|
|
Kubernetes (K8s) installations frequently present issues from multiple perspectives, including pods, services, ingress, non-responsive clusters, control planes, and high-availability configurations. Kubernetes pods are the smallest deployable units in the Kubernetes ecosystem, each containing one or more containers that share resources and a network. Pods are intended to execute a single instance of an app or process and are built and destroyed as required. Pods are essential for scaling, updating, and sustaining applications in a Kubernetes environment. In this article, we will explore Pod troubleshooting strategies in Kubernetes, offering expert insights to help you ensure the seamless performance of your applications. What is Kubernetes Troubleshooting?Kubernetes troubleshooting is the process of finding, diagnosing, and resolving issues with Kubernetes clusters, nodes, pods, or containers. Kubernetes troubleshooting, as a broader term, encompasses effective ongoing fault management and preventative measures for Kubernetes components. Kubernetes troubleshooting can be extremely difficult. This article will address frequent issues like
The Three Pillars of Kubernetes TroubleshootingThere are three aspects to effective troubleshooting in a Kubernetes cluster: understanding the problem, managing and remediating the problem, and preventing the problem from recurring. Understanding the problemIn a Kubernetes context, it can be difficult to understand what happened and identify the core cause of the issue. This often includes:
Managing and Remediating the ProblemIn a microservices architecture, it is common for each component to be developed and managed by a separate team. Because production incidents often involve multiple components, collaboration is essential to remediate problems quickly. Once the problem is identified, there are three techniques to resolving it:
PreventionSuccessful teams make prevention their top priority. Over time, this will reduce the time invested in identifying and troubleshooting new issues. Preventing production issues in Kubernetes involves:
Types of Pod ErrorsBefore diving into pod debugging, it’s essential to understand different types of Pod errors. Container & Image ErrorsAll these error states are part of the kubernetes container package & Kubernetes image package. Following is the list of official Kubernetes pod errors with error descriptions.
How to Troubleshoot Pod Errors ?The first step in troubleshooting a pod is getting the status of the pod. Run the below command to know the status of the pods. kubectl get pods
Now that you know the error type, describe the individual pod and look through the events to see what is generating the pod error. To get detailed information about the pod. Run the below command. kubectl describe pod <pod-name>
Now let’s look at some of the most common pod errors and how to troubleshoot them. Troubleshoot ErrImagePullBackOffRun the below command to get the pod details. kubectl get pods
If you see ErrImagePullBackOff in pod status, it is most likely for the following reasons.
If you check the pod events, you will see the ErrImagePull error followed by ErrImagePullBackOff. This means the kubelet stops trying to pull the image again and again. kubectl describe pod <pod-name>
1. Troubleshoot Error: InvalidImageNameRun below command to know status of the pods. kubectl get pods
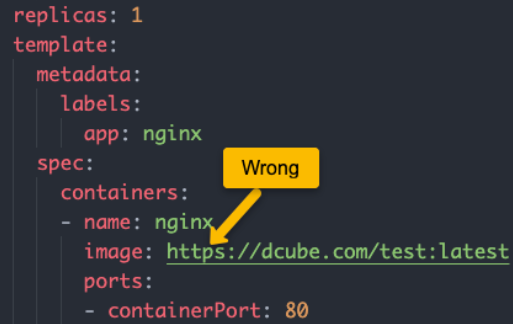
For example, if you have a private container registry and you mention the image name with https, it will throw the ‘InvalidImageName’ error. You need to specify the image name without https.
2. Pod Configmap & Secret Errors[CreateContainerConfigError]CreateContainerConfigError is one of the common errors related to Configmaps and Secrets in pods. This normally occurs due to two reasons.
If you describe the pod you will see the following error.
If you have a typo in the key name, you will see the following error in the pod events.
To rectify this issue,
Let’s look at the correct example. Here is a configmap where service-name is the key that is needed as an env variable inside the pod.
Here is the correct pod definition using the key (service-name) & configmap name (nginx-config)
ConclusionTroubleshooting Pod failures in Kubernetes can initially seem daunting. However, with a systematic approach, you can identify and solve most issues. Always start with the basics: check the Pod status, describe the Pod for details, examine logs, and inspect configurations. Remember, every failure is an opportunity to learn and improve your Kubernetes skills. Kubernetes Pods – FAQ’swhat are some common issues with Kubernetes pods?
What should we do when a pod is stuck in pending state?
What are Kubernetes pods?
What to do when my pod’s containers are not starting or crashing?
How can I troubleshoot issues related to networking?
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Kubernetes |
| Related |
|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 14 |