|
|
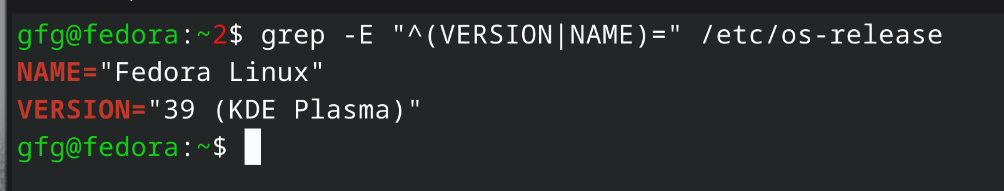
Setting up the Apache Web Server on Linux operating systems such as Ubuntu, Fedora, and RHEL is a routine job for web developers and system managers. Apache stands out among web servers for its adaptability, robust security measures, and compatibility with different web technologies. This manual will guide you through the installation process of Apache on Ubuntu, Fedora, and RHEL, making sure your web server operates smoothly. Whether you’re a novice or a seasoned user, this instruction will assist you in installing Apache on your chosen Linux system. In this article, we will install Apache Web Server on various Linux distributions like Ubuntu, Fedora, Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), etc. Table of Content How to Install Apache Web Server in Linux?Step 1: Check your Linux distributionUse the following command to check which Linux distribution you are using. command: grep -E '^(VERSION|NAME)=' /etc/os-release
 Checking linux distribution (fedora) Step 2: Update Your SystemOn Ubuntu/Debian based systemscommand: sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
On Fedora based systemscommand: sudo dnf update -y
On RHEL based systemscommand: sudo yum update -y
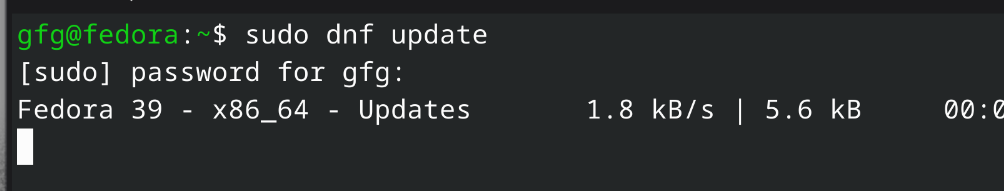 Updating system (fedora) Step 3: Install Apache Web ServerOn Ubuntu/Debian based systemscommand: sudo apt install apache2 -y
On Fedora based systemscommand: sudo dnf install httpd -y
On RHEL based systemscommand: sudo yum install httpd -y
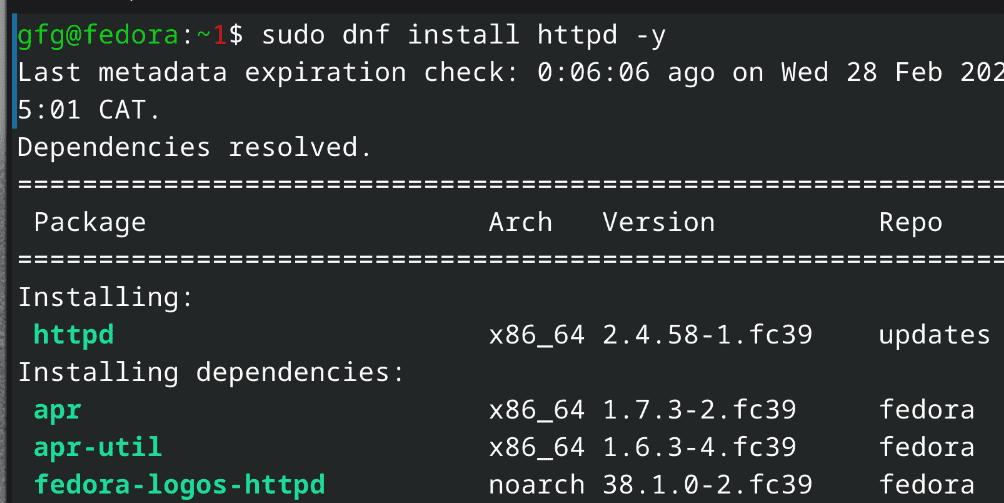 installing apache web server Step 4: Enable the ServicesOn Ubuntu/Debian based systemscommand: sudo systemctl enable apache2
On Fedora based systemscommand: sudo systemctl enable httpd.service
On RHEL based systemscommand: sudo systemctl enable httpd.service
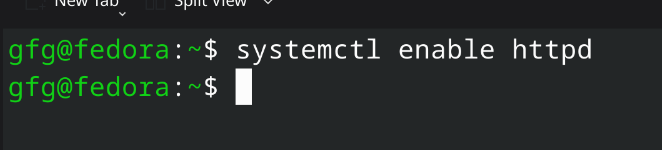 starting services for Apache Web Server Step 5: Test the Server by Hosting Simple WebsiteFirst, we will create a directory for our test website using following command. command: sudo mkdir /var/www/html/test_website/
Now we will add index.html for our test website along with some testing code using following command. command: echo '<html><head><title>Example</title></head><body><h1>GFG</h1><p>This is a test.</p></body></html>' | sudo tee /var/www/html/test_website/index.html
Now we will add configuration file using following command command: Once we created the required config file and test website, we will need to own the Apache website directory for permissions. command: Now you can see locally hosted website on localhost.
