|
|
For loop is one of the most widely used loops in Programming and is used to execute a set of statements repetitively. We can use for loop to iterate over a sequence of elements, perform a set of tasks a fixed number of times. In this article, we will learn about the basics of For loop, its syntax along with its usage in different programming languages.
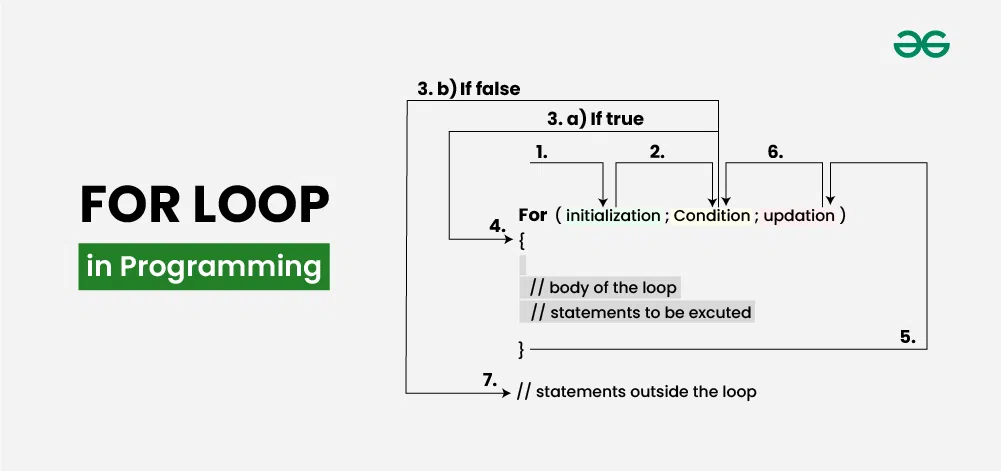
Table of Content What is For Loop?For loop is a control flow statement in programming that allows you to execute a block of code repeatedly based on a specified condition. It is commonly used when you know how many times you want to execute a block of code. For Loop Syntax:The general syntax of for loop varies slightly depending on the programming language, but it typically consists of three main components: initialization, condition, and increment (or decrement). for (initialization; condition; increment/decrement) {
// Code to be executed repeatedly
}Here’s a basic overview of how a for loop works:
How does For Loop work?The for loop is a fundamental construct in programming that allows you to iterate over a sequence of values or execute a block of code a specified number of times. It works by repeatedly executing a block of code until a certain condition is met. Here’s a breakdown of how a for loop works:
This process continues until the loop condition evaluates to false, at which point the loop terminates, and the program execution proceeds to the next statement following the loop. For Loop in different programming languages:Different programming languages may have variations in the syntax and behavior of for loops. While the basic functionality remains the same—iterating over a sequence of values or executing a block of code a specified number of times—there are language-specific nuances to be aware of. Let’s explore some examples of language-specific for loops: 1. For Loop in C:C is a general-purpose, procedural programming language developed by Dennis Ritchie in the early 1970s. It is widely used for system programming, embedded systems, and low-level programming tasks. Output 0 1 2 3 4 2. For Loop in C++:C++ is a powerful general-purpose programming language created by Bjarne Stroustrup. It is an extension of the C programming language with additional features such as object-oriented programming. Output 0 1 2 3 4 3. For Loop in Java:Java is a popular object-oriented programming language developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems. It is known for its “write once, run anywhere” approach, as Java programs can be executed on any platform with the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). Output 0 1 2 3 4 4. For Loop in C#:C# (pronounced as C sharp) is a modern, multi-paradigm programming language developed by Microsoft as part of the .NET framework. It is commonly used for developing Windows applications, web applications, and games. Output 0 1 2 3 4 5. For Loop in Python:Python is a high-level, interpreted programming language known for its simplicity and readability. It emphasizes code readability and allows developers to express concepts in fewer lines of code compared to other languages. Output 0 1 2 3 4 6. For Loop in JavaScript:JavaScript is a versatile scripting language commonly used for web development. It is primarily used for client-side scripting in web browsers but can also be used on the server-side through frameworks like Node.js. Output 0 1 2 3 4 For Loop in PHP:PHP is a server-side scripting language designed for web development but also used as a general-purpose programming language. It is embedded within HTML and is widely used for creating dynamic web pages and web applications. Output 0 1 2 3 4 For Loop Use Cases:For loops are widely used for iterating over sequences (such as lists, tuples, or strings), generating sequences of numbers, and performing repetitive tasks a fixed number of times. They provide a concise and readable way to implement iteration in programming languages. The for loop is a versatile construct used in various programming scenarios where iteration