
|
|
PL/SQL, an extension of SQL developed through Oracle, empowers builders with robust programming skills for powerful database management. Among its many capabilities, arrays stand out as an essential tool for organizing and manipulating data correctly. In this article, we’ll dive deep into the sector of PL/SQL arrays, overlaying their definition, introduction, and realistic examples. In this article, we are going to discuss the different types through which arrays can be declared in PL/SQL. we will delve into the concept of indexes in SQL, exploring their types, and best practices for creating and managing them. Arrays in PL/SQLArrays, mainly called Varrays (Variable Arrays), are dynamic information systems that permit the storage of multiple values of the same information type underneath a single variable name. Unlike simple variables, arrays offer an effective approach to dealing with statistics collections, facilitating streamlined facts control and manipulation of data. Creating a Varray Type: To harness the power of Varrays, it is essential to outline a kind that specifies the detail type and the range of elements the array can preserve. For instance: CREATE TYPE num_array AS VARRAY(10) OF INT;
Examples of PL/SQL ArrayExample of Varray using INT Data TypeLet’s delve into a practical example using a Varray of integers. In this situation, we declare and use a Varray named `numbers`: DECLARE In this case, the Varray ‘numbers’ is initialized with integers from 1 to 5 and operations are performed, showcasing the simplicity of dealing with numerical collections. Output:  Example of Varray using INT Data Type Explanation: This PL/SQL code publicizes a variable number of the VARRAY type num_array, initializes it with values, plays operations on it (displaying elements), updates one among its factors, after which shows the updated factors.
Output: Element 1: 1
Output: Updated Element 1: 1 Example of Varray using CHAR Data TypeVarrays are versatile and no longer restrained to numerical statistics sorts. Consider a scenario where you create and use a Varray of characters: CREATE TYPE char_array AS VARRAY(5) OF CHAR(10);
This example introduces a `char_array` Varray able to protect as much as 5 strings, each with a most period of 10 characters. DECLARE Output: 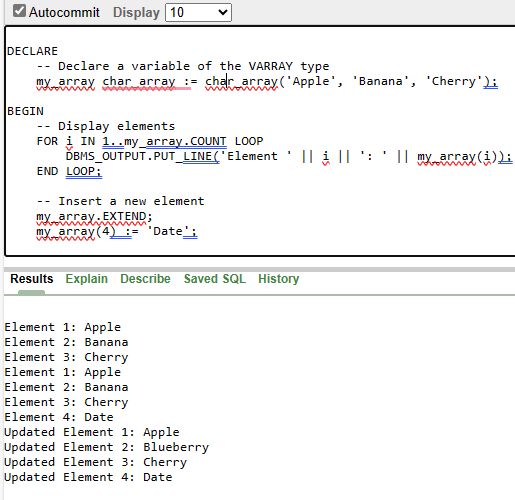 Varray using CHAR Data Type Explanation This PL/SQL code broadcasts a variable my_array of the VARRAY (Variable Size Array) kind char_array and plays various operations on it, which includes showing factors, inserting a new detail, updating an existing element, and displaying the elements again after each operation.
Output: Element 1: Apple
Output: Element 1: Apple
Updated Element 1: Apple Data Type Example of Varray using %ROWTYPE or %TYPEPL/SQL offers the flexibility to define a Varray based at the records sort of a table column using `%ROWTYPE` or `%TYPE`: CREATE TYPE empp.CROWTYPE AS TABLE OF VARCHAR2(50); In this situation, `emp_details` is a Varray designed to save up to 50 rows from the `emp` table, demonstrating the adaptability of PL/SQL arrays to numerous statistics sorts. ConclusionPL/SQL arrays, particularly Varrays, function a cornerstone for powerful records organization and manipulation in Oracle databases. This article has explored their advent, utility, and versatility, supplying builders with a complete know-how of how to harness the whole ability of PL/SQL arrays. By studying those ideas, developers can elevate their ability to construct green and scalable database applications, making PL/SQL arrays an critical tool of their toolkit. |
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Databases |
| Related |
|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 13 |