|
|
EJS (Embedded JavaScript) is a simple templating language that lets you induce HTML language with plain JavaScript. It’s especially popular in Node.js operations for rendering dynamic web runners. It is used to dynamically render HTML pages on the server side. This article will give a detailed companion on how to pass data to EJS templates. Step to Create a NodeJS and Installing ModuleFirstly, let’s set up a basic Node.js project with EJS. Step 1: Create a new directory for a project using the command: mkdir ejs-DataPass
cd ejs-DataPassStep 2: Initialize NPM using the command which will create a package.json file: npm init -yStep 3: Install the EJS module with Express dependency using the command: npm i express ejsProject Structure: Project Structure The updated dependencies in the package.json file will look like this. "dependencies": {
"ejs": "^3.1.6",
"express": "^4.17.1"
}Example: Below is an example to Passing Data to EJS Templates. Output:  Output Passing Data to the TemplateIn the app.js file, the res.render method is used to pass data to the EJS template. The second argument to res.render is an object containing key-value pairs. The keys correspond to the variable names in the EJS template, and the values are the data you want to pass. In the example provided, the data object {name: “YourName”} is passed to the template. Within index.ejs, <%= name %> is placeholder that will be replaced with the actual value. Dynamic Data ExampleTo demonstrate passing dynamic data, let’s modify our example to include a list of items. 1. Update the route in index.js to include an array of items. 2. Modify index.ejs to iterate over the items array and display each item. Example: In this example, <% items.forEach(item => { %> and <% }) %> are EJS syntax for looping over the array and inserting each item’s value into the HTML. Output:  Output Using PartialsEJS supports partials, which are reusable snippets of code. To use partials, you typically create a partials directory inside views. Create a Header Partial: In views/partials/header.ejs, add some HTML content. <header> Create a Footer Partial: In views/partials/footer.ejs, add some HTML content. <footer> Include the Partial: Modify index.ejs to include the partials. The <%- include(“partials/header”) %> and <%- include(“partials/footer.ejs”) %> line includes the content of header.ejs and footer.ejs in the index.ejs template. Output:  Output Handling Form DataEJS can also be used to render forms and handle form submissions. Here’s a simple example: Update index.js to Handle Form Submission:Use body-parser to handle form data (body-parser is a Middleware). Output: 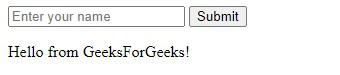 Output ConclusionEJS is a powerful yet simple templating language that integrates seamlessly with Node.js. By following this guide, you should be able to set up an EJS-powered application, pass dynamic data to your templates, use partials to organize your code, and handle form data efficiently. EJS allows for the creation of maintainable and dynamic web applications, making it a valuable tool in any web developer’s toolkit. |
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Express.js |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 12 |