|
Given the root node of a binary search tree (BST) and a target value. The task is to find the k values in the BST that are closest to the target value. The answer can be returned in any order. It is guaranteed that there is only one unique set of k values in the BST that are closest to the target.
Example:
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4], target = 3.714286, k = 2
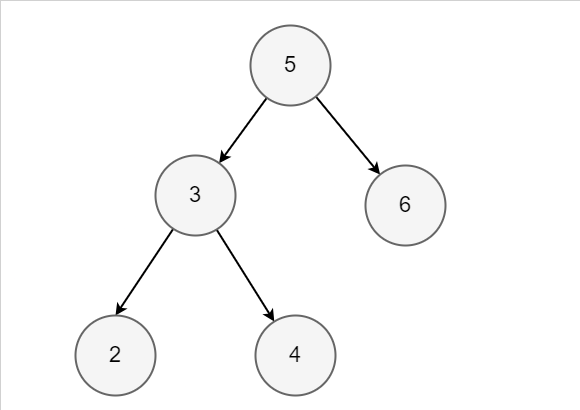 Input BST Output: [4,3]
Input: root = [1], target = 0.000000, k = 1
Output: [1]
Approach:
The idea is to perform an any traversal on the BST, during which the absolute difference between each node’s value and the target is calculated. These differences are stored in a max heap along with their corresponding node values. The heap is structured such that it retains only the k smallest differences (closest values) by discarding the largest difference whenever the heap’s size exceeds k. This ensures that, at the end of the traversal, the heap contains the k values with the smallest distances to the target. The values are then extracted from the heap to form the final result. This method efficiently narrows down the closest values in a single traversal, making good use of the properties of BST and max heap.
Steps-by-step approach:
- Start at the root of the BST.
- Calculate the distance of the current node’s value from the target.
- Push this (distance, value) pair onto the max heap.
- If the heap size exceeds k, remove the element with the largest distance (farthest from the target). This ensures we keep the k closest values.
- Recursively explore the left and right subtrees
- After traversing the entire tree, the max heap will contain the k closest values. We extract these values from the heap and return them as the result.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode()
: val(0)
, left(nullptr)
, right(nullptr)
{
}
TreeNode(int x)
: val(x)
, left(nullptr)
, right(nullptr)
{
}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right)
: val(x)
, left(left)
, right(right)
{
}
};
// Max heap to store the k closest values and their
// distances from the target.
priority_queue<pair<double, int> > maxH;
// Recursive helper function to traverse the tree and find
// the closest values.
void solve(TreeNode* root, double target, int k)
{
if (root == nullptr) {
return;
}
// Calculate the distance from the current node's value
// to the target.
double distanceFromTarget
= abs((double)root->val - target);
// Push the node's value and distance onto the max heap.
maxH.push({ distanceFromTarget, root->val });
// If the heap size exceeds k, remove the element with
// the largest distance.
if (maxH.size() > k) {
maxH.pop();
}
// Recursively explore the left and right subtrees.
solve(root->left, target, k);
solve(root->right, target, k);
}
// Function to find the k closest values in a binary search
// tree to a given target.
vector<int> closestKValues(TreeNode* root, double target,
int k)
{
// Clear the max heap before each call.
maxH = priority_queue<pair<double, int> >();
// Traverse the tree and find the closest values.
solve(root, target, k);
// Extract the k closest values from the max heap and
// store them in a vector.
vector<int> result;
while (!maxH.empty()) {
result.push_back(maxH.top().second);
maxH.pop();
}
// Return the vector of k closest values.
return result;
}
int main()
{
/*
Let's create the following BST:
5
/ \
3 6
/ \
2 4
*/
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(5);
root->left = new TreeNode(3);
root->right = new TreeNode(6);
root->left->left = new TreeNode(2);
root->left->right = new TreeNode(4);
double target = 3.714286;
int k = 2;
vector<int> result = closestKValues(root, target, k);
cout << "The closest " << k << " values to " << target
<< " are: ";
for (int val : result) {
cout << val << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {}
TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right)
{
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
public class ClosestKValuesBST {
// Max heap to store the k closest values and their
// distances from the target.
static PriorityQueue<Pair<Double, Integer> > maxH;
// Recursive helper function to traverse the tree and
// find the closest values.
static void solve(TreeNode root, double target, int k)
{
if (root == null) {
return;
}
// Calculate the distance from the current node's
// value to the target.
double distanceFromTarget
= Math.abs((double)root.val - target);
// Push the node's value and distance onto the max
// heap.
maxH.offer(
new Pair<>(distanceFromTarget, root.val));
// If the heap size exceeds k, remove the element
// with the largest distance.
if (maxH.size() > k) {
maxH.poll();
}
// Recursively explore the left and right subtrees.
solve(root.left, target, k);
solve(root.right, target, k);
}
// Function to find the k closest values in a binary
// search tree to a given target.
static List<Integer>
closestKValues(TreeNode root, double target, int k)
{
// Initialize the max heap.
maxH = new PriorityQueue<>(
(a,
b) -> Double.compare(b.getKey(), a.getKey()));
// Traverse the tree and find the closest values.
solve(root, target, k);
// Extract the k closest values from the max heap
// and store them in a list.
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
while (!maxH.isEmpty()) {
result.add(maxH.poll().getValue());
}
// Return the list of k closest values.
