reckoned with.Helping teams to worker real ownership of their work and giving them the capability to hold them accountable is one of the most powerful forces that may help drive performance. Close leadership gaps for metrics and KRs’ definitions by inclined teams or singular members. Provide updates and opportunities for reviewing progress regularly to have a stand-by for what is achieved. Make available the required resources and tools.There is no doubt that building your team and adequately arming them with tools and resources that are crucial to their success is the backbone of their pursuit of affordable energy. Invest in data-analytical and project management tools that allow you to assess the progress of the project and understand the results. Make available courses, workshops, and sessions targeted at upgrading capabilities and updating know-how. Establish Ongoing Review and Feedback ProcessesRegular observation of progress on NSM and subsequent touching up by collecting information and handling the statistics contributes to the goal of achieving the umbrella effort. Schedule routine reviews to evaluate achievements made against KRs and NSMs. Definitely, during these meetings the obstacles must be identified; also, the venues to enhance things and resource redistribution should be talked about if resource reallocation is essential. Celebrate Milestones and SuccessesTo say that we point at the victories and rest moments in time is to keep the team inspired and moving. Acknowledge the progress when a milestone or a set of key results (KRs) is reached. In terms of recognition, instruct the teams to plan on the organizational goals. This can be a company-wide event or a small team get-together to reward the employees. Challenges in Applying the the
Maximizing the Impact of the North Star Framework1. Establish Clear Alignment with Business GoalsTo make sure the setup NSM is more in parallel with your organization’s business goals’ verticals. This alignment is amplified and supplies work as the pillar of a sustainable growth blueprint and its role model for success. 2. Create Cross-Functional OwnershipCreate a culture of cross-functional networking in which different units or departments will be in charge of the NSMs. This elected leadership indicates the spirit of joint ownership, breaks up silos, and provides leadership for coordinating programs to realize the NSM. 3. Introduce Agile Iterations and Feedback Loops.Adopt agile methodologies, with the ability to refine NSM and successfully track the related metrics. Create feedback mechanisms that allow for iterative testing, strong learning, and adjustment to real-time information; this will, in return, enlarge the sphere for ongoing improvement. 4. Leverage Data-Driven InsightsCapturing the power of data analysis in marketing allows for analyzing consumer behaviour in more detail, forecasting trends and how NSM initiatives influence the market. It is then upon your management to harness those insights for the formulation of strategic choices, refining of business operations and investigation of new market prospects. 5. Empower Worker Autonomy and InnovationEngage each employee at all levels to provide elements of ideas and activities that link to the given NSM. Revere autonomy and creativity by allowing for an environment that is resourceful and where individuals feel the satisfaction and emanation of being responsible for creating a positive change. 6. Invest in the Continuous Development and Training.Emphasize learning and development measures that grant employees the skills and expertise necessary to effectively perform in the modern digital world. To accomplish this, incorporate training programs, workshops, and resources on data analysis, critical thinking, and problem-solving into the curriculum. 7. Communicate results and celebrate achievements.Sustaining the open channels of communication ensures that all stakeholders, especially the sentence are in the loop for advancement towards the NSM. Give your team even the slightest chance to breathe and celebrate these achievements. Reward the individual as well as the whole group’s efforts and remind them how the NSM campaign can make their company achieve these targets. 8. Adapting and Evolving Over TimeUnderstand that the world is not standing still and the NSM could transform and turn obsolete if not properly adapted. Keep an eye on the situation pertinent to the NMS and develop an adaptable nature to respond to any changes in the hierarchy due to market conditions, ever-changing customer needs, and dynamics in the management. The Future of the North Star Product Framework1. Integration of AI and Predictive AnalyticsWith the advance of AI and predictive analytics technologies they all the more will become the leading factor in NSM identifying and fine-tuning. By using machine learning algorithms the amount of data taken for analysis, which identifies the patterns and trends can loop the organization to the point of making effective and accurate predictions about what is going on with the customer’s behaviour; thus, the process of NSM can be optimized to a high-quality level. 2. Extension To Inductualisation And Customisation.While the North Star Framework may incorporate any improvement, metrics related to personalization and experience are more likely to be stressed. As customers now favour superior products and offerings that suit their choice, it will be pertinent for organizations to focus the metrics on satisfaction, involvement and loyalty at an individual level. 3. Focus on Sustainability and Social ImpactConsidering increasingly sustainable and responsible business approaches, the future NSM likely will be at to the metrics dealing with environmental impacts, diversity, equity, and inclusion. Social begins to come to lead the market and ensure that a company’s interests are more like society’s objective and require business measurement of better than financial metrics. 4. Real-time Monitoring and Adaptive Approaches.Smart data collection and technology implementation will make it possible to monitor the NSM and the measures supporting real-time. Organizations are expected to switch to more flexible and adaptable tactics by adjusting the way they address changing customer tastes, market ecosystem or competitive setup. Consequently, the alignment of the vision with the North Star is maintained. 5. Collaboration Across EcosystemsThe future of the North Star Master Plan could be a collaboration of ecosystems and organisations may partner to strategically approach the same goal. Multiple cross-industry alliances and partner ecosystems will be established, combining forces of collaboration, co-creation, and the development of shared value in the direction of a common goal. 6. Increased Transparency and AccountabilityStakeholders relevant to organizations should expect transparency and accountability of the NSM approach and nobody will be satisfied with the alignment of NSM with broad societal values or contributions to positive outcomes. There must be transparency in stages including data collection, measurement methods, and decision-making processes to build a name and credibility. Related Articles:
ConclusionIn conclusion, the North Star Product Framework is going to be one of the vital components of the strategic product development process, proving to be a driving force of brand growth. With the advent of more advanced technologies and changes in consumer preferences, the framework will become more and more custom to cover emerging trends like AI, personalization and sustainability. Through the framework of Value-Based Management, innovation and societal impact, the organizations can visualize their quest for broadened impact creating value for all the stakeholders. North Star Product Framework – FAQsHow do you ensure that the North Star Metric remains relevant over time?
What role does leadership play in driving the adoption of the North Star Framework within an organization?
How do you balance short-term gains with long-term strategic objectives when defining the North Star Metric?
What are some common pitfalls to avoid when implementing the North Star Framework?
How do you measure the impact of the North Star Metric on overall business performance?
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Product Management |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 18 |