
|
|
In MySQL, a composite key is a combination of two or more columns in a table that uniquely identifies each entry. It is a candidate key made up of many columns. MySQL guarantees column uniqueness only when they are concatenated. If they are extracted separately, the uniqueness cannot be maintained. Any key, such as the primary key, super key, or candidate key, can be referred to as a composite key if it has more than one characteristic. A composite key is important when the database has to uniquely identify each record that contains more than one characteristic. A composite key column may include a variety of data types. Thus, the columns do not have to have the same data type to form a composite key in MySQL. A composite key can be added in two ways:
Let us see both ways in detail. Composite Key Using CREATE StatementHere, we will look at how composite keys operate in MySQL. Let us first construct a table called “employees” using the following statement: CREATE TABLE employee ( In this example, the employee table is created with three columns: employee_id, department_id, and employee_name. The PRIMARY KEY constraint is applied to the combination of employee_id and department_id. This means that each pair of employee_id and department_id values must be unique within the table. We can verify the same using the command as below: DESCRIBE employee;
After the successful execution, It means we have successfully added the composite primary key on employee_id and department_id columns. Next, we need to insert the values into this table as given below: INSERT INTO employee (employee_id, department_id, employee_name) VALUES Next, execute the below command to show the table data: SELECT * FROM employee;
Output:  Output Composite Key Using ALTER StatementIn some cases, you might need to add a composite key to an existing table. MySQL allows you to achieve this using the ALTER TABLE statement. Let’s consider a scenario where we want to add a composite key to an existing orders table based on the columns order_id and product_id. Assuming the initial structure of the orders table is as follows: -- Initial table structure without a composite key Now, let’s use the ALTER TABLE statement to add a composite key: -- Add a composite key to the existing table In this example, the ALTER TABLE statement is used to modify the orders table. The ADD PRIMARY KEY clause is then used to define the composite key based on the columns order_id and product_id. Next, we need to insert the values into this table as given below: INSERT INTO orders (order_id, product_id, quanitity) VALUES Next, execute the below command to show the table data: SELECT * FROM orders; Output: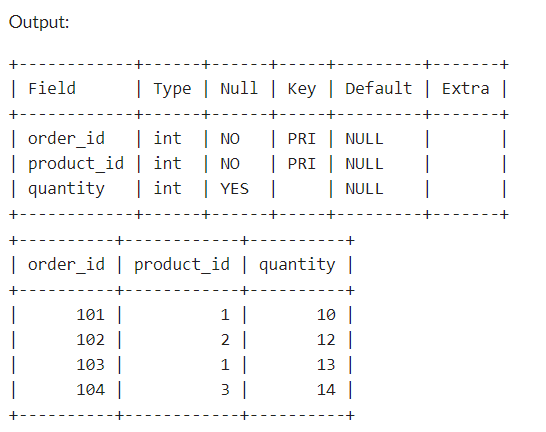 Output ConclusionIn the relational databases, the proper utilization of keys is essential for maintaining data integrity and ensuring efficient data retrieval. MySQL offers a robust solution in the form of composite keys, allowing us to create unique identifiers based on combinations of multiple columns. Through this article, we explored the creation of composite keys using both the CREATE TABLE and ALTER TABLE statements. FAQs on MySQL Composite KeyWhat is a composite key in MySQL?
How is a composite key different from a single column primary key?
Can composite keys contain NULL values?
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Databases |
| Related |
|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 16 |