|
|
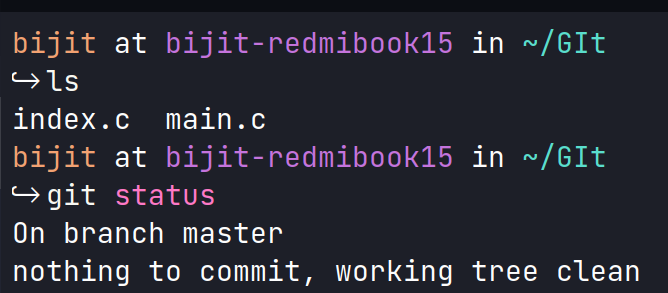
Git is a widely used distributed version control and source code management system. It effectively tracks changes to source code, enabling effortless branching, merging, and versioning. There may be instances where we need to remove a file from the Git repository, but want to keep it in your local filesystem. This situation can arise for a configuration file. Steps to Remove a File from a Git Repository without Deleting it From the Local FilesystemStep 1: Check the current status of your repositorySuppose we’re working on a Git repository. Now we want to see all the files in the filesystem and the current status of the Git repository. For Linux or MacOS: ls && git status
For Windows: dir && git status
 Output I have two C source files named “index.c” and “main.c”. Both of these files have been committed and are currently being tracked by Git. Step 2: Remove the File from the Git RepositoryTo remove a file from the Git repository without deleting it from your local filesystem, we’ll need to use the git rm command with the –cached option. Now let’s try to remove index.c from the git repository git rm --cached file-name.extension
Output: 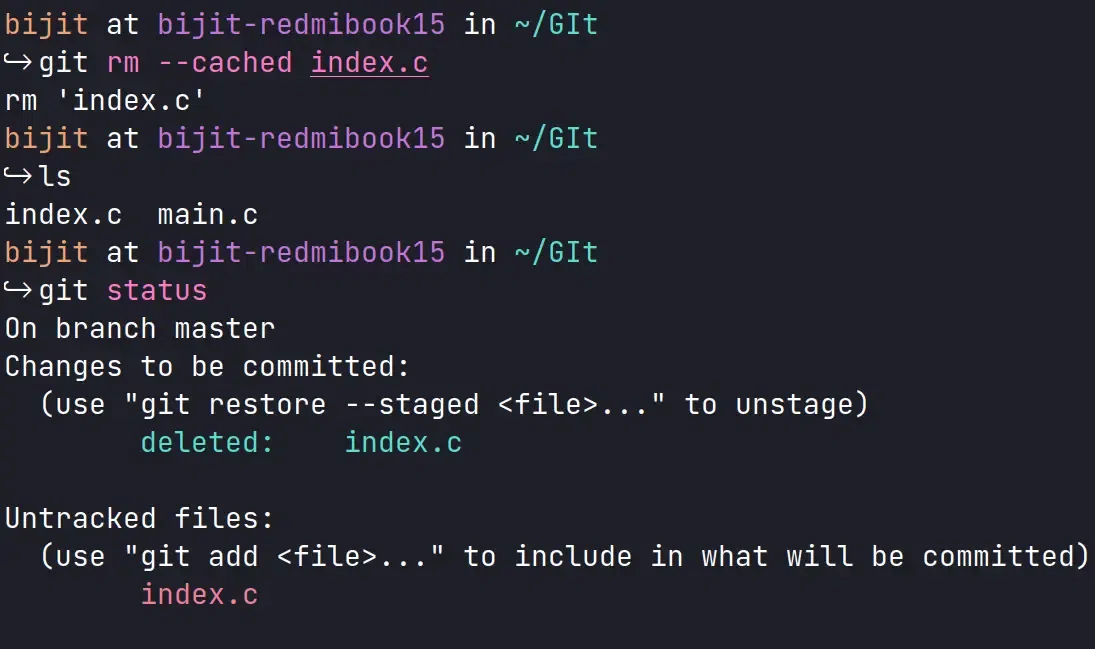 Output We can see, the index.c file is “deleted“. Further, since its local copy is still there, it has been marked as “untracked”. Step 3: Commit ChangesNow commit the changes git commit -m "commit message"
Output:  Output We can see index.c is deleted from the git repository. Step 4: Final OutputNow check the currently staged files. git ls-files
and all files in the local filesystem respectively. ls
Output:  Output The output shows the index.c file is not there anymore. But local copies are kept. We have removed the file from the git repository successfully and the file is now untracked but remember that the files removed by git rm -–cached still live in Git’s commit history. |
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Git |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 16 |