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/*
Let's create the following BST:
5
/ \
3 6
/ \
2 4
*/
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(5);
root.left = new TreeNode(3);
root.right = new TreeNode(6);
root.left.left = new TreeNode(2);
root.left.right = new TreeNode(4);
double target = 3.714286;
int k = 2;
List<Integer> result
= closestKValues(root, target, k);
System.out.print("The closest " + k + " values to "
+ target + " are: ");
for (int val : result) {
System.out.print(val + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// Pair class for storing distance and value
static class Pair<K, V> {
private final K key;
private final V value;
public Pair(K key, V value)
{
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
public K getKey() { return key; }
public V getValue() { return value; }
}
}
import heapq
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x, left=None, right=None):
self.val = x
self.left = left
self.right = right
# Max heap to store the k closest values and their distances from the target.
maxH = []
# Recursive helper function to traverse the tree and find the closest values.
def solve(root, target, k):
if root is None:
return
# Calculate the distance from the current node's value to the target.
distanceFromTarget = abs(root.val - target)
# Push the node's value and distance onto the max heap.
heapq.heappush(maxH, (-distanceFromTarget, root.val))
# If the heap size exceeds k, remove the element with the largest distance.
if len(maxH) > k:
heapq.heappop(maxH)
# Recursively explore the left and right subtrees.
solve(root.left, target, k)
solve(root.right, target, k)
# Function to find the k closest values in a binary search tree to a given target.
def closestKValues(root, target, k):
# Clear the max heap before each call.
maxH.clear()
# Traverse the tree and find the closest values.
solve(root, target, k)
# Extract the k closest values from the max heap and store them in a list.
result = [val for distance, val in maxH]
# Return the list of k closest values.
return result
''' Let's create the following BST:
5
/ \
3 6
/ \
2 4
'''
root = TreeNode(5)
root.left = TreeNode(3)
root.right = TreeNode(6)
root.left.left = TreeNode(2)
root.left.right = TreeNode(4)
target = 3.714286
k = 2
result = closestKValues(root, target, k)
print(f"The closest {k} values to {target} are: {' '.join(map(str, result))}")
// TreeNode class to represent nodes in the BST
class TreeNode {
constructor(val, left = null, right = null) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
// Pair class for storing distance and value
class Pair {
constructor(key, value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
getKey() {
return this.key;
}
getValue() {
return this.value;
}
}
// Function to find the k closest values in a binary search tree to a given target
function closestKValues(root, target, k) {
// Max heap to store the k closest values and their distances from the target
const maxHeap = new PriorityQueue((a, b) => b.key - a.key);
// Recursive helper function to traverse the tree and find the closest values
function solve(node) {
if (!node) {
return;
}
// Calculate the distance from the current node's value to the target
const distanceFromTarget = Math.abs(node.val - target);
// Push the node's value and distance onto the max heap
maxHeap.push(new Pair(distanceFromTarget, node.val));
// If the heap size exceeds k, remove the element with the largest distance
if (maxHeap.size() > k) {
maxHeap.pop();
}
// Recursively explore the left and right subtrees
solve(node.left);
solve(node.right);
}
// Traverse the tree and find the closest values
solve(root);
// Extract the k closest values from the max heap and store them in a list
const result = [];
while (!maxHeap.isEmpty()) {
result.push(maxHeap.pop().value);
}
// Return the list of k closest values
return result;
}
// Implementation of PriorityQueue in JavaScript
class PriorityQueue {
constructor(comparator = (a, b) => a - b) {
this.comparator = comparator;
this.heap = [];
}
size() {
return this.heap.length;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0;
}
push(val) {
this.heap.push(val);
this.bubbleUp();
}
pop() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
this.swap(0, this.size() - 1);
const removed = this.heap.pop();
this.bubbleDown();
return removed;
}
peek() {
return this.isEmpty() ? null : this.heap[0];
}
bubbleUp() {
let index = this.size() - 1;
while (index > 0) {
const parentIndex = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
if (this.comparator(this.heap[index], this.heap[parentIndex]) < 0) {
this.swap(index, parentIndex);
index = parentIndex;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
bubbleDown() {
let index = 0;
while (index < this.size()) {
const leftChild = 2 * index + 1;
const rightChild = 2 * index + 2;
let smallerChild = leftChild;
if (rightChild < this.size() && this.comparator(this.heap[rightChild], this.heap[leftChild]) < 0) {
smallerChild = rightChild;
}
if (leftChild >= this.size() || this.comparator(this.heap[index], this.heap[smallerChild]) <= 0) {
break;
}
this.swap(index, smallerChild);
index = smallerChild;
}
}
swap(i, j) {
[this.heap[i], this.heap[j]] = [this.heap[j], this.heap[i]];
}
}
// Example usage
const root = new TreeNode(5);
root.left = new TreeNode(3);
root.right = new TreeNode(6);
root.left.left = new TreeNode(2);
root.left.right = new TreeNode(4);
const target = 3.714286;
const k = 2;
const result = closestKValues(root, target, k);
console.log(`The closest ${k} values to ${target} are: ${result.join(' ')}`);
OutputThe closest 2 values to 3.71429 are: 3 4
Time Complexity: O(N * log K)
Auxiliary Space: O(K)
|
