|
Creating a Contact Us form in Next.js involves setting up a form component, handling form submissions, and potentially integrating with a backend service or API to send the form data. In this article, we will create a Contact Us Form with NextJS.
Output Preview: Let’s have a look at what our final project will look like:
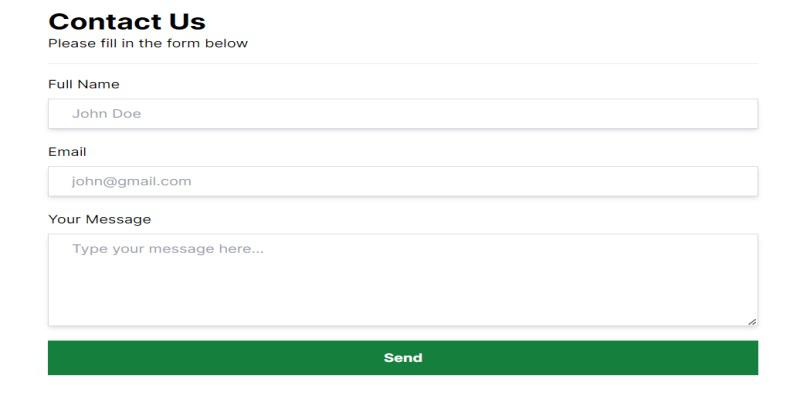 Building a Contact Us Form with Next.js Prerequisites: ApproachTo create contact us form using Next.js, we will use:
- The Home component to renders the contact form.
- The ContactForm component handles user input, submission, and displays success or error messages.
- Accepts POST requests with contact form data.
- Uses Mongoose to connect to MongoDB and store the contact information.
- Returns JSON responses indicating success or failure, including error messages for validation failures.
- The database setup uses MongoDB with Mongoose for defining a schema and interacting with the database.
Steps to Build a Contact Us Form with NextJSStep 1: Set up NextJS project using the command
npx create-next-app@latest What is your project named? > contact-us
Would you like to use TypeScript with this project? > No
Would you like to use ESLint with this project? > Yes
Would you like to use Tailwind CSS with this project? > Yes
Would you like to use 'src/'directory with this project? > No
Use App Router (recommended)? > Yes
Would you like to customize the default import alias? > No Step 2: Navigate to the project folder using the below command.
cd contact-us Step 3: Install the mongoose package using the command.
npm i mongoose Project Structure: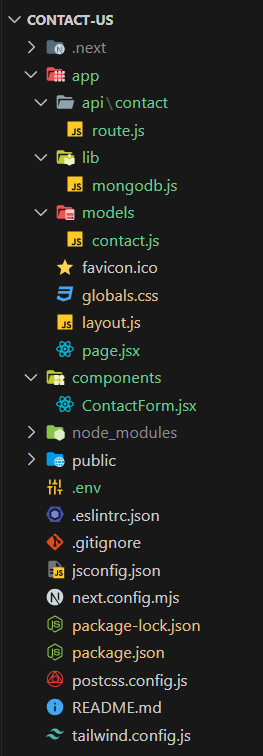 Project Structure of Contact Us Form with Next.js The updated dependencies in the package.json file are:
"dependencies": {
"mongoose": "^8.5.1",
"next": "14.2.4",
"react": "^18",
"react-dom": "^18"
}Step 4: Set up MongoDB for database.
- Simply search for MongoDB Atlas and create a free account.
- Create a cluster.
- Create a New Project as ContactForm .
- Build a Database using the Free version.
- Create a username and password.
- Add the IP Address as 0.0.0.0/0 so that we can access this database from anywhere.
- Click on Connect and select MongoDB for VS Code.
- Copy the connection string and replace <password> with your password.
Create a file as .env in the project folder . Paste the connection string you have just copied and put it equal to MONGODB_URL variable with contact_db appended at the end of the connection string as given below.
MONGODB_URL=mongodb+srv://<username>:<password>@cluster0.jxzdjvc.mongodb.net/contact_db
Explanation:
- Create a folder “components” and add a new file in it namely ContactForm.jsx.
- Create a folder “api” under the folder app . Create a sub-folder contact and add a new file in it namely route.js.
- Create a folder “lib” under the folder app and add a new file in it namely mongodb.js.
- Create a folder “models” under the folder app and add a new file in it namely contact.js.
- Modify files of the folder app i.e. global.css, layout.js, and page.jsx.
Example: Below is an example of building a Contact Us Form with NextJS.
