|
|
Running code alongside Tkinter’s event loop consists of integrating background tasks with Tkinter’s main loop without freezing the user interface. This is essential for creating responsive applications that perform tasks such as updating the UI, handling network requests, or running computations concurrently. In this article, we will explore two different approaches to running code alongside Tkinter’s event loop. Run Code Alongside Tkinter’s Event LoopBelow are the possible approaches to running code alongside Tkinter’s event loop.
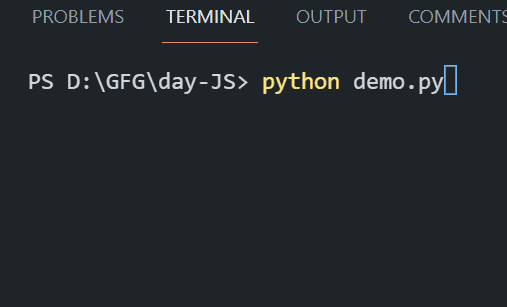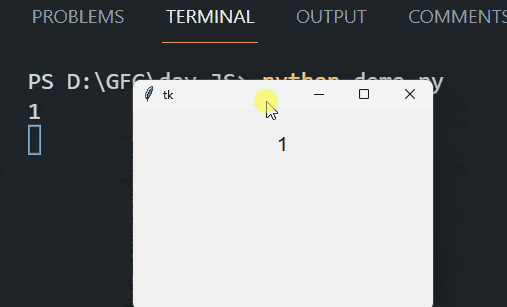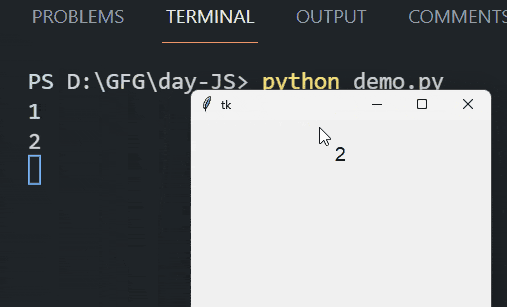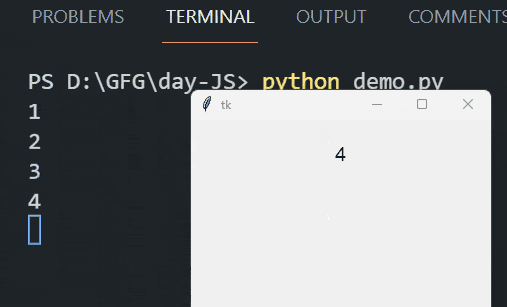
Run Code Alongside Tkinter’s Event Loop Using the After MethodIn this example, we are using the after method in Tkinter to schedule the update_label function to run every 1000 milliseconds (1 second). This function updates a label with a counter value and prints the value to the console, incrementing the counter each time until it reaches 10. Output:  Run Code Alongside Tkinter’S Event Loop Using the Threading ModuleIn this example, we are using the threading module to run the run_in_thread function in a separate thread. This function updates a label with different combinations of “GeeksforGeeks” and prints them to the console every second, allowing the Tkinter event loop to run concurrently without blocking. Output: .gif) |
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Python |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 17 |