|
|
PL/SQL is a Procedural Language/Structured Query Language and it enables users to write procedural logic directly within the database, including procedures, functions, triggers, and packages. In this article, we will understand Nested select statements in PL/SQL along with the examples and so on. Understanding Nested Select Statement in PL/SQLThe nested select statement in PL/SQL is a feature that allows for the retrieval of data from multiple tables in a single query. It involves using a SELECT statement within another SELECT statement to fetch data based on specified conditions. The main concept of a nested select statement in PL/SQL involves using a SELECT statement within another SELECT statement. This allows for the retrieval of data from multiple tables or views based on specified conditions. The syntax for a nested select statement is as follows: Syntax: -- Outer SELECT Statement: Retrieves data from table1 based on conditions Explanation of Syntax: Outer SELECT Statement:
Nested SELECT Statement:
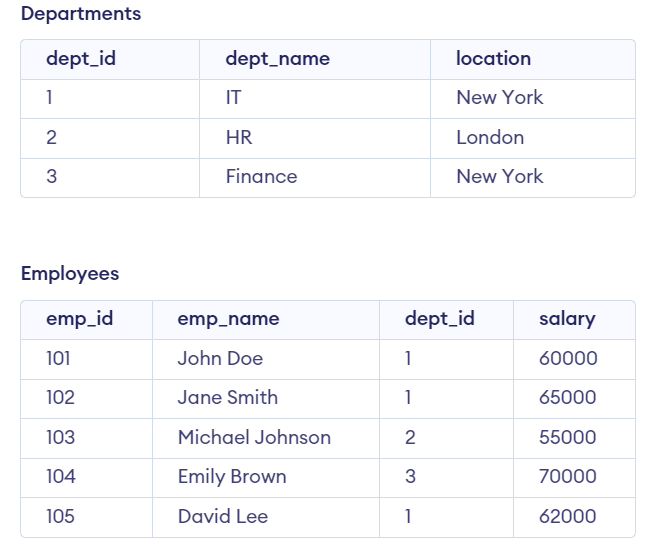
Examples of Nested Select Statement in PL/SQLExamples 1Let’s Say we have two tables, “employees” and “departments.” with the Following Data. We will create the Employees and Departments table which defines the table structure with columns such as emp_id, emp_name, dept_Id and Salary of Employees TABLE and dept_Id, dept_name, and location of departments TABLE which specify the appropriate data types for each column to store information about employees and departments. Query: -- Create departments table After inserting data into the departments and employees table, The table looks:  Departments and Employees tables In this example we want to retrieve the names of employees along with their corresponding department names. We can achieve this using a nested select statement as shown below: Query: SELECT emp_name, Output: 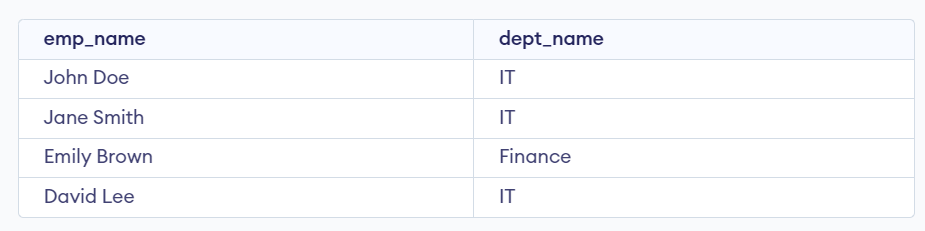 Output Explanation: We can observe that we get the names of employees along with their corresponding department names. Examples 2Let’s Say we have two tables Students and Grades with the Following Data. We can create the Students and Grades table using the following query which defines the table structure with columns such as student_id, and name of Students TABLE and student_id, course, and grade of Grades TABLE which specify the appropriate data types for each column to store information about Students and Grades. Query: -- Create students table After inserting data into the students table, The table looks: 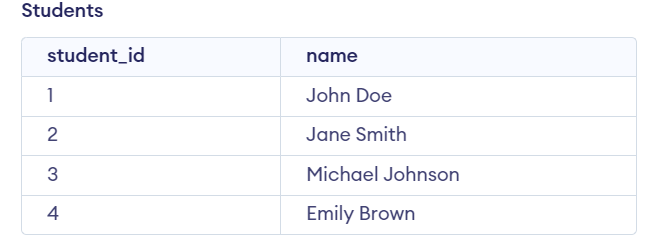 Students Table After inserting data into the grades table, The table looks: 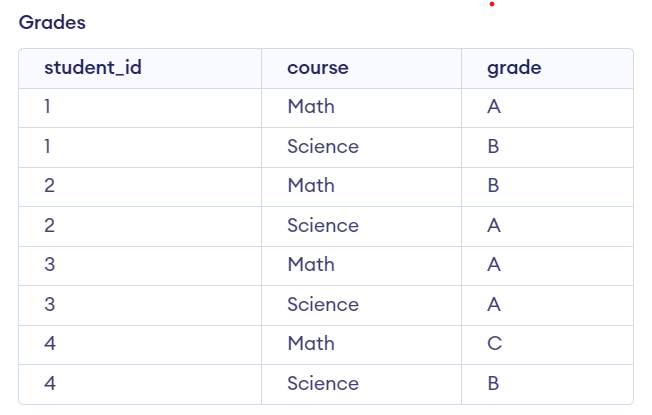 Grades Table In this example We want to retrieve the names of students who have achieved an ‘A‘ grade in any course. We can achieve this using a nested select statement. Query: SELECT name Output: 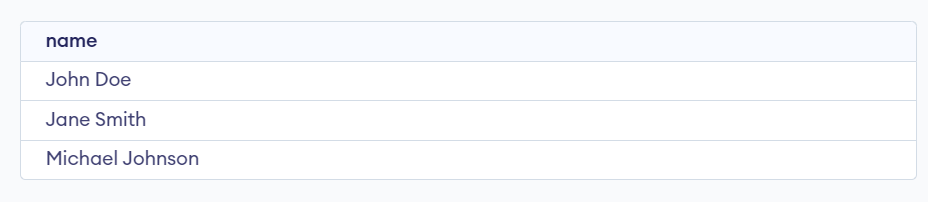 Output Explanation: We can observe that the names of students who have achieved an ‘A‘ grade in any course. ConclusionOverall, the nested select statement in PL/SQL provides a method for retrieving data from multiple tables based on specified conditions. By using single SELECT query within another which allow the user to efficiently perform query and manipulate data across related tables in a single operation. With a good understanding of nested select statements you can easily write more complex and efficient SQL queries. |
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Databases |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 13 |