|
|
Phytoremediation is an emerging technology that uses living plants to remove, degrade, or contain environmental contaminants such as heavy metals, pesticides, solvents, explosives, and crude oil. There are various phytoremediation types including phytoextraction, phytostabilization, rhizofiltration, and phytodegradation each utilising plants to clean the environment. Phytoremediation plants are specially selected vegetation that absorbs, metabolizes, or transforms pollutants from soil, water, or air. In this article, we will cover phytoremediation meaning, phytoremediation types, examples, and phytoremediation notes in detail. Table of Content What is Phytoremediation?Phytoremediation is a plant-based technique for extracting and eliminating elemental contaminants from the environment or decreasing their bioavailability in soil. Plants may take ionic compounds from the soil via their root systems, even in low quantities. Plants extend their root systems into the soil matrix, generating a rhizosphere ecosystem that accumulates heavy metals and controls their bioavailability while also recovering damaged soil and controlling fertility. Also Read: Bioremediation – Meaning, Examples & Types of Bioremediation Phytoremediation TypesVarious types of phytoremediation can be employed depending on the type and extent of contamination. The types of phytoremediation are mentioned below:
PhytoextractionPhytoextraction, also known as photoabsorption and phytoaccumulation, occurs when plants absorb soil contaminants and water through their roots and accumulate biomass through translocation. It is a fascinating process where plants absorb and accumulate pollutants from soil or water into their roots, shoots, or leaves above ground. This method relies on the roots’ ability to uptake elements from the surrounding environment and transport them into the aerial parts of the plant. Certain plants, known as hyperaccumulators, excel at this task, demonstrating a remarkable capacity for absorbing and storing pollutants.
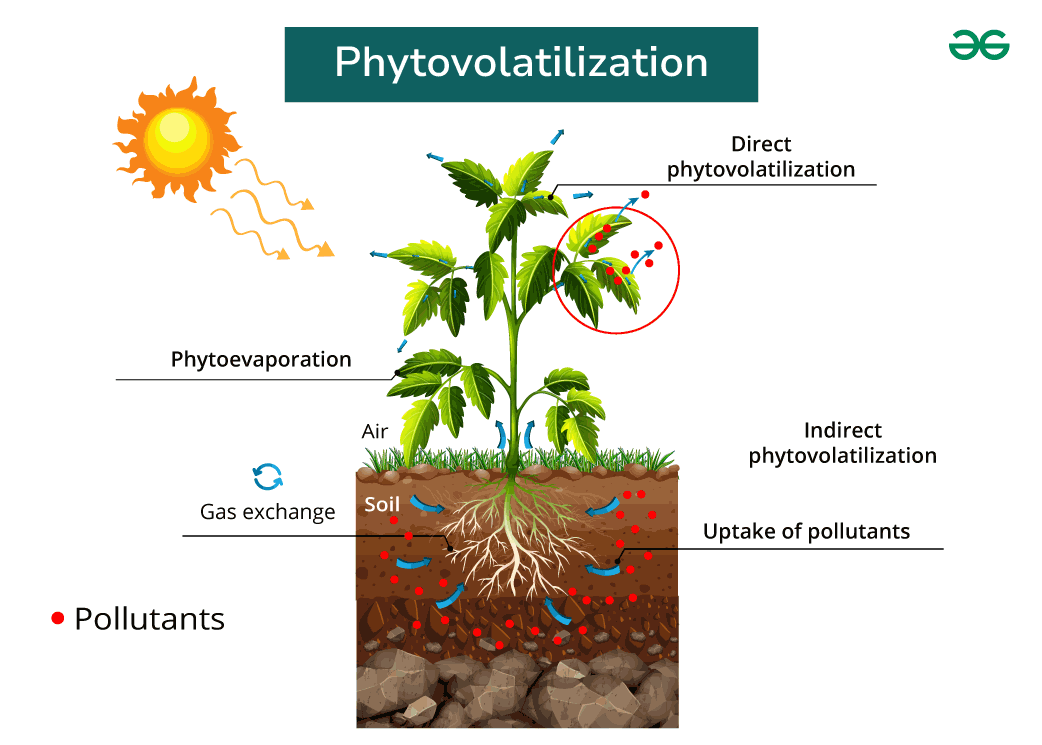
Also Read: Environmental Pollution PhytodegradationPhytotransformation, also referred to as phytodegradation, represents a vital process in environmental remediation where organic pollutants from soil, sediments, or water are converted into more stable and less hazardous forms by plants. This transformation occurs as plant roots secrete enzymes that break down organic chemicals, which are then absorbed and expelled through transpiration. Phytotransformation is particularly effective with herbicides, trichloroethylene, and methyl tert-butyl ether. This mechanism of environmental detoxification involves plant metabolism directly altering compounds, resulting in their inactivation, degradation (phytodegradation), or immobilization (phytostabilization). PhytostabilizationPhytostabilization is a crucial method employed to mitigate the movement and dispersion of contaminants in soil. This process involves plants immobilizing leachable elements by adsorbing and bonding them into their structures, forming a stable mass from which toxins cannot easily re-enter the environment. By attaching contaminants to soil particles near their roots, plants effectively reduce the availability of these pollutants for uptake by other