|
|
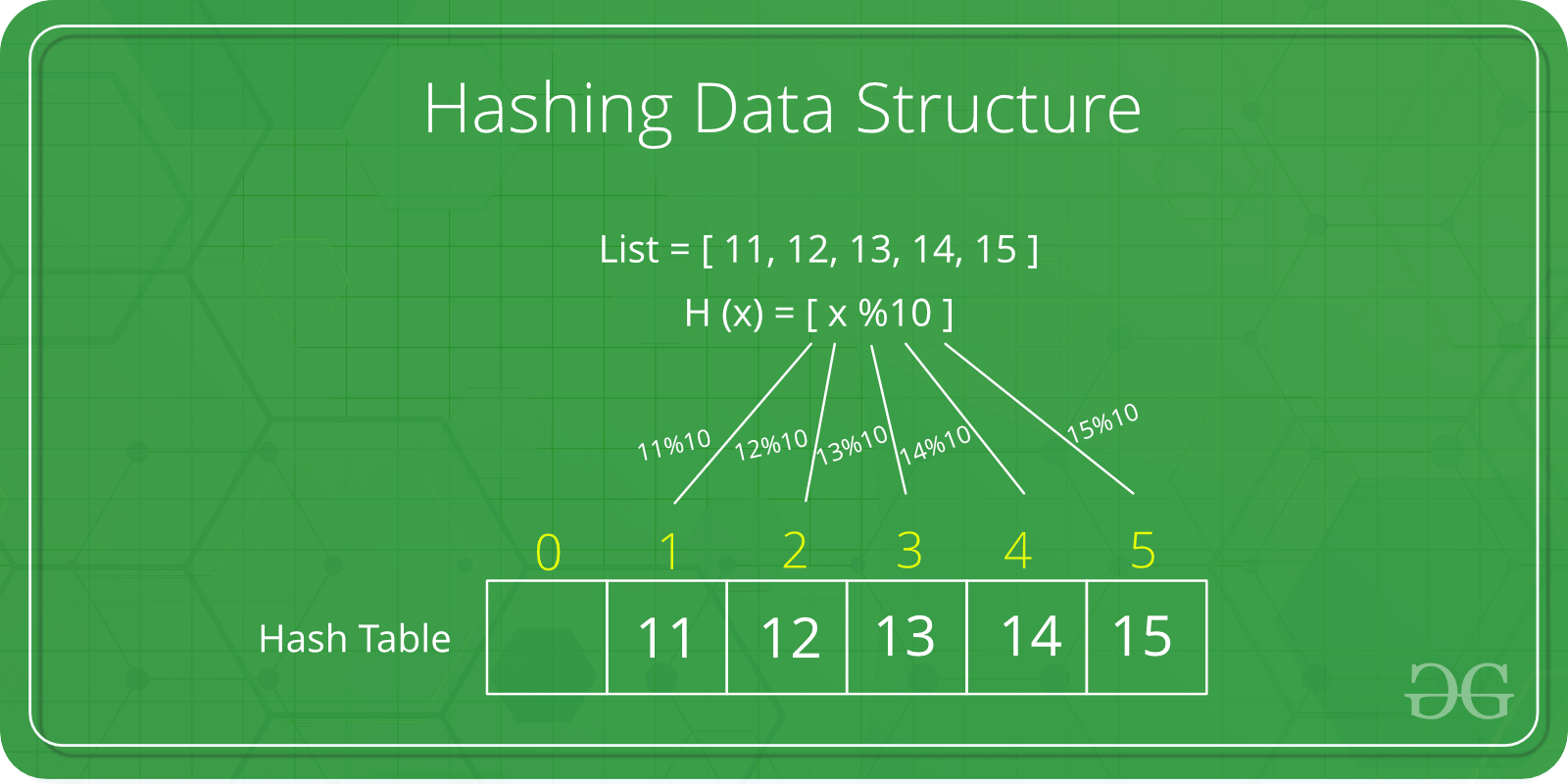
Hashing is a technique used in data structures that efficiently stores and retrieves data in a way that allows for quick access. It involves mapping data to a specific index in a hash table using a hash function that enables fast retrieval of information based on its key. This method is commonly used in databases, caching systems, and various programming applications to optimize search and retrieval operations. The great thing about hashing is, we can achieve all three operations (search, insert and delete) in O(1) time on average.  Data Structures – Hashing Table of Content What is Hashing in Data Structure?Hashing is a technique used in data structures to store and retrieve data efficiently. It involves using a hash function to map data items to a fixed-size array which is called a hash table. Below are basic terminologies in hashing.
Hash Table in Data StructureA hash table is also referred as a hash map (key value pairs) or a hash set (only keys). It uses a hash function to map keys to a fixed-size array, called a hash table. This allows in faster search, insertion, and deletion operations. Hash FunctionThe hash function is a function that takes a key and returns an index into the hash table. The goal of a hash function is to distribute keys evenly across the hash table, minimizing collisions (when two keys map to the same index). Common hash functions include:
What is a Hash Collision?A hash collision occurs when two different keys map to the same index in a hash table. This can happen even with a good hash function, especially if the hash table is full or the keys are similar. Causes of Hash Collisions:
Collision Resolution TechniquesThere are two types of collision resolution techniques:
Applications of HashingHash tables are used wherever we have a combinations of search, insert and/or delete operations.
Please refer Applications of Hashing for more detailed list. Basics of Hashing in Data Structure
Easy Problem on Hashing
Medium Problem on Hashing
Hard Problem on Hashing
Quick Links :
Recommended: |
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| DSA |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 14 |