|
|
Error boundaries are React components that detect JavaScript errors anywhere in their child component tree, log them, and display a fallback UI rather than the crashed component tree. Error boundaries catch errors in rendering, lifecycle functions, and constructors for the entire tree below them. Table of Content Prerequisites: What are Error Boundaries in React?Error boundaries are a powerful tool in React for handling errors gracefully and preventing them from crashing the entire application. Imagine an error boundary like a safety net surrounding specific components. When an error occurs within the wrapped components, the error boundary catches it and prevents it from propagating further. Instead of crashing, the error boundary displays a custom fallback UI, often informing the user and providing potential solutions. When to Use Error Boundaries?Use error boundaries when you want to prevent crashes in your app caused by unexpected errors in certain parts of your UI. It helps keep your app running smoothly even if something goes wrong. Example: Imagine you have a component that fetches data from a server. If the server is down or there’s an issue with the data, instead of crashing the whole app, you can use an error boundary to handle that error gracefully and show a user-friendly message instead. Steps to Implement an Error Boundary in ReactSo we are going to discuss steps to install and create React apps: Step 1: Create a React application with the help of the below command: npx create-react-app my-appStep 2: After creating your project folder i.e. my-app, move to it using the following command: cd my-appStep 3: After setting up the react environment on your machine, we are able to start by creating an App.js file and a directory named after the components in which we will write our required function. Project Structure:
Updated Dependencies in package.json File: Ensure that your package.json file includes the necessary dependencies: "dependencies": {
"react": "^18.2.0",
"react-dom": "^18.2.0",
"react-scripts": "5.0.1",
"web-vitals": "^2.1.4"
}Example: Below is a simple example demonstrating the usage of error boundaries in a React application. In the code, we can see how to use error boundaries in a React application to easily handle errors that occur during rendering. It includes
Overall, the code showcases the implementation of error boundaries to prevent the entire application from crashing and provide a better user experience in case of errors. When you run this code and view the application in a browser or a development environment, you will see that the error thrown by MyComponent is caught by the ErrorBoundary. Instead of crashing the entire application, the error boundary displays a message indicating that something went wrong. This demonstrates how error boundaries can help prevent crashes and gracefully handle errors within a React application. Output: 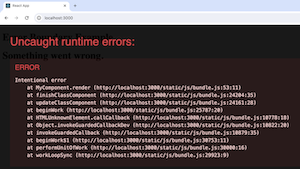 Uncaught runtime error By following these steps and approaches, you can effectively implement error boundaries in your React applications to enhance error handling and provide a better user experience. Limitations of Using Error BoundaryLet’s discuss the limitations of using error boundaries in React in simple terms:
Encountering Errors with Error Boundaries Example:Let’s say you have a component that renders a list of items. If there is an error while rendering one of the items, the error boundary will catch it and display a friendly message like “Oops! Something went wrong. Please try again later.” Error Boundary vs Try…Catch
Error boundaries in React are a special mechanism for handling errors within React components, while try…catch blocks in JavaScript are a general-purpose feature for handling errors in any JavaScript code. When Should You Use Error Boundary?Use error boundaries in React when you want to gracefully handle errors in UI components and prevent crashes from affecting the whole app. When Should You Use Try…Catch?Use try…catch in JavaScript for handling errors in synchronous code or functions, especially when you’re dealing with operations that might throw exceptions, like accessing properties of an object that might be null or undefined. |
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| ReactJS |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 17 |