|
|
Python, a versatile and widely used programming language, provides a plethora of features and command-line options to facilitate various tasks. One such option that might pique your interest is the -m switch. In this article, we will explore what Python -m is and how it can be used, accompanied by four illustrative code examples. What is Python -m?The -m switch in Python is a command-line option that allows you to run a module as a script. This means you can execute Python code directly from the command line without the need for an external script file. By using -m, you can invoke Python modules as standalone programs. Python -M ExamplesBelow are some of the ways by which we can understand about Python -m command in Python:
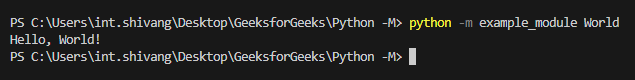
Running Python FilesIn this example, the -m switch allows us to run the example_module as a script, passing the argument “World” to the greet function. Consider a Python module named example_module. To execute it using the -m switch, create a file named example_module.py with the following content: Python3
Now, run the module using the -m switch: python -m example_module World
Output:
Module within a PackageLet’s extend our understanding to modules within packages. Consider a package named example_package with a module submodule: Python3
To run the submodule using -m, use the following command: python -m example_package.submodule Output:
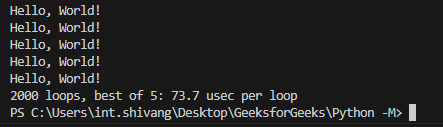
The -m switch enables us to execute modules within packages, specifying the package path with dots. Running Built-In ModulesThe -m switch is not limited to user-defined modules; it can also be used with built-in modules. For instance, you can run the timeit module to measure the execution time of a code snippet: Python3
This will display the time taken to execute the specified code snippet. Output:
ConclusionIn conclusion, the Python -m switch is a powerful tool that allows you to run modules as scripts directly from the command line. Whether it’s user-defined modules, modules within packages, or built-in modules, the -m switch enhances the flexibility of Python’s command-line interface. Experiment with this feature to streamline your development and testing processe |
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Geeks Premier League |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 14 |