|
|
Angular Components are the building blocks of Angular applications, containing the template, styles, and behavior of a part of the user interface. This article provides an overview of Angular components, including their structure, features, and how to create and use them effectively. Table of Content What are Angular Components ?Angular components are the building blocks of Angular applications. They encapsulate a part of the user interface, including its template, styles, and behavior. Each component represents a reusable piece of UI functionality and can be composed together to create complex applications. Components in Angular follow the principles of encapsulation, reusability, and maintainability, making them essential in Angular development. Component StructureThe structure of an Angular component consists of three main parts:
Component LifecycleAngular components have a lifecycle consisting of various lifecycle hooks that are executed at different stages of the component’s lifecycle. These lifecycle hooks allow to hook into specific moments in the component’s lifecycle and perform actions such as initialization, cleanup, or handling changes. Some of the most commonly used lifecycle hooks include:
Data BindingData binding in Angular allows for communication between the component’s TypeScript code and its template. There are three types of data binding in Angular:
Input and Output PropertiesInput properties allow data to be passed into a component from its parent component, while output properties allow a component to emit events to its parent component. Input properties are defined using the @Input decorator, while output properties are defined using the @Output decorator along with EventEmitter. Component communicationComponent communication in Angular involves passing data between components and coordinating their behavior. There are several methods for component communication:
Features
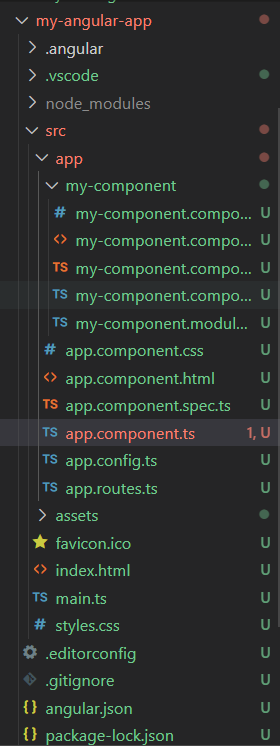
Steps to Create App, Example with Output:Step 1: Create a new Angular app: ng new my-angular-appStep 2: Move to the Project Directory: cd my-angular-appStep 3: Generate a new component: ng generate component my-componentProject Structure:
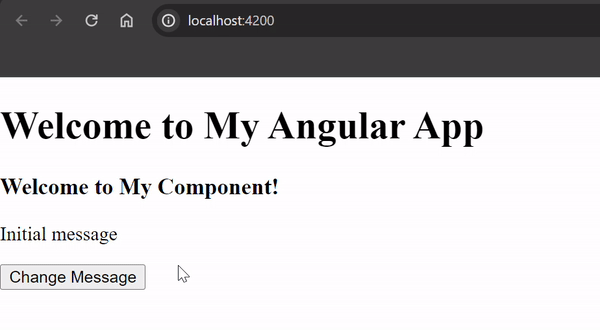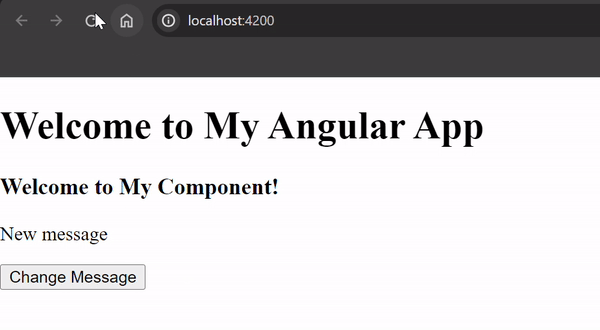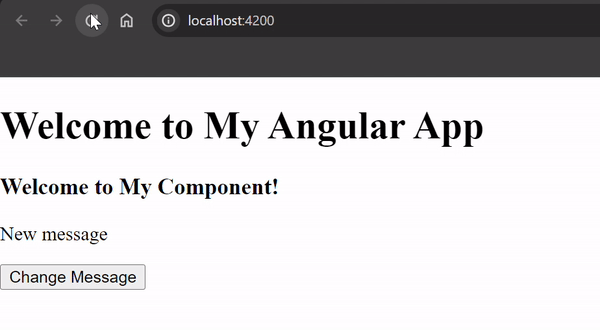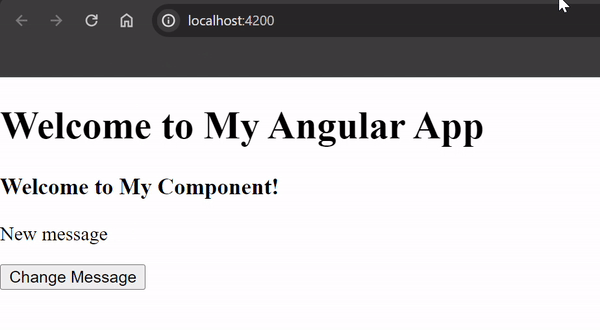
Edit the generated component files (`my-component.component.html`, `my-component.component.css`, `my-component.component.ts`) to define the template, styles, and behavior of the component. Step 5: Run your Application: ng serveOutput:When you run your Angular app (`ng serve`), you’ll see the message “Welcome to My Comonent!” displayed on the screen. Clicking the “Change Message” button will update the message to “New message” dynamically.
ConclusionAngular components are powerful building blocks for creating dynamic and interactive web applications. Understanding their structure, features, and how to create and use them effectively is essential for Angular development. This article provides a comprehensive overview of Angular components, helping developers get started with building Angular applications. FAQs1. What is the difference between a component and a directive in Angular?In Angular, a component is a type of directive with a template. Components are typically used to create reusable UI elements with associated behavior and styling. Directives, on the other hand, are used to add behavior to elements in the DOM or to modify the structure of the DOM itself. 2. Can a component have multiple templates?No, a component in Angular can only have one template associated with it. However, you can use structural directives like ngIf, ngFor, and ngSwitch within the template to conditionally render different parts of the UI based on certain conditions. 3. What is the purpose of the @ViewChild decorator in Angular components?The @ViewChild decorator in Angular is used to access child components, directives, or DOM elements from the parent component. It allows the parent component to query and interact with its child components programmatically. 4. How can I optimize the performance of Angular components?To optimize the performance of Angular components, you can use techniques like lazy loading, code splitting, and preloading modules to minimize initial load times. Additionally, you can implement change detection strategies like OnPush and memoization to reduce unnecessary re-renders and improve rendering performance. |
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| AngularJS |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 14 |