|
|
Redux is one of the most popular state management libraries used today for building a complex application that requires global state management.
In this article, you will learn the top Redux interview questions and answers that are most frequently asked in interviews. Before proceeding to learn Redux interview questions and answers, it is beneficial if you learn the complete Redux Tutorial. 1. What is Redux?Redux is a popular open-source state management library for JavaScript applications. It provides a way to centralize the state of an application in a single store, making it easier to debug, test, and reason about the state changes in the application. 2. What are the problems that Redux solves?Redux solves many problems faced while building complex front-end web applications.
3. What are the advantages of Redux in React?
4. Explain the core principles of Redux.Three principles that Redux follows are:
5. What is the difference between Redux and Context API.
6. Explain some features of React Redux.Some of the major features of Redux are as follows:
7. Is it necessary to keep all the component states in the Redux store?No, it’s not necessary to keep all component states in the Redux store. While Redux provides a centralized state management solution, it’s not meant to replace local component state entirely. There are several factors to consider when deciding whether to use Redux for a particular piece of state. 8. How do you connect a React component to a Redux store?The connect() function connects a React component to a Redux store. It provides its connected component with the pieces of the data it needs from the store, and the functions it can use to dispatch actions to the store. Javascript
9. Can you write the Implementation of the Redux Store.Javascript
10. What is the significance of immutability in Redux?The significance of immutability in Redux lies in ensuring a predictable state and simplifying state management. Using immutable states allows us to write code that can quickly tell if the state has changed, without needing to do a recursive comparison on the data, which is usually much faster. 11. Explain the difference between Redux and React’s local state.React state is stored locally within a component. To share this state with other components in the application, props are passed to child components, or callbacks are used for parent components. Redux state, on the other hand, is stored globally in the store.
12. What are pure functions in the context of Redux?A pure function is defined as any function that doesn’t alter input data, doesn’t depend on the external state, and can consistently provide the same output for the same input. As opposed to React, Redux depends on such pure functions. 13. What are the key components of Redux architecture?Key components of Redux architecture.
14. What do you understand about Redux Toolkit?Redux toolkit is a npm package that is made to simplify the creation of redux store and provide easy state management. Before the introduction of the Redux toolkit state management was complex in simple redux. The Redux toolkit acts as a wrapper around redux and encapsulates its necessary functions. Redux toolkit is flexible and provides a simple way to make a store for large applications. It follows SOPE principle which means it is simple, Opinionated, Powerful, and Effective. 15. What is the purpose of the Redux store?Store is an object which provides the state of the application. This object is accessible with help of the provider in the files of the project. The only way to change the state inside it is to dispatch an action on it. There are three important parts of the store:
