
|
|
In the landscape of digital infrastructure, maintaining optimal performance, high availability, and robust security are very important. Enter load balancers – the silent architects behind the seamless distribution of incoming traffic across servers or computing resources. From small-scale web applications to large enterprise environments, load balancers greatly optimize resource utilization, enhance reliability, and protect against potential disruptions.  Load Balancer Use Cases What is a load balancer?A load balancer is a crucial component in modern network infrastructure that distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers to ensure no single server becomes overwhelmed. This helps improve the responsiveness and availability of applications, services, and websites. Here’s an overview of what a load balancer does and its key features: Functions of a Load Balancer
Load Balancer Use CasesHere are six use cases for load balancers, each explained in detail along with illustrative images: 1. Web ApplicationsWeb applications often experience variable traffic loads, especially during peak usage times. A load balancer distributes incoming HTTP requests across multiple web servers to ensure consistent performance and availability.
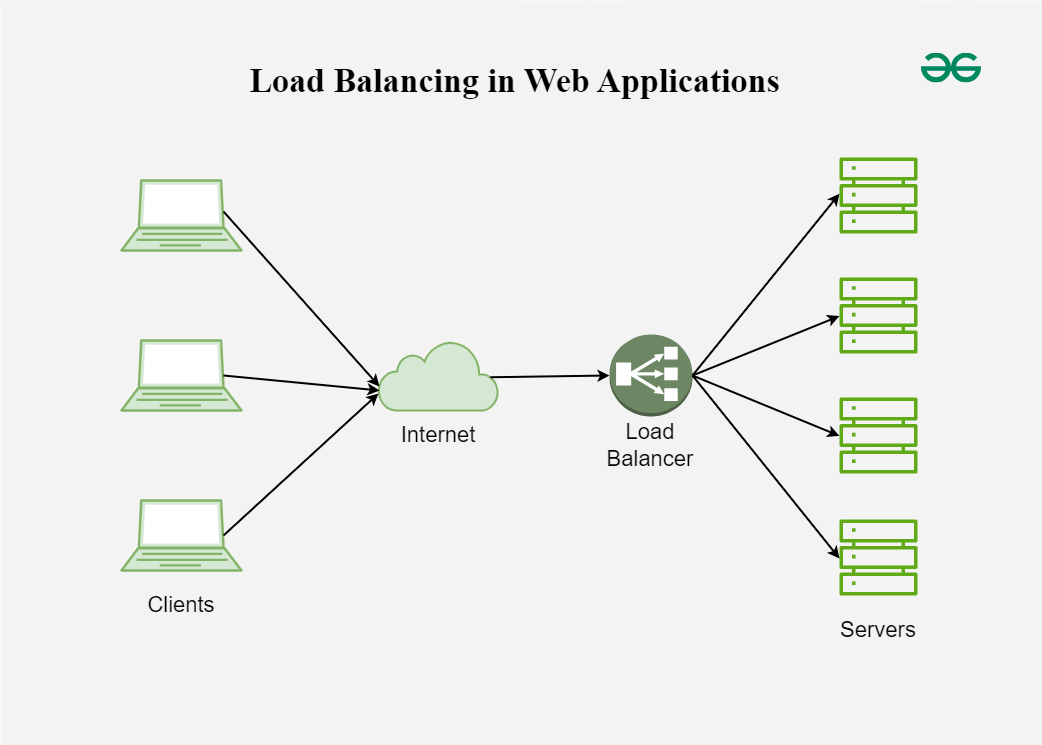
2. Microservices ArchitecturesIn a microservices architecture, different services need to communicate efficiently. A load balancer manages the load among these services to ensure smooth operation and high performance.

3. E-commerce SitesE-commerce sites require high availability and fast response times, especially during sales events. A load balancer helps handle the high volume of transactions and ensures smooth user experience.
.png)
4. APIsAPIs need to handle a large number of requests from different clients. A load balancer distributes these requests across multiple API servers to ensure reliability and performance.
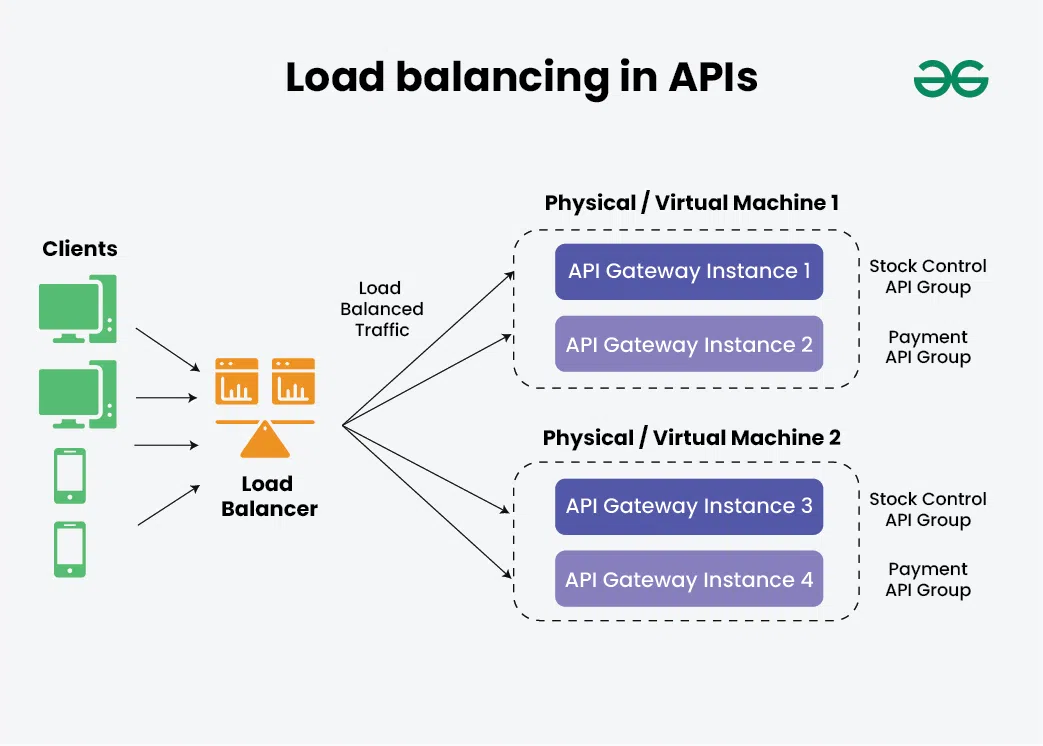
5. Cloud ServicesCloud services need to scale dynamically based on demand. Cloud-based load balancers distribute traffic across various instances, ensuring seamless scaling and high availability.
.png)
6. Content Delivery Networks (CDN)CDNs distribute content to users from the closest edge server. Load balancers manage traffic across these edge servers to ensure fast and reliable content delivery.

|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| System Design |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 17 |