|
In Java, Deserializing an array to an object means converting the Java Array into a Single Object this is mainly done when working with object serialization.
To deserialize an array to an object in Java, we typically use the Jackson library. Jackson unlocks diverse use cases, such as transforming API responses or manipulating structured data within an application.
Note: Deserializing a JSON array into a single Java object directly with Jackson isn’t typically possible due to type erasure in Java.
Step-by-Step Implementation
Below are the steps and implementation of deserializing JSON array to a single Java object with Jackson.
Step 1: Create a Maven Project
- Open any preferred IDE and create a new Maven project. Here we are using IntelliJ IDEA, so, we can do this by selecting File -> New -> Project.. -> Maven and following the wizard.
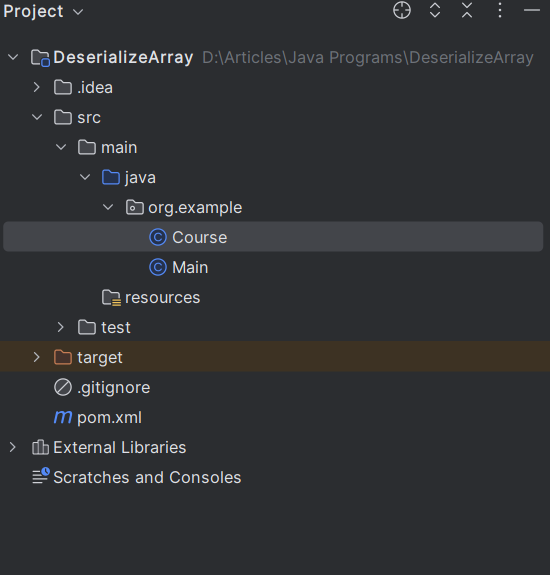
Project Structure:
Below is the Structure of the Project that we have created.
Step 2: Add Jackson Dependency to POM.xml
Now, we will add Jackson dependency to the XML file.
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>DeserializeArray</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.13.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>21</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>21</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
</project>
|
Step 3: Create the Java POJO Class
After adding dependencies to pom.xml file, now we will create the POJO class.
Course.java
Java
package org.example;
public class Course
{
private int id;
private String courseName;
private long coursePrice;
public Course() {}
public Course(int id, String courseName,
long coursePrice)
{
this.id = id;
this.courseName = courseName;
this.coursePrice = coursePrice;
}
public int getId()
{
return id;
}
public void setId(int id)
{
this.id = id;
}
public String getCourseName()
{
return courseName;
}
public void setCourseName(String courseName)
{
this.courseName = courseName;
}
public long getCoursePrice()
{
return coursePrice;
}
public void setCoursePrice(long coursePrice)
{
this.coursePrice = coursePrice;
}
}
|
The Course class defines a POJO to map JSON data with id, courseName, and coursePrice properties. Getters and setters are provided for Jackson to populate objects.
Step 4: In the Main class add logic of Deserialization of Java Array to Java Object
After creating POJO class, we will add logic of Deserialization of Java Array to Java Object in the main class.
Java
package org.example;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String json
= "[{\n"
+ " \"id\": 1,\n"
+ " \"courseName\": \"Introduction to Java\",\n"
+ " \"coursePrice\": 30000.99\n"
+ "}\n]";
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
try {
Course[] course
= mapper.readValue(json, Course[].class);
Course courses = course[0];
System.out.println(courses.getId());
System.out.println(courses.getCourseName());
System.out.println(courses.getCoursePrice());
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
In this example, we use the readValue() method of the ObjectMapper class to deserialize the JSON array into an array of Person objects. Then, we can access the first element of the array to get a single Person object.
Output:
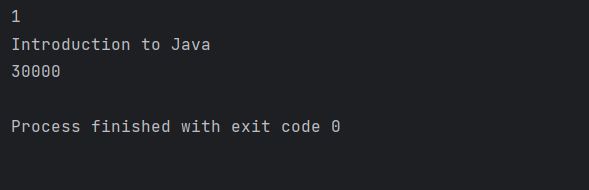
Note: readValue() method handles all the conversion between JSON and Java objects based on naming conventions.
|


