|
An array data structure is a fundamental concept in computer science that stores a collection of elements in a contiguous block of memory. It allows for efficient access to elements using indices and is widely used in programming for organizing and manipulating data.
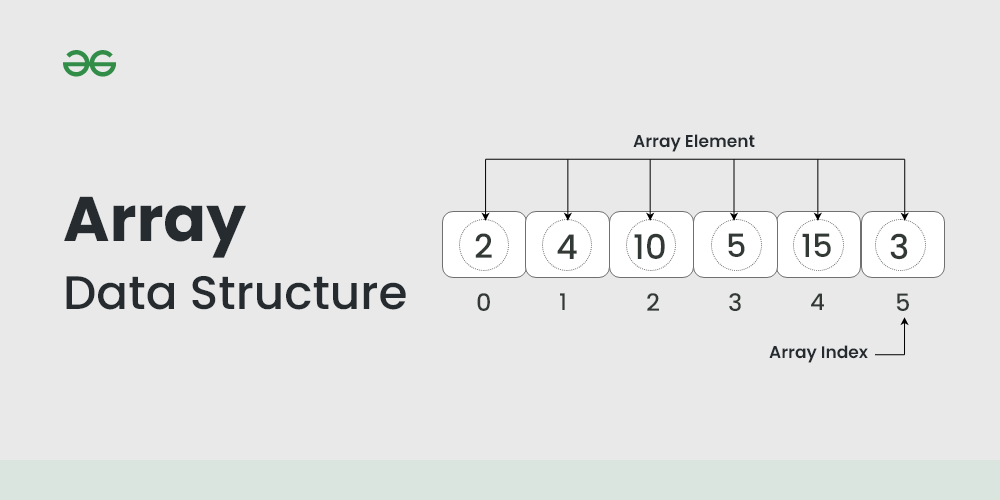 Array Data Structure What is an Array?
An array is a collection of items of the same variable type that are stored at contiguous memory locations. It’s one of the most popular and simple data structures and is often used to implement other data structures. Each item in an array is indexed starting with 0 . Each element in an array is accessed through its index.
Need of Array Data Structures
Arrays are a fundamental data structure in computer science. They are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Storing data for processing
- Implementing data structures such as stacks and queues
- Representing data in tables and matrices
- Creating dynamic data structures such as linked lists and trees
Types of Array
There are two main types of arrays:
- One-dimensional arrays: These arrays store a single row of elements.
- Multidimensional arrays: These arrays store multiple rows of elements.
Array Operations
Common operations performed on arrays include:
- Traversal : Visiting each element of an array in a specific order (e.g., sequential, reverse).
- Insertion : Adding a new element to an array at a specific index.
- Deletion : Removing an element from an array at a specific index.
- Searching : Finding the index of an element in an array.
Applications of Array
Arrays are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Storing data for processing
- Implementing data structures such as stacks and queues
- Representing data in tables and matrices
- Creating dynamic data structures such as linked lists and trees
Learn Basics of Array:
Array in Different Language:
Basic Operations on Array:
Easy Problems on Array:
Medium Problems on Array:
Hard Problems on Array:
Quick Links :
Recommended:
|

