|
|
Git is a widely used distributed version control and source code management system. It effectively tracks changes to source code, enabling easy branching, merging, and versioning. In this article, we will explore the concept of Git submodules, their benefits, and best practices for integrating them into your development workflow. Table of Content What is Submodule?A submodule is a record within a host git repository that points to a specific commit in another external git repository. In simple terms, A submodule in Git is a nested Git repository within another Git repository. It allows you to include another Git repository as a subdirectory within your own repository. This is useful when you want to include external codebases or libraries in your project without copying their full contents into your repository. Suppose we are working on a repository GFG, now we will add the submodule in this git directory. Here is the basic setup of the repository that we are working on:
How to add Submodule in Git?To add a new submodule you can use the `git submodule add` command with the absolute or relative URL of the project you would like to start tracking. In this example, we’ll add a library called “experimental” repo from my account. Command to add Submodule: git submodule add <repository_URL>
git submodule add https://github.com/shravanngoswamii/experimental.git
By default, submodules will add the subproject into a directory named same as the submodule repository, In this case “experimental” in root git directory. You can add a different path at the end of the command if you want it to go elsewhere in case of managing multiple submodules. Command: git submodule add <repository_URL> <path>
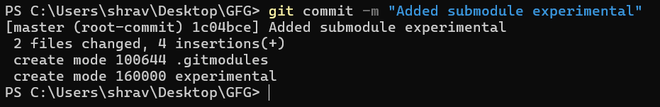
If you run git status at this point, you’ll notice a few things.
Two new files came in out git repository – .gitmodules for tracking submodules and submodule experimental so now commit these changes and then move forward to other steps:
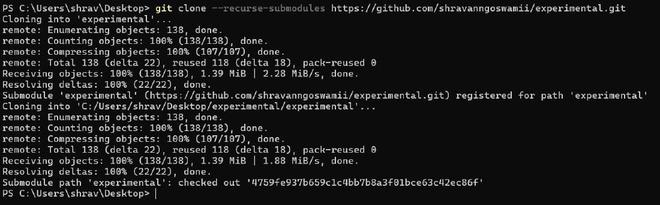
That’s it you added a submodule successfully in your repository. Cloning a Project with SubmodulesIn case you want to contribute to a project which uses submodules in it then there are some additional steps you need to take. For proper understanding, I added a submodule experimental in the repository experimental itself so let’s clone the experimental repo along with its submodules. Submodule in a repo in Github will quite look like this:
git clone https://github.com/shravanngoswamii/experimental.git
After cloning the repository with submodules, by default you get the directories that contain submodules, but none of the files within them yet:
In the main cloned repo, there is an submodule with a name experimental but you can see that its empty. You must run two commands to initialize your local configuration file, and to fetch all the data from that project and check out the appropriate commit listed in your superproject: git submodule init
There is another easy way to do this which is a little simpler. If you pass –recurse-submodules to the git clone command, it will automatically initialize and update each submodule in the repository, including nested submodules if any of the submodules in the repository have submodules themselves.
If you already cloned the project and forgot –recurse-submodules, you can combine the git submodule init and git submodule update steps by running git submodule update –init. To also initialize, fetch and checkout any nested submodules, you can use the foolproof git submodule update –init –recursive. Benefits of Git Submodules:
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Git |
| Related |
|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 16 |