
|
|
As backend developers, diving into front-end technologies can be a challenging task. However, with the rise of JavaScript frameworks like Vue.js, the transition is becoming smoother. Vue.js offers a gentle learning curve and powerful features that align well with backend development principles. In this article, we’ll explore essential concepts in Vue.js specifically for backend developers. Understanding Vue.jsVue.js is a progressive JavaScript framework That is used to build user interfaces. It is designed to be incrementally adoptable, meaning you can start using it in small sections of your projects and gradually scale it up as needed. Vue.js focuses on the view layer of web applications, providing a simple and flexible approach to building interactive user interfaces. List of what to learn in VueJS for Backend Developers1. Reactive InterfacesVue.js excels in building reactive interfaces, meaning UI elements automatically update when data changes. This reactivity is achieved through Vue’s virtual DOM and reactive data-binding system, making it effortless to create dynamic user experiences. // Define reactive data 2. Declarative RenderingWith Vue.js, you focus on what you want to achieve rather than how to achieve it. Declarative rendering allows you to describe your UI’s desired state, and Vue takes care of updating the DOM to match that state efficiently. <!-- Template syntax --> 3. Data BindingVue.js provides two-way data binding out of the box, enabling seamless synchronization between the model and the view. Changes in the data automatically reflect in the UI, and vice versa, without manual intervention. <!-- Two-way data binding --> 4. DirectivesDirectives in Vue.js are markers on the DOM elements that tell Vue.js to do something to the DOM. They are prefixed with “v-” to indicate that they are special attributes provided by Vue. <!-- Example of v-if directive --> 5. Template LogicVue.js allows you to embed JavaScript expressions within your templates, facilitating dynamic content generation. This enables you to incorporate logic directly into your markup, enhancing the flexibility of your frontend. <!-- Conditional rendering --> 6. Component and NestingVue.js promotes a component-based architecture, where UIs are composed of reusable and composable components. Components encapsulate both structure and behavior, promoting modularity and maintainability. Additionally, Vue supports nesting components, allowing you to build complex UIs from simpler ones. // Define a component 7. Event HandlingVue.js provides intuitive event handling mechanisms, allowing you to respond to user interactions efficiently. Whether it’s listening to DOM events or triggering custom events between components, Vue offers a clean and concise syntax for event management. <!-- Handling click event --> 8. Computed PropertiesComputed properties in Vue.js enable you to derive values based on other data properties dynamically. They are reactive and cache their results, ensuring optimal performance by only recalculating when necessary. // Define a computed property 9. SSR (Server-Side Rendering)Vue.js supports Server-Side Rendering (SSR), allowing you to pre-render Vue components on the server before sending them to the client. SSR enhances SEO, performance, and initial page load speed, making your Vue applications more robust and accessible. // Server-side rendering with Vue 10. Handling FormsVue.js simplifies form handling with its two-way data binding and built-in form input directives. Additionally, Vue’s form validation and submission features streamline the process of managing user input, ensuring data integrity and user experience. <!-- Form input binding --> 11. Reusability & CompositionVue.js emphasizes reusability and composition, enabling you to create modular and maintainable codebases. By encapsulating functionality within components and leveraging mixins, slots, and scoped styles, you can maximize code reuse and promote code organization. // Mixin for common functionality 13. TestingVue.js provides comprehensive tools and libraries for testing Vue components, making it easy to write unit tests, integration tests, and end-to-end tests for your Vue applications. Testing ensures the reliability and robustness of your frontend codebase, contributing to overall application quality. // Unit test example using Jest 14. DeploymentDeploying Vue.js applications is straightforward, whether you choose traditional hosting, serverless architecture, or containerized deployment. With Vue CLI’s built-in deployment capabilities and various hosting options, you can efficiently deploy your Vue applications to production environments. # Build for production Similarities to Backend TechnologiesFor backend developers familiar with frameworks like Express.js or Flask, Vue.js shares some common concepts and patterns:
Benefits for Backend DevelopersFor backend developers venturing into frontend development, Vue.js offers several advantages:
VueJS ExampleStep 1: Create the VueJS application using the following command.vue create counter-appSelect the following option while creating the app. 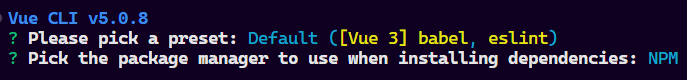 Step 2: Go to the project directorycd counter-appStep 3: Start the application using the following commandnpm run serveFolder Structure: Folder Structure Dependencies:"dependencies": { Example: This is the basic example of using VueJS. Output: 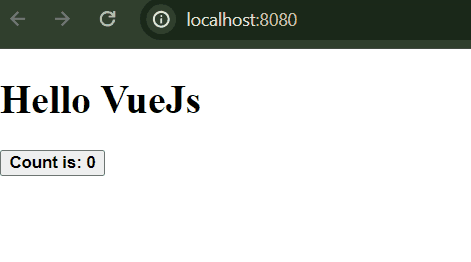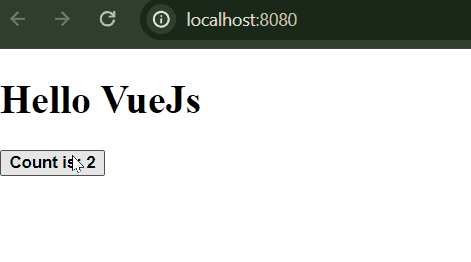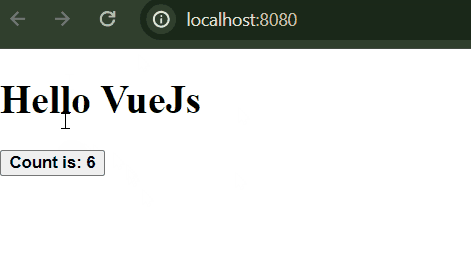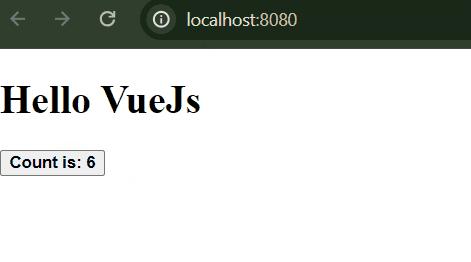 |
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| JavaScript |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 12 |