|
|
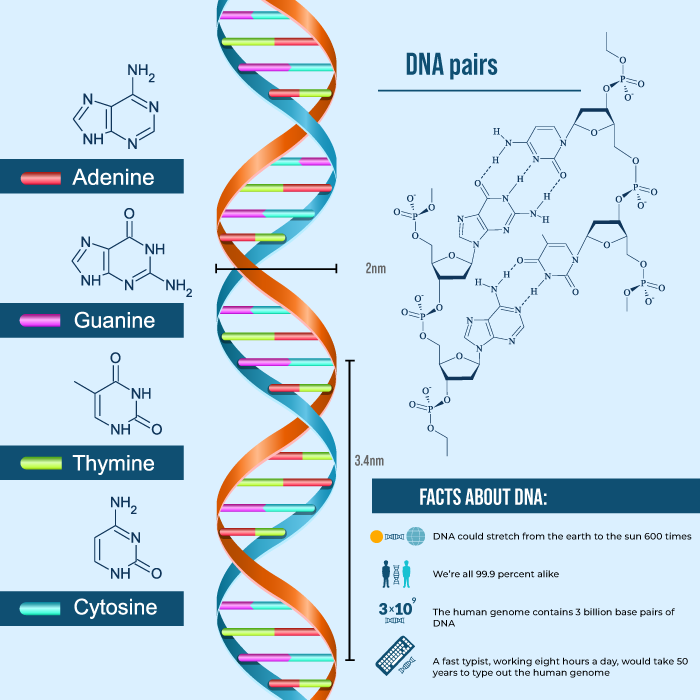
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule that contains the genetic instructions necessary for the development and functioning of all known living organisms. It consists of two long chains, known as strands, that coil around each other to form a double helix. The DNA is negatively charged. In this article, we will learn the answer to “Why is DNA Negatively Charged,” and the structure and function of DNA in detail. Table of Content What is DNA?DNA is a genetic material that is present in every single organism from unicellular to multicellular organisms. It carries genetic information about a particular species. The full form of DNA is Deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA was discovered by a Swiss Biologist Johannes Friedrich Miescher, in the year 1869. Structurally, DNA is a double helix formed by two complementary strands of nucleotides, each containing a sugar-phosphate backbone and nitrogenous bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine). The sequence of these bases encodes genetic information. DNA is located in the cell’s nucleus in eukaryotes and in the nucleoid region in prokaryotes. Replication of DNA occurs during cell division, ensuring the inheritance of genetic material. Also Read: Why Thymine is present in DNA instead of Uracil? Structure of DNADNA or deoxyribonucleic acid is double helical polynucleotide chains. It contains genetic code that is unique for every individual. Genetic code is composed of three DNA nucleotides (codon) that correspond with a specific protein that is responsible for making different Structures, Enzymes & organs of our body. Now let’s study more about the structure of DNA. DNA is composed of a sugar-phosphate backbone and nitrogenous base pairs. There are two types of nitrogenous base pairs:
Purine can form hydrogen bonds with pyrimidine, since they are present in pairs that is why we call it a nitrogenous base pair.
Why is DNA Negatively Charged?DNA is negatively charged because of the presence of negatively charged phosphate groups. In the phosphate group there is single negatively charged oxygen, which makes the entire DNA negatively charged. Negativity of DNA helps in joining two strands of DNA together to form a double helical structure. Now let’s make the concept more clear about Double helical structure of DNA.
It is made up of two antiparallel polarities (one end of strand is 3’ to 5’ and ends of other strand is 5’ to 3’) nucleotides backbone which consists of Sugar-phosphate and one nitrogenous base on each strand. The nitrogenous base of one strand makes hydrogen bonds with corresponding nitrogenous bases and forms a helical structure. The two strands are right coiled handed. The pitch of the helix is 3.4 nm, around 10 base pairs and 0.34 nm is the distance between two base pairs that are present in turn of the helix. Also Read: Difference Between DNA Polymerase 1, 2 And 3
Discovery of DNAThe discovery of DNA’s role as the genetic material transferring from generation to generation was confirmed by Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase’s 1952 experiment using bacteriophages.
Types of DNAThere are three types of DNA namely :
Also Read: DNA Replication – Definition, Classification, Process, Examples Functions of DNAFunction of the DNA are:
Also Read: What is the importance of Variation? Conclusion – Why Is DNA Negatively Charged?In conclusion, DNA is negatively charged because of the presence of phosphate groups in nucleotides. The phosphate backbone of DNA is negatively charged, which is due to the presence of bonds created between the phosphorus and oxygen atoms. In DNA structure, a phosphate group comprises one negatively charged oxygen atom, which is responsible for the entire strand of DNA to be negatively charged.
FAQs on Why Is DNA Negatively Charged?Who Discovered DNA for the First Time?
Why DNA is a Genetic Material?
How Many Base Pairs are there in One Full Turn of the Double Helix DNA?
Where is DNA Located ?
Which Part of Helix is Called as Backbone of DNA?
What Part of DNA is Negatively Charged?
What is the Charge of DNA in Gel Electrophoresis?
Why is DNA negativley Charged and Why is it Important for Gel Electrophoresis?
Is DNA more Negatively Charged than RNA?
Why is DNA Acidic in Nature?
What is the Advantage of Negative Charge DNA?
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| School Biology |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 14 |