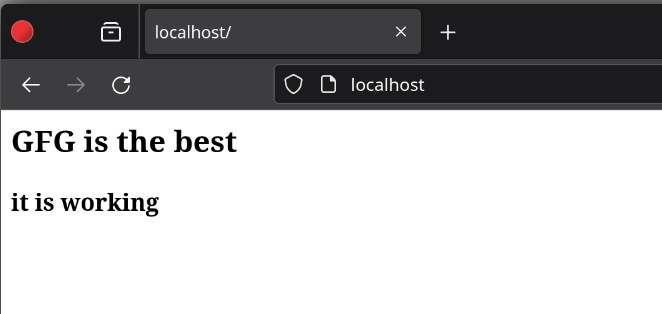 testing website on local server If the above mentioned steps performed correctly, Apache Web Server will run successfully! However, If it didn’t work, then you can uninstall Apache Web Sever and can start installation again. How to Uninstall Apache Web Server?On Ubuntu/Debian based systemscommand: sudo apt remove apache2
On Fedora based systemscommand: sudo dnf remove httpd
On RHEL based systemscommand: sudo yum remove httpd
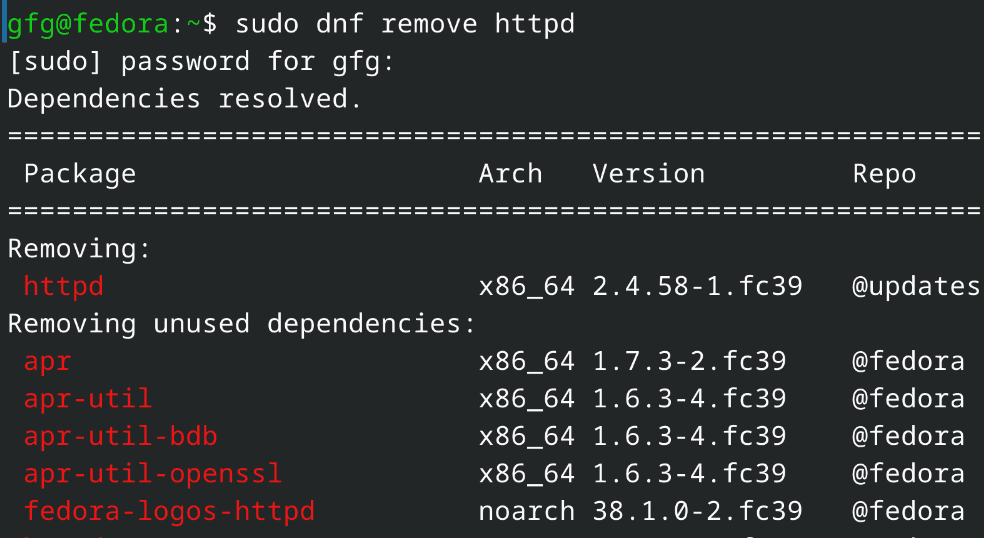 Uninstalling Apache Server Hence we have successfully uninstalled Apache Web Server in Linux! ConclusionInstalling the Apache Web Server on Linux systems like Ubuntu, Fedora, and RHEL is an easy task if you adhere to the proper procedures. After installing Apache, you can utilize its robust capabilities to efficiently host and control your websites. It’s essential to perform routine upkeep and updates to maintain the security and efficiency of your Apache server. This article equips you with the necessary understanding to install and configure Apache on your Linux machine, making it simpler to deploy and manage web applications. Also Read
How to Install Apache Web Server in Linux: Ubuntu, Fedora, RHEL – FAQsWhat is Apache, and why is it used?
What are virtual hosts, and when are they used?
What are some best practices for managing multiple websites with Apache?
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| TechTips |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 15 |