plants or humans. Unlike phytoextraction, which involves extracting contaminants into the plant tissues, phytostabilization focuses on sequestering pollutants within the soil matrix. PhytostimulationPhytostimulation involves the breakdown of pollutants through activity in the rhizosphere. This process is driven by the presence of proteins and enzymes produced by plants or soil organisms like bacteria, yeast, and fungi. These biological agents play a crucial role in breaking down pollutants. For instance, certain bacteria are capable of degrading hazardous contaminants such as fuels and solvents, transforming them into benign and harmless byproducts. RhizofiltrationRhizofiltration is a technique for eliminating hazardous substances and excess nutrients from water by filtering it through a network of roots. Pollutants are absorbed by the roots or transmitted to them. This approach is commonly used to clean up contaminated groundwater by either planting directly in the contaminated region or removing the contaminated water and transporting it to the plants off-site. Plants are often cultivated in a greenhouse under controlled circumstances in either scenario. This approach is used to reduce pollution in wetlands and estuaries. PhytovolatilizationPhytovolatilization is a process by which plants absorb contaminants from the soil or water and release them into the atmosphere in the form of volatile compounds. This mechanism involves the uptake of pollutants by plant roots, followed by their transport through the plant tissues and subsequent release into the air through transpiration or other plant processes.
Phytoremediation PlantsSome plants which are useful in the phytoremediation process are given below:
Application of PhytoremediationPhytoremediation has been successfully applied in various settings to address a wide range of environmental issues, including:
Advantages of PhytoremediationPhytoremediation offers several advantages over conventional remediation methods, including:
Disadvantages of PhytoremediationHowever, phytoremediation also has disadvantages, such as:
Examples of PhytoremediationHere are some examples of phytoremediation applications:
Conclusion – PhytoremediationPhytoremediation offers a promising and sustainable solution to address environmental contamination issues. By leveraging the natural abilities of plants, this approach provides a cost-effective and eco-friendly alternative to traditional remediation methods. While there are challenges to overcome, ongoing research and advancements in this field continue to expand the potential applications and effectiveness of phytoremediation. As we strive for a cleaner and healthier environment, phytoremediation represents a valuable tool in our arsenal of remediation strategies.
FAQs on PhytoremediationWhat is Phytoremediation with Example?
What is the Principle of Phytoremediation?
What are the Three Types of Phytoremediation?
What is the Significance of Phytoremediation?
Where can I Find Phytoremediation Notes?
What Types of Contaminants can be Treated by Phytoremediation?
What Plants are Commonly used for Phytoremediation?
How long does Phytoremediation take?
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| School Biology |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 16 |