over a sequence of values or executing a block of code a specified number of times is required. Here are some common use cases where the for loop is preferred or widely used: 1. Iterating Over Collections: One of the most common use cases for for loops is iterating over elements in collections such as arrays, lists, tuples, or dictionaries. This allows you to process each item in the collection individually. Output Alice Bob Charlie 2. Generating Sequences of Numbers: For loops are often used to generate sequences of numbers, either in ascending or descending order. This is useful for tasks like creating indices for array access or implementing mathematical algorithms. Output 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 3. Performing Operations a Fixed Number of Times: When you need to execute a block of code a predetermined number of times, the for loop provides a concise and readable solution. This is useful for tasks such as iterating over elements in a grid or matrix. Output Iteration 1 Iteration 2 Iteration 3 Iteration 4 Iteration 5 4. Processing Text or String Manipulation: For loops can be used to iterate over characters in a string, making them useful for tasks like parsing text, searching for patterns, or performing string manipulation operations. Output Number of vowels: 2 5. Iterating Over File Contents: When working with files, for loops can iterate over lines of text or records in a file, making them convenient for tasks such as reading data from files or processing log files. 6. Nested Loops: For loops can be nested within other loops, allowing you to iterate over multiple dimensions or perform iterative operations within iterative operations. Output 1 2 3 4 5 2 4 6 8 10 3 6 9 12 15 4 8 12 16 20 5 10 15 20 25 Types of For Loops:For loops come in various forms, each suited for different use cases and scenarios. Here are the common types of for loops: 1. Basic For Loop:for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}The basic for loop is the most common type, used for iterating over a range of values or executing a block of code a fixed number of times. It consists of an initialization, condition, and increment (or decrement) statement. 2. For Each Loop:int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
for (int number : numbers) {
System.out.println(number);
}The for each loop (or enhanced for loop) is used for iterating over elements in a collection, such as arrays, lists, or sets. It simplifies the syntax of iterating over collections and does not require explicit indexing. 3. For Loop with Iterator:colors = ["red", "green", "blue"]
for color in colors:
print(color)Some programming languages, such as Python and JavaScript, allow for loops to iterate over iterators or generators. This allows for more flexible iteration over custom data structures or sequences. 4. For Loop with Multiple Variables:for (int i = 0, j = 10; i < 5 && j > 0; i++, j--) {
System.out.println("i: " + i + ", j: " + j);
}In languages like C, C++, and Java, it’s possible to have multiple loop control variables in a for loop. This can be useful for nested loops or iterating over multi-dimensional arrays. 5. Infinite For Loop:for (;;) {
// Infinite loop
}An infinite for loop has no termination condition, causing it to iterate indefinitely. It can be useful for tasks like event handling or continuously running programs. 6. For Loop with Step/Stride:for i in range(0, 10, 2):
print(i) # Output: 0, 2, 4, 6, 8Some languages support specifying a step or stride value in the for loop declaration. This allows you to control the increment or decrement of the loop control variable. These are some of the common types of for loops found in various programming languages, each offering unique features and functionalities to cater to different programming needs. For Loop vs other loops:Below is a comparison table between the for loop and other common loop types, including the while loop and the do-while loop:
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Programming |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 15 |