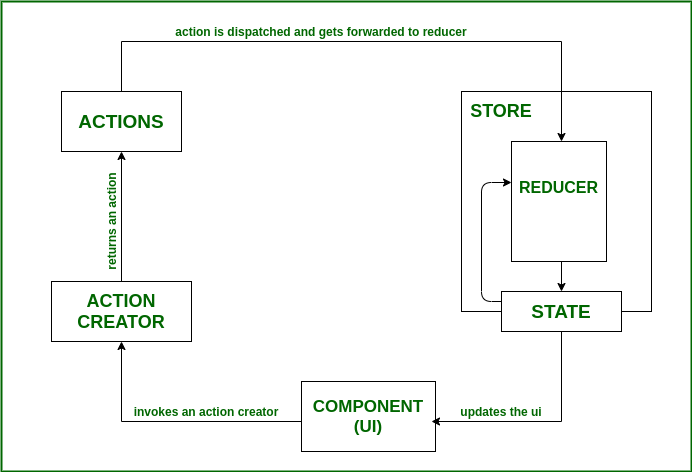
16. What’s the typical flow of data like in a React with Redux app ?
17. What are actions in Redux.Actions are JavaScript object that contains information. Actions are the only source of information for the store. It basically carries a payload of information from the application to the store. It only tells us what has happened. Actions have a type property that they must include as type property tells what kind of action to perform. Action can also contain the payload(data field in the action) to describe the action. 18. What is a reducer in Redux?In Redux, reducers are pure functions that handle state logic, accepting the initial state and action type to update and return the state, facilitating changes in React view components. Syntax: (State,action) => newState
19. How Reducers can be used in React.Javascript
20. Explain the concept of immutability in Redux.In Redux, immutability refers to the principle of not mutating state directly. Instead, when you need to update the state, you create a new copy of the state object with the desired changes applied. This ensures that the original state remains unchanged, and provides predictable state management and efficient change detection. 21. What is the purpose of the
|
| Feature | Synchronous Middleware | Asynchronous Middleware |
|---|---|---|
| Execution Order | Executes in a sequential manner, one after the other | Executes concurrently or in a non-blocking manner |
| Blocking Behavior | May block the execution of subsequent middleware or actions until completion | Does not block subsequent middleware or actions, allowing for concurrent execution |
| Use Cases | Ideal for tasks that require immediate response or have strict ordering requirements | Suitable for tasks that involve asynchronous operations, such as fetching data from an API or performing I/O operations |
| Example | Logging middleware, error handling middleware | Thunk middleware, Saga middleware |
29. What are action chaining in Redux middleware?
Action chaining in Redux middleware refers to the process of dispatching multiple actions in response to a single dispatched action. This technique is often used to handle complex sequences of actions or to arrange multiple asynchronous operations.
30. Discuss the strategies for handling side-effects in Redux applications.
There are several strategies for handling side-effects in Redux include using middleware like Redux Thunk for asynchronous actions and Redux Saga for more complex scenarios. These tools manage side-effects outside reducers.
- Redux-Thunks: Thunks are functions that wrap an action creator and can perform asynchronous logic before dispatching actions. They provide a way to handle side-effects in Redux without introducing additional middleware.
- Redux-Saga: Redux-Saga is a middleware library for handling side-effects in Redux applications. It uses generator functions to describe asynchronous logic as a series of simple, composable effects.
31. What do you understand about the Redux Saga?
Redux-Saga is a library that aims to make application side effects (i.e., asynchronous things like data fetching and impure things like accessing the browser cache) easier to manage, more efficient to execute, easy to test, and better at handling failures.
32. What are the differences between call() and put() in redux-saga?
call() and put() are both effects that can be used in Redux Saga to manage asynchronous operations, but they have different purposes:
| Feature | call() |
put() |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Invokes functions or promises and waits for result | Dispatches actions to the Redux store |
| Effect | Suspend Saga until function/promise resolves/rejects | Dispatch an action to the Redux store |
| Example Usage | yield call(api.fetchData, action.payload) |
yield put({ type: 'INCREMENT' }) |
| Blocking Behavior | Blocks Saga until function/promise completes | Does not block Saga, continues execution |
| Return Value | Returns result of function/promise | No return value, only dispatches action |
33. Explain the purpose of the redux-thunk middleware.
The purpose of the redux-thunk middleware is to enable Redux to handle asynchronous logic more easily, particularly when dealing with actions that don’t immediately return an object, but instead return a function. Redux-thunk extends Redux functionality by allowing action creators to return functions instead of plain action objects. These functions, known as thinks and have access to the dispatch and getState functions of the Redux store.
34. What is the role of the dispatch function in Redux?
The role of the dispatch function in Redux is to send actions to the store. It’s a method provided by the Redux store that accepts an action object as its argument and initiates the process of updating the application’s state based on that action.
35. How does Redux ensure that the UI components are updated when the state changes?
Redux ensures that the UI components are updated when the state changes by using a subscription mechanism. Components re-render when the state they depend on updates.
36. Explain the concept of “single source of truth” in Redux?
The global state of an app is stored within an object tree in a single store. As a result, it becomes easier to build universal apps due to the server’s state being serialized into the client without any extra codes. A single state tree, in turn, makes it easy to inspect an app. Besides this, it also enables a faster and shorter development cycle. Furthermore, some of the functionalities that have been traditionally tough to implement, such as Undo/Redo, can become trivial for implementation when the state is in a single tree.
37. What are the advantages of using Redux over local component state?
Using Redux for state management in React applications provides various advantages over local component state:
- Centralized State Management: Redux provides a centralized store for managing application state, that makes it easier to maintain and manage state across multiple components.
- Predictable State Changes: Redux follows a strict unidirectional data flow, where state changes are triggered by dispatching actions to reducers.
- Easier State Debugging: Redux comes with powerful developer tools, such as Redux DevTools, which provide real-time state inspection, time-travel debugging, and action logging.
- Improved Scalability: Redux can be integrated with large and complex applications, as it provides a structured approach to managing state and organizing code.
- Easier State Sharing: Redux provides state sharing between components, allowing multiple components to access and update the same state without passing props manually through intermediate components.
