|
|
The Next.js file conventions include specific directories and filenames like pages, app, layout.js, and middleware.js, which automatically define routes, layouts, middleware, and other configurations, ensuring a structured and efficient project organization. In this article, we will learn about the different different file conventions provided by next.js. NextJS File ConventionsNextJS provides a file structure convention that simplifies the development process of your applications. These file conventions help you to handle errors and define the structure of your application. It provides default.js, error.js, not-found.js, layout.js, loading.js, page.js, route.js, middleware.js, etc. to manage your applications easily.
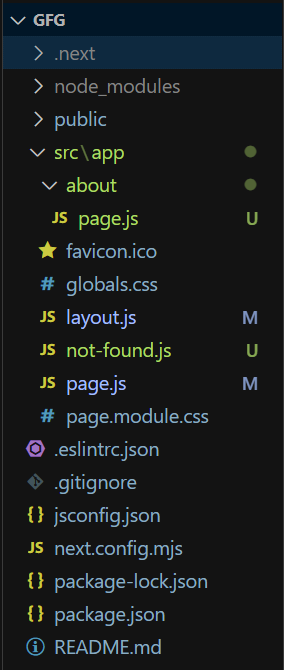
default.jsdefault.js file is a fallback page that is rendered when NextJS cannot determine which page to render. It happens when a user refreshes the page or navigates to a URL that does not match any of the defined routes. It is a React component or a function that returns a React component. const DefaultLayout = ({ children }) => ( error.jserror.js file defines an error UI boundary for a route segment. It is useful for catching unexpected errors that occur in Server Components and Client Components and displaying a fallback UI. const ErrorPage = () => ( layout.jslayout.js is a React component that is shared between multiple pages in an application. It allows us to define a common structure and a same appearance for a group of pages. It should accept and use a children prop. During rendering, children will be populated with the route segments the layout is wrapping. const Layout = ({ children }) => ( loading.jsloading.js file is typically designed to be displayed during page transitions when content is being fetched from the server. If the content is already present in cache memory, such as when a user revisits a page they’ve previously loaded, the loader may not be displayed since there is no need to fetch data from the server. const Loading = () => ( middleware.jsmiddleware.js that has access to request, response objects and the next middleware function. It allows you to intercept and manipulate requests and responses before they reach route handlers. export function middleware(req, res, next) { not-found.jsnot-found.js file renders a custom user interface (UI) when the notFound function is called within a route segment. When user enters a wrong route path, this not-found.js file will be automatically displayed. const NotFound = () => ( page.jspage.js is a react component that is used to create a UI for each routes within specific route directory. const HomePage = () => ( route.jsDefines custom routing logic, allowing for more advanced route handling beyond default page-based routing. export function customRouteHandler(req, res) { Steps to Create NextJS Application:Step 1: Create a NextJS application using the following command. npx create-next-app@latest gfgStep 2: It will ask you some questions, so choose as the following. √ Would you like to use TypeScript? ... No
√ Would you like to use ESLint? ... Yes
√ Would you like to use Tailwind CSS? ... No
√ Would you like to use `src/` directory? ... Yes
√ Would you like to use App Router? (recommended) ... Yes
√ Would you like to customize the default import alias (@/*)? ... NoStep 3: After creating your project folder i.e. gfg, move to it using the following command. cd gfgProject Structure:Example: The below example demonstrates the use not-found.js, page.js, layout.js File Conventions in Next.js. Start your application using the command: npm run devOutput:
ConclustionFile conventions in Next.js, such as pages, app, layout.js, and middleware.js, streamline project organization by automatically defining routes, layouts, and configurations. This structured approach enhances code maintainability and development efficiency in Next.js applications. |
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| ReactJS |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 14 |