CSS
/* Filename - globals.css */
@tailwind base;
@tailwind components;
@tailwind utilities;
form>div {
@apply flex flex-col gap-2;
}
input,
textarea {
@apply shadow-md px-6 py-2 border border-slate-300;
}
// Filename - page.jsx
import ContactForm from "@/components/ContactForm";
export default function Home() {
return (
<div className="p-4 max-w-3xl mx-auto">
<h1 className="text-3xl font-bold">
Contact Us
</h1>
<p>Please fill in the form below</p>
<ContactForm />
</div>
);
}
// Filename - layout.js
import { Inter } from "next/font/google";
import "./globals.css";
const inter = Inter({ subsets: ["latin"] });
export const metadata = {
title: "Contact Us",
description: "Generated by create next app",
};
export default function RootLayout({ children }) {
return (
<html lang="en">
<body className={inter.className}>
{children}
</body>
</html>
);
}
// Filename - components/ContaxtForm.jsx
"use client";
import { useState } from "react";
export default function ContactForm() {
const [fullname, setFullname] = useState("");
const [email, setEmail] = useState("");
const [message, setMessage] = useState("");
const [error, setError] = useState(null);
const [success, setSuccess] = useState(false);
const handleSubmit = async (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
console.log("Full name: ", fullname);
console.log("Email: ", email);
console.log("Message: ", message);
const res = await fetch("api/contact", {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify({
fullname,
email,
message,
}),
});
const { msg, success } = await res.json();
setError(msg);
setSuccess(success);
if (success) {
setFullname("");
setEmail("");
setMessage("");
}
};
return (
<>
<form
onSubmit={handleSubmit}
className="py-4 mt-4 border-t flex flex-col gap-5"
>
<div>
<label htmlFor="fullname">Full Name</label>
<input
onChange={(e) => setFullname(e.target.value)}
value={fullname}
type="text"
id="fullname"
placeholder="John Doe"
/>
</div>
<div>
<label htmlFor="email">Email</label>
<input
onChange={(e) => setEmail(e.target.value)}
value={email}
type="text"
id="email"
placeholder="[email protected]"
/>
</div>
<div>
<label htmlFor="message">Your Message</label>
<textarea
onChange={(e) => setMessage(e.target.value)}
value={message}
className="h-32"
id="message"
placeholder="Type your message here..."
></textarea>
</div>
<button className="bg-green-700 p-3 text-white font-bold"
type="submit">
Send
</button>
</form>
<div className="bg-slate-100 flex flex-col">
{error && (
<div
className={`${success ? "text-green-800" : "text-red-600"
} px-5 py-2`}
>
{error}
</div>
)}
</div>
</>
);
}
// Filename - api/contact/route.js
import connectDB from "@/app/lib/mongodb";
import Contact from "@/app/models/contact";
import { NextResponse } from "next/server";
import mongoose from "mongoose";
export async function POST(req) {
const { fullname, email, message } = await req.json();
try {
await connectDB();
await Contact.create({ fullname, email, message });
return NextResponse.json({
msg: ["Message sent successfully"],
success: true,
});
} catch (error) {
if (error instanceof mongoose.Error.ValidationError) {
let errorList = [];
for (let e in error.errors) {
errorList.push(error.errors[e].message);
}
console.log(errorList);
return NextResponse.json({ msg: errorList });
} else {
return NextResponse.json({
msg: ["Unable to send message."]
});
}
}
}
// Filename - lib/mongodb.js
import mongoose from "mongoose";
const connectDB = async () => {
try {
if (mongoose.connection.readyState === 0) {
await mongoose.connect(process.env.MONGODB_URL);
console.log("db connected");
}
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
};
export default connectDB;
// Filename - modals/contact.js
import mongoose, { Schema } from "mongoose";
const contactSchema = new Schema({
fullname: {
type: String,
required: [true, "Name is required."],
trim: true,
minLength: [2, "Name must be larger than 2 characters"],
maxLength: [50, "Name must be lesser than 50 characters"],
},
email: {
type: String,
required: [true, "Email is required."],
match: [/^[\w.%+-]+@[\w.-]+\.[A-Za-z]{2,}$/i,
"Invalid email address"],
},
message: {
type: String,
required: [true, "Message is required."],
},
date: {
type: Date,
default: Date.now,
},
});
const Contact =
mongoose.models.Contact || mongoose.model("Contact",
contactSchema);
export default Contact;
Start your application using the following command.
npm run dev Output : Open web-browser and type the following URL http://localhost:3000/
 Building a Contact Us Form with NextJS
|



