|
|
PHP (Hypertext Preprocessor) is a powerful scripting language widely used for web development. Whether you’re looking to create dynamic web pages, handle form data, interact with databases, or build web applications, PHP has you covered. In this guide, we’ll take you through the basics of PHP, covering fundamental concepts and providing code examples along with their outputs to help you get started.
Introduction to PHPPHP (Hypertext Preprocessor) is a server-side scripting language which was originally designed for web development. It operates on the server, dynamically generating HTML content, which is then sent to the client’s browser. This functionality enables websites to deliver dynamic and interactive content to users, enhancing their browsing experience. Dynamic Content Generation:
Interactivity and Responsiveness:
Integration with Databases:
Extensive Functionality and Libraries:
Basic Concepts in PHPData Types:PHP supports the following data types:
Variables in PHP are preceded by the dollar sign ($) and can store different types of data. Example: <?php Control Statements:In PHP, control statements like if…else, switch, and the ternary operator (?:) play a crucial role in decision making, allowing developers to execute specific blocks of code based on certain conditions. Let’s delve into each of these control statements to understand their functionality and usage in more detail: If Else Statement:The if else statement evaluates the given condition and executes a block of code only if the condition is true. If the condition is false, it executes an alternative block of code specified by the else clause. Switch Statement:The switch statement evaluates an expression and executes different blocks of code based on the value of the expression. It provides a more concise alternative to multiple if-else statements. Ternary Operator (?:):The ternary operator is a shorthand version of the if…else statement and is used to assign a value based on a condition. Loops:In PHP, loops are essential constructs used to execute a block of code repeatedly based on a specific condition. Let’s delve into the various types of loops supported by PHP and understand their syntax, functionality, and usage in detail: For Loop:The for loop is used to iterate over a block of code a fixed number of times. It consists of an initialization, condition, and increment/decrement expression. While Loop:A while loop is a programming structure that repeatedly executes a block of code as long as a specified condition remains true. It iterates based on the truth of the condition, ensuring code execution until the condition evaluates to false. Do-While Loop:The do-while loop is a control flow structure that executes a block of code at least once, regardless of the condition. It then checks the condition, and if true, repeats the execution. This loop guarantees the block’s execution before evaluating the condition, suitable for initialization-dependent scenarios. Functions:Functions in PHP play a crucial role in organizing code, promoting reusability, and enhancing the maintainability of web applications. They encapsulate a set of instructions that can be called multiple times within a script or across different scripts. Arrays:An array in PHP is a fundamental and flexible data structure that enables you to store and organize multiple values within a single variable name. Arrays are widely used in PHP programming for various tasks such as storing lists of items, grouping related data, and managing collections of elements. Key Features of Arrays in PHP:
Strings:In PHP, a string is a fundamental data type that represents a sequence of characters, including letters, numbers, symbols, and whitespace, enclosed within single quotes (”) or double quotes (“”). Strings are extensively used in PHP for storing and manipulating textual data, such as user input, file contents, and database records.. Creating Strings:
PHP with HTMLTo run PHP code embedded within HTML, you need to have access to a web server environment that supports PHP. You can set up a local development environment on your computer using software packages like XAMPP, WAMP, or MAMP, which provide Apache web server, MySQL database, and PHP interpreter. Alternatively, you can upload your PHP files to a web hosting provider that supports PHP scripting. Once you have a web server environment set up, you can create a PHP file with HTML markup and save it with a .php extension. Then, you can access the PHP file through a web browser by navigating to its URL. Example: This example shows the basic use of PHP in HTML file. Output: 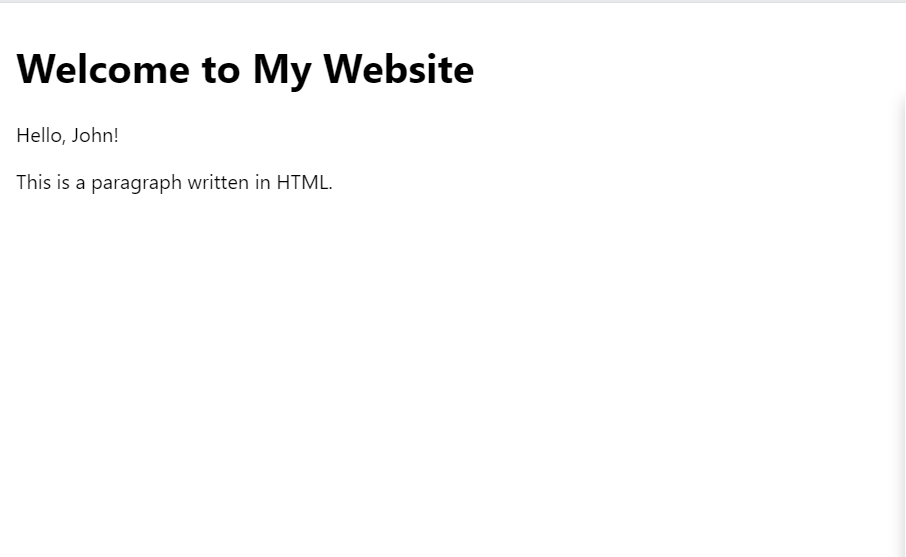 output Advantages
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| PHP |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 13 |