|
|
In database management, MySQL stands as one of the most popular relational database management systems. As developers strive to extract specific data from their databases, the judicious use of SQL operators becomes imperative. Among these operators, the IN and LIKE operators play crucial roles in facilitating flexible and precise data retrieval. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide on combining the MySQL IN and LIKE operators. By understanding the nuances and syntax of these operators, developers can enhance their proficiency in crafting SQL queries that meet the demands of complex data filtering scenarios. IN OperatorThe IN operator in MySQL is a powerful tool for filtering data based on a predefined set of values. It allows developers to specify a list of values and retrieve records where a particular column matches any of those values. This operator is particularly useful when dealing with scenarios where data needs to be filtered against multiple possibilities. Syntax:
LIKE OperatorThe LIKE operator in MySQL is employed for pattern matching within a specified column. It enables developers to retrieve records where a particular column’s value matches a specified pattern. This pattern can include wildcard characters such as % (matches any sequence of characters) and _ (matches any single character), offering a versatile means of searching for data. Syntax:
IN and LIKE OperatorsCombining the IN and LIKE operators in MySQL can be especially beneficial in scenarios where data needs to be filtered based on multiple values and a flexible pattern. This combination empowers developers to construct intricate queries that cater to nuanced search criteria. Syntax:
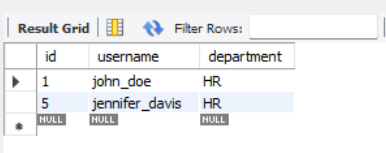
Examples of MySQL IN and LIKE OperatorsExample 1: Combining IN and LIKE for Flexible FilteringConsider a scenario where we created the DB as GeeksforGeeks you have a ‘GFG’ table, and you want to retrieve users who belong to a specific department (IN operator) and whose usernames start with a particular pattern (LIKE operator). -- SQL Code Output:  output Explanation: The output includes users from both the ‘HR‘ and ‘Finance‘ departments whose usernames start with the letter ‘j‘. In this case, it retrieves ‘john_doe‘ and ‘jennifer_davis‘ from the ‘HR’ department and ‘sam_jones’ from the ‘Finance’ department. The condition Example 2: Using IN and LIKE with Multiple ConditionsLet’s consider a more complex scenario where you have a ‘products‘ table, and you want to retrieve products with specific categories (IN operator) and whose names contain a certain keyword (LIKE operator). -- SQL Code Output: 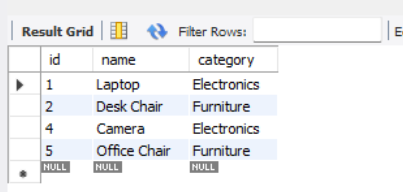 output Explanation: The output includes products from both the ‘Electronics‘ and ‘Furniture‘ categories whose names contain the letter ‘a’. The conditions category IN (‘Electronics’, ‘Furniture’) and name LIKE ‘%a%‘ filter the results based on the specified criteria. ConclusionThe combination of MySQL `IN` and `LIKE` operators allows for sophisticated data querying in relational databases. The `IN` operator is efficient for predefined values, while the `LIKE` operator offers flexibility for intricate patterns. By combining these operators, developers can create queries that cater to complex search criteria, enabling them to navigate diverse scenarios. Mastering these operators enhances database operations efficiency and contributes to the development of robust applications that rely on seamless interaction with MySQL databases. |
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Databases |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 13 |