|
|
Automating software installation and configuration tasks is fundamental for efficient DevOps practices. Ansible, an open-source automation tool, works on this interaction by permitting you to characterize the framework as code and automate tasks across various servers. In this article, we will zero in on utilizing Ansible to introduce Apache Tomcat, a broadly utilized Java Servlet compartment, on servers inside your infrastructure. Apache Tomcat is a vital part of sending Java-based web applications, giving a solid and versatile environment for hosting servlets and JSP pages. However, manually installing and arranging Tomcat on various servers can be time-consuming and error-prone. Ansible streamlines this interaction by empowering you to define declarative configuration files called playbooks, which indicate the ideal condition of your foundation and the tasks to be executed. Ansible is an open-source automation tool designed for configuration management, application organization, and assignment coordination. It allows system administrators and DevOps groups to automate repetitive tasks, smooth out complex work processes, and oversee infrastructure productively. What Is Ansible?Ansible works by pushing changes out to all your servers and re-quires no extra software to be installed on your servers (thus no extra memory footprint and no extra daemon to manage), unlike other configuration management tools like Puppet and Chef. Configuration management is all about taking your hosts and getting them to their end desired state. So we don’t necessarily know what the state is now, but we can declare the desired end state, and config management tools are really good about taking you from where you are to where you want to go At its center, Ansible works utilizing a basic and agentless architecture, making it simple to convey and use across different conditions. It uses SSH connections to speak with remote servers and execute tasks defined in YAML-formatted configuration called playbooks. Playbooks portray the ideal condition of systems and characterize the undertakings to accomplish that state. Key Highlights Of Ansible
Ansible ArchitectureAnsible architecture is designed to provide a simple, scalable, and agentless automation solution for managing infrastructure and applications. At its core, Ansible follows a client-server model, where a central control node communicates with managed nodes (servers or devices) over SSH or PowerShell remoting. Let’s break down the components of the Ansible architecture:
Control Node:
Managed Nodes:
Inventory:
Modules:
Playbooks:
Roles:
Step-By-Step Process to Install tomcat using ansible playbookStep-1: Launch an EC2 InstanceLaunch EC2 instance with Amazon Linux2 Kernel 5.10(AMI) along with port numbers set SSH – 22, HTTP 8o and select storage t2.micro.
Now connect with git bash or any other terminals as you like.
Step-2:Now install Ansible to our local machine by using following command sudo amazon-extras-linux install ansible2
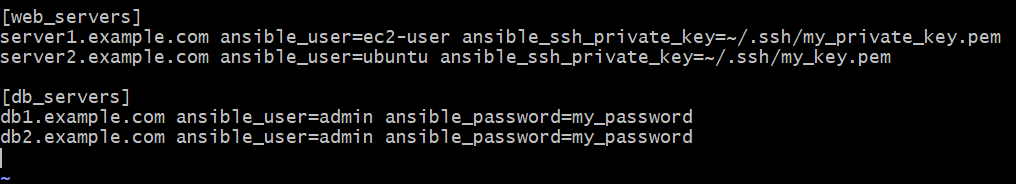
Step-3: Create a inventory fileIn this section we creating inventory file and inside that file we are providing hosting address. Create file by using following command vi <filename.ini> # inventory.ini [web_servers]
Step-4: Creating playbookIn this section we are creating playbook by using following command vi playbook.yml Playbooks are written in YAML Configuration. For YAML configuration we need “.yml” extension - name: Install Tomcat
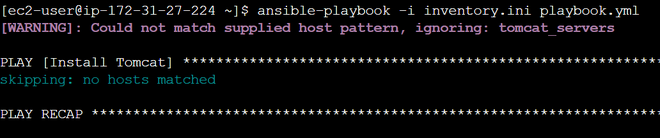
Step-5: Run the PlaybookExecute the playbook using the ansible-playbook command, specifying the inventory file. ansible-playbook -i <filename.ini> <filename>.yml
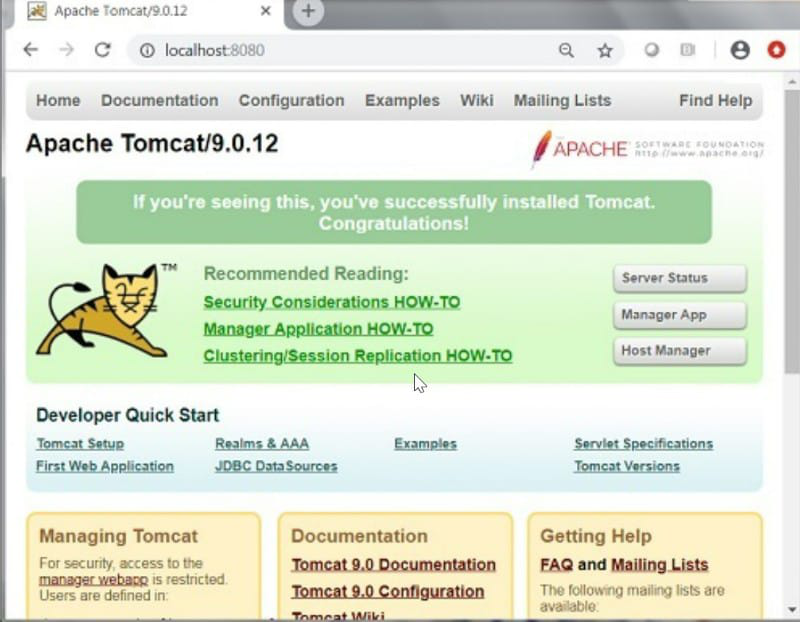
Step 6: Verify InstallationNow access Tomcats’ management console through a web browser (http://<server_ip>:8080) to verify that Tomcat is installed and running correctly.
ConclusionIn conclusion, deploying Apache Tomcat using an Ansible playbook offers a streamlined and repeatable way to deal with managing Tomcat installations across different servers. By characterizing installation steps, configuration management, and service management tasks inside the playbook, administrators can ensure consistency and dependability in the deployment cycle. Ansible’s idempotent nature ensures that playbook executions are idempotent, meaning they can be securely re-run without causing accidental changes or interruptions. Also, the utilization of Ansible playbooks advances infrastructure as code works on, empowering version control, collaboration, and automation in Tomcat deployment work processes. Generally speaking, utilizing Ansible for Tomcat installation works on organization tasks, speeds up sending cycles, and improves the viability of Tomcat installations in big enterprise conditions. Tomcat Using Ansible Playbook – FAQ’sCould Ansible install Tomcat on multiple servers at the same time?
Does Ansible handle dependencies for Tomcat installation consequently?
Could I configure custom settings for Tomcat (e.g., server.xml) utilizing Ansible?
How would I deal with authentication for deploying Tomcat with Ansible?
Is it possible to upgrade Tomcat versions using Ansible playbooks?
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Dev Scripter |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 15 |