38. What are selectors in Redux?
Selectors in Redux are the functions that extract specific pieces of data from the Redux store state. They provide a way to pass the data from the state in an efficient manner. Selectors are mainly used to encapsulate the process of accessing and transforming state data which makes it easier to manage and reuse across multiple components.
39. Explain the concept of “container components” in React Redux.
Container components are React components that are responsible for interacting with the Redux store. They are connected to the Redux store using the connect() function. Container components acts as the bridge between the Redux store and presentational components, providing them with the necessary data from the store and actions to dispatch.
40. What are “presentational components” ?
Presentational components, also known as stateless components, are React components that are used for rendering UI elements based on the props they receive. They are responsible for presenting data to the user and typically do not have any dependencies on the application’s state or logic.
41. How can you optimize performance in a React Redux application?
Optimizing performance in a React Redux application involves several strategies which focusses at reducing unnecessary renders, improving data fetching and caching, and optimizing component rendering.
- Utilize memoized selectors get data from Redux in a smart way so that it doesn’t slow down.
- Implement shallow equality checks to prevent unnecessary component renders.
- Batch updates with React.StrictMode or libraries like react-batch-updates to minimize DOM manipulations.
- Use React Hooks like useSelector and useDispatch for more efficient state management in functional components.
- Consider server-side rendering (SSR) and code splitting to improve initial load times and perceived performance.
42. What are the advantages of using selectors in Redux?
There are several advantages of using selectors in Redux.
- Efficiency: Selectors optimize performance by efficiently deriving data from the Redux store.
- Abstraction: It abstract the complexity of accessing and transforming state data, making code easier to manage and reuse.
- Reusability: Selectors are reusable functions that can be used in multiple parts of the application to access the same state data.
- Encapsulation: It encapsulate state access and transformation logic within a single function, improving code organization.
- Performance Optimization: Selectors help optimize performance by reducing unnecessary re-renders of components through memoization.
43. What tools and libraries can you use for debugging Redux applications?
There are several tools and libraries available which can be used for debugging Redux applications.
- Redux DevTools Extension
- Redux DevTools
- React DevTools
- redux-logger
- redux-saga-devtools
- redux-immutable-state-invariant
- redux-trace
44. Describe the concept of Redux DevTools.
Redux DevTools is a powerful debugging tool for Redux applications that provides you with insights into the state and actions of their Redux store. It offers a range of features designed to simplify the debugging process and improve the development experience.
- Time-Travel Debugging
- State Inspection
- Action Replay
- Middleware Integration
- Customization Options
45. What are Redux DevTools extensions?
Redux DevTools extensions are browser add-ons designed to enhance the debugging experience for Redux-powered applications. They integrate seamlessly with web browsers like Chrome and Firefox, offering features such as time-travel debugging, state inspection, action replay, middleware integration, and customization options. These extensions simplify the debugging process by providing insights into the state and actions of the Redux store directly within the browser’s developer tools, making it easier for developers to identify and troubleshoot issues in their Redux applications.
46. Explain time-travel debugging in Redux.
Time-travel debugging in Redux lets you go back and forth through the history of actions in the Redux store. It helps you understand how the application’s state changes over time and makes it easier to pinpoint and fix bugs by replaying specific scenarios. It’s like rewinding and fast-forwarding through time to see how the state evolves.
47. What are Redux middleware composition.
Redux middleware composition is refers to the process of combining multiple middleware functions to enhance the behavior of the Redux store. Each middleware function can modify actions, perform tasks like logging or asynchronous operations, and pass the action along to the next middleware. By chaining these functions together, developers can create custom pipelines to handle various aspects of action processing, making it easier to manage complex logic and extend the capabilities of Redux.
48. What is the purpose of the reselect library in Redux?
The purpose of the Reselect library in Redux is to optimize the performance of selectors. It provides a memoization mechanism that caches the results of selector functions based on their input selectors. This means that if the input selectors and arguments to a selector function remain unchanged between invocations, Reselect will return the cached result instead of recomputing it, leading to significant performance improvements.
49. Can I dispatch an action in the reducer?
In Redux, while it’s possible to dispatch actions within reducers, itis not suggested to do that. Reducers should remain pure functions, and responsible only for updating the state based on the dispatched action and returning a new state object.
50. How can we access a redux store outside a react component?
To access the Redux store outside a React component, you need to import the store instance from your Redux setup file. Then, you can use methods provided by Redux, such as store.getState() to access the current state of the store, or store.dispatch(action) to dispatch actions directly.
store = createStore(reducer);export default store;
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Interview Questions |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 16 |