|
|
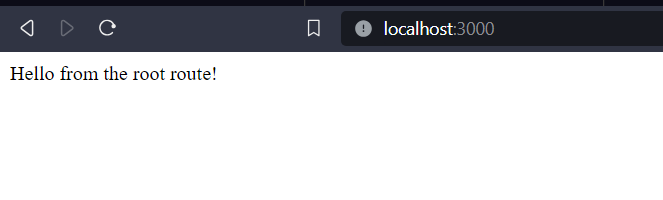
If you’ve used Express even a little, you know how important middleware is. Those little functions run on every request and let you do stuff like logging, authentication, file uploads, and more. In this article, we will see what is Application-level middleware and Router-level middleware and what are the key differences between them. Table of Content Application-Level Middleware:Application-level middleware is like a personal assistant that helps out with every incoming request to your Express app. No matter which route a client hits, this middleware jumps in to work its magic. For example, you can use app-level middleware to log every request that comes in for debugging. Or to check authentication for your entire application. Or even set global headers that you want on every response. Syntax: app.use(params...); Key Features:
Example: Javascript
Output:
Console Output:
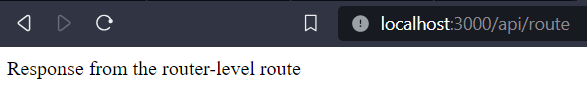
Router-Level Middleware:Router-level middleware is more specialized – it only applies to particular routing paths you choose. Think of it like a special helper that comes in to handle requests for certain routes. For example, you could set up some router-level middleware that checks for authentication on your /account routes or validation middlewares that check data before your /purchase or /signup routes. Syntax: router.use(params...); Key Features:
Example: Javascript
Output:
Console Output:
Difference between Application and Router level Middleware:Application middleware is better for global concerns like logging, while router middleware is better for things you only want to apply to certain routes, like authentication.
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Express.js |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 10 |