|
|
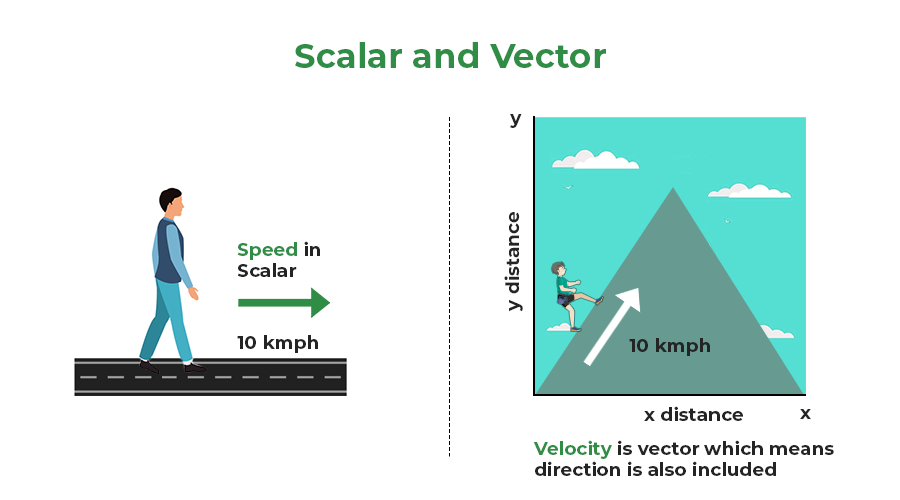
Vector Resolution is splitting a vector into its components along different coordinate axes. When a vector is expressed in terms of its components, it becomes easier to analyze its effects in different directions. This process is particularly useful when dealing with vector quantities such as forces, velocities etc. Vector resolution is a powerful tool in physics and engineering, that enables the analysis and prediction of complex physical phenomena by simplifying vectors into manageable components. Table of Content What are Vectors?In mathematics and physics, a vector is a mathematical object that has magnitude(or length) and direction and obeys the vector law of addition. Vectors are often represented as arrows in space with a particular length(as magnitude) and a particular direction while quantities that have both direction and magnitude are called scalar quantities.  Vectors can be used to represent various physical quantities such as displacement, velocity, acceleration and force. What is Vector Resolution?Vector Resolution refers to the process of breaking down a vector into its components along specified axes or directions. This decomposition allows for simplified calculations or analyzing the effects of a vector in different directions. This involves decomposing the vector into two perpendicular components, often along the horizontal and vertical axes. For instance, if you have a vector representing a force acting at an angle to a surface, you might resolve it into horizontal and vertical components to understand how much of the force is acting in each direction. As we will see in the next section, this can be done using trigonometry. The concept of vector resolution is fundamental to both physics and engineering, especially when studying forces, velocities, and other vector quantities. To successfully carry out vector resolution, we must understand vector addition. 2 different laws provide geometric interpretations of vector addition:
Triangle Law of Vector AdditionThis law states that,
Parallelogram Law of Vector AdditionThis law states that,
Rectangular Components of a VectorRectangular components are the projections of that vector onto the coordinate axes of a Cartesian coordinate system. In a two-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system, a vector can be decomposed into its horizontal and vertical components.
Horizontal ComponentHorizontal component lies along the x-axis. If the angle between the vector and the horizontal axis is θ, then:
Vertical ComponentVertical component lies along the y-axis. If the angle between the vector and the horizontal axis is θ, then:
Method of Resolving a VectorVectors can be easily resolved into its rectangular components and the steps for the same are,
Write down resolved vector components, specifying both their magnitudes and directions. Trigonometric Method of Vector ResolutionTrigonometric method is a technique used to break down a vector into its components along specified directions using trigonometric functions. This method is particularly useful when dealing with vectors in two dimensions. Let’s say we have a vector
Applications of Vector ResolutionApplication of Vector Resolution in Physics and Engineering are as, Projectile Motion: When studying the motion of projectiles, such as objects thrown or launched into the air, vector resolution helps break down the initial velocity into horizontal and vertical components. This allows for analyzing the motion independently along each axis, making calculations more manageable. Force Analysis: In mechanics, vector resolution is used to break down forces acting on an object into components along specified axes. This simplifies the analysis of forces, especially when dealing with forces acting at angles. Statics and Dynamics: Vector resolution is essential in analyzing the equilibrium or motion of objects under the influence of multiple forces. By resolving forces into horizontal and vertical components, we can determine conditions for equilibrium or calculate the resulting motion. Engineering applications of Vector Resolution are as follows: Robotics: Vector resolution plays a vital role in robotics for analyzing the motion and forces acting on robotic manipulators and end-effectors. Engineers use it to decompose forces and velocities in robot kinematics and dynamics, enabling precise control and motion planning. Fluid Mechanics: In fluid engineering applications, vector resolution is used to analyze fluid flow behavior, such as velocity profiles, pressure distributions, and shear forces. Engineers use it to decompose fluid velocities and forces into components, aiding in the design of pipelines, pumps, and hydraulic systems. Common Mistakes of Resolution VectorCommon mistakes and misconceptions relating to Resolution of Vector are:
Conclusion: Resolution VectorVector resolution involves breaking down vectors into components along different axes, typically horizontal and vertical. This simplifies analysis by isolating effects in specific directions. Trigonometric relationships aid in determining component magnitudes based on vector angles, which are then combined through addition to reconstruct the original vector.
Examples for Vector ResolutionExample 1: A body is moving with a velocity of 10 m/s at an angle of 60° to the horizontal. Break the velocity down into its horizontal and vertical components. Solution:
Example 2: A force of 50N is acting on a body at an angle of 30 degrees with the horizontal What force is pushing the body forward? Solution:
Practice Problems on Resolution of VectorVarious practice problems on resolution of vector are, Problem 1: A force of 80 N is applied at an angle of 45 degrees with the horizontal. Determine the horizontal and vertical components of the force. Problem 2: A velocity of 15 m/s is directed at an angle of 60 degrees with the horizontal axis. Find the horizontal and vertical components of the velocity. Problem 3: An airplane is flying with a velocity of 300 km/h at an angle of 30 degrees with the horizontal. Determine the horizontal and vertical components of the velocity. FAQs on Resolution VectorHow is Vector Resolution Used in Real Life?
Can Vector Resolution Be Applied to Non-Physical Fields?
What Are the key challenges in learning Vector Resolution?
How Does Vector Resolution Differ in Two-Dimensional and Three-Dimensional Spaces?
|
||||||||
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Class 11 |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 13 |
