
|
|
Fetching the last 25% of rows from a result set is a common query that provides insights into the most recent trends in data. This technique is particularly useful for quick analytics or reporting, especially when dealing with large datasets. In this article, we will explore how to list the last 25% of rows in a result set using MySQL, focusing on two primary methods: using the ‘ How to List the Last 25% Rows in a Result Set in MySQLMySQL provides us with various methods through which we can achieve our task. We need to perform some basic math to get our result set. We will calculate the total number of rows in the table first and then perform necessary actions accordingly. We will see the two main methods to achieve our desired task:
Setting Up the EnvironmentTo understand how to list the last 25% of rows in a result set in MySQL, we need a table on which we will perform various operations and queries. Here we will consider a table called ‘horje‘ as shown below:  horje Table Create Table: CREATE TABLE horje( Insert Values: INSERT INTO horje(id,name,course) Using LIMIT ClauseFor this example, we’ll use the LIMIT clause with OFFSET. Firstly, we will calculate the total number of rows in our table. Then, we’ll determine 75% of the total number of rows as our starting value. Finally, we’ll find the difference between the total number of rows and 75% of the total number of rows to get the total number of rows in the result set. Here’s a simpler explanation: Query: SELECT * Output:  Output Explanation: In the above image, we can see that last 25% rows of the result set are displayed here. Our total number of rows is 7. Therefore, last 2 rows are displayed here. In the query, we can see that, we have used subqueries to calculate the total number of rows of the table and for calculating 75% of the total number of rows. LIMIT (5, 2) will display 2 rows skipping the first 5 rows. Specifying ConditionWe can also fetch the last 25% rows of the result set with some condition. In this case, we will consider a result set where all rows have course ‘Python‘. Query: SELECT * Output:  Output Explanation: In the above image, we can see that only last row of the resultant set is displayed. This is because there are only 3 rows in the resultant set ( rows which contain ‘Python‘ in their course column). This means only one row will be displayed (25% 3 = 1 (approx). Using Window FunctionAnother approach is to use the Query: SELECT id, name, course Output: 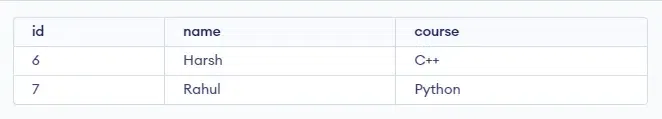 Output Explanation: In the above image, we can see that the last 25% rows of the result set are displayed. As ROW_NUMBER() function assigns a default starting value 1 to starting row, 2 for second row, and so on. Thus, we have specified a condition to display the rows only if the row number is greater than our calculated value, in this case, it is 5. This will eventually give us our last 25% rows of the result set. ConclusionListing the last 25% of rows in a result set is a useful technique for analyzing recent trends in large datasets. This article covered two prominent methods: using the LIMIT clause and using the ROW_NUMBER() function. By understanding and applying these methods, you can efficiently query and analyze the most recent portions of your data in MySQL. FAQs on How to List the Last 25% Rows in a Result Set in MySQLWhat is the purpose of fetching the last 25% of rows in a result set?
How do you calculate the starting point for the last 25% of rows using the
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Databases |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 14 |