|
|
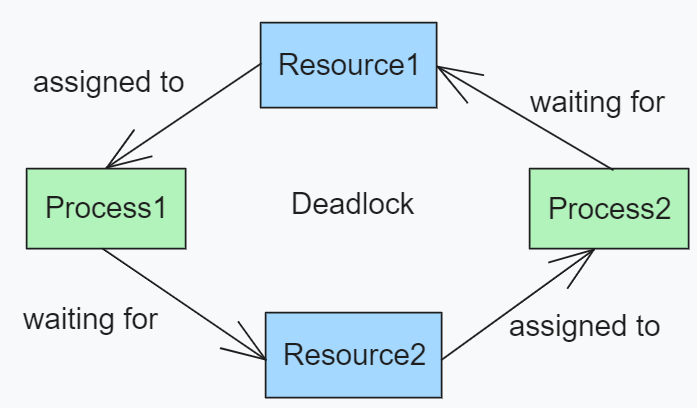
The Synchronization is an important concept in operating systems that ensures the smooth and coordinated execution of processes and threads. It is the task of coordinating the execution of processes in such a way that no two processes can access the same shared data and resource. It is a critical part of operating system design which ensures that processes or threads can safely share resources without interfering with each other. Synchronization is important because it helps in avoiding Data inconsistency between multiple processes or threads, Deadlocks and Race conditions. It is generally used in multi-processing systems, where process concurrently attempt to access the same shared resource of piece of data. Primary TerminologiesDeadlockDeadlock is a bug present in process or thread synchronization method. It is a condition where two or more processes are waiting for some resource availability which will never be available as it is required by another process which is busy with some other processes. These are said to be in a deadlock situation.
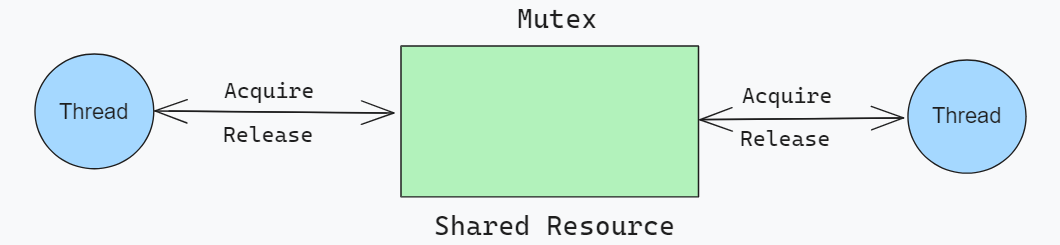
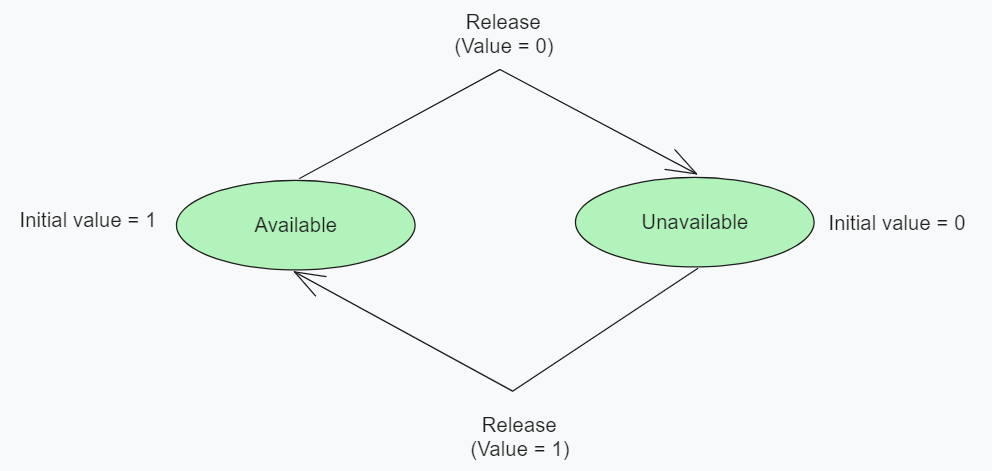
MutexMutex means “mutual exclusion”. It is synchronization primitive that is used to prevent multiple threads to simultaneously access shared resources. Only one thread or process can enter the critical section of code at a time. So, it ensures that resources are not accessed by multiple processes or threads concurrently.
SemaphoresIt is a synchronization method. It is an integer value that is equal to number of resources. It is used to control access to a shared resource by multiple processes or threads. It maintains a counter and when counter reaches zero then further attempts to acquire the semaphore are blocked until its value become greater than zero. These are of two types:
Race ConditionRace condition occurs when two or more threads or processes can access the shared data and try to change it at same time. Because in thread scheduling algorithms, we can swap between threads at any time. We do not know the order in which threads attempt to access the shared data and change the data. So, both threads are racing to access and change the data cause the race condition. Critical SectionRefers to segment of the code where processes/threads access shared resources such as common variable, file and perform read/write operation on them. Mutex and semaphore methods are used to ensure that only one thread/process can access critical section at a time. ExamplesProducer-Consumer ProblemIt is also known as bounded buffer problem. Here, we have two threads one is producer thread and other is consumer thread. Critical section (buffer) is a shared resource. We do not want that inconsistency will be produced so we want synchronization between producer and consumer thread.
Solution (with the help of semaphores) => we will use both binary and counting semaphores here. So, we will take as:
Producer solution Consumers solution Reader-Writer ProblemHere, we want synchronization that at one time only one writer can write and multiple readers can read. Here, we have two threads one is Read and other is Write/Update.
Solution (using semaphores)
Writer solution Reader solution do { ConclusionIn conclusion, synchronization in operating systems is essential for managing shared resources, preventing conflicts, and ensuring system stability. Through mechanisms like mutexes and semaphores, processes and threads coordinate access to critical sections of code, maintaining data integrity and preventing race conditions. Examples such as the producer-consumer and reader-writer problems illustrate the practical significance of synchronization in real-world scenarios. Despite challenges like deadlocks and performance overhead, understanding and implementing synchronization techniques are crucial for building reliable and efficient computing systems. Ultimately, synchronization is a cornerstone of modern computing, enabling the seamless execution of concurrent tasks and the smooth operation of operating systems. Frequently Asked Questions on Synchronization Examples – FAQsHow do mutex locks work?
What are condition variables used for?
What is the purpose of synchronization in operating systems?
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Operating Systems |
| Related |
|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 15 |