|
An Expense Tracker or Budget Management application using the MERN stack (MongoDB, Express, React, Node) is a powerful and versatile solution for individuals or businesses looking to manage their finances effectively. This stack provides a seamless and efficient way to build a full-fledged web application with a robust backend and a dynamic front end. Here’s a brief introduction to creating an Expense Tracker using the MERN stack.
Preview of final output: Let us have a look at how the final application will look like.
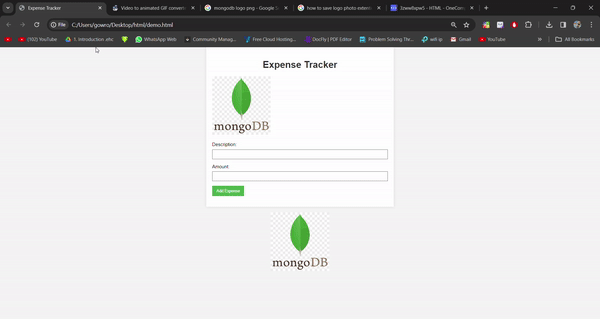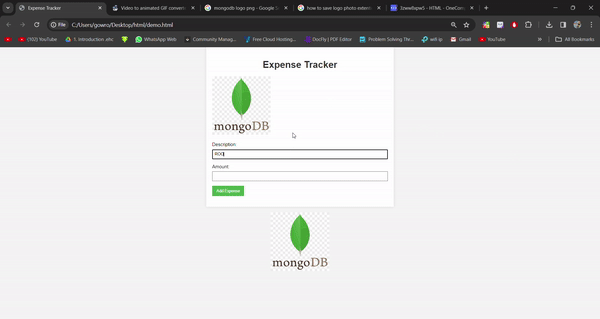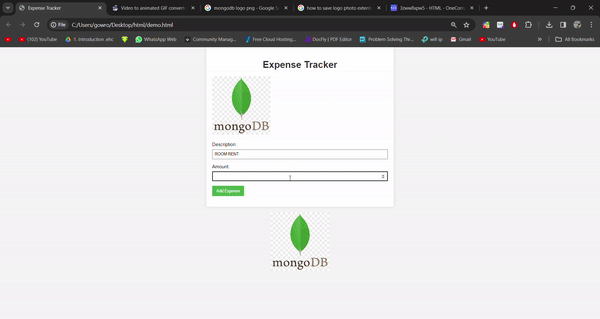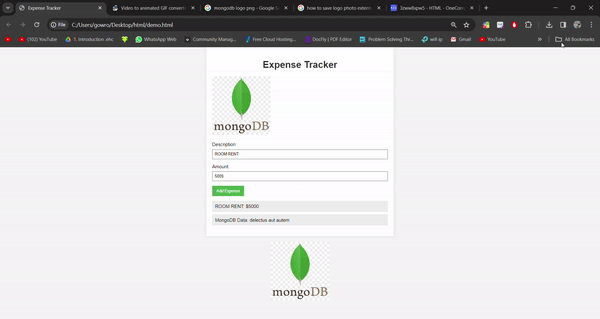 Output Preview Prerequisites:
Approach and Features:
- User Authentication:
- Implement user authentication to allow users to securely create accounts and log in.
- Use techniques like JWT (JSON Web Tokens) for secure token-based authentication.
- Dashboard:
- Create an intuitive dashboard where users can get an overview of their financial status.
- Display charts and graphs to represent income, expenses, and overall budget trends.
- Expense Tracking:
- Enable users to add, edit, and delete expenses.
- Categorize expenses to provide a detailed breakdown of spending patterns.
- Implement features for recurring expenses to simplify regular budgeting.
- Budget Planning:
- Allow users to set budget goals for different categories.
- Provide notifications or alerts when users exceed predefined budget limits.
- Transaction History:
- Maintain a transaction history that users can review and analyze.
- Implement filters and search options for easy navigation through transaction records.
- Reports and Analytics:
- Generate detailed reports and visual analytics to help users understand their financial habits.
- Use charts and graphs to represent data trends and patterns.
- Responsive Design:
- Ensure that the application is accessible and user-friendly on various devices, including desktops, tablets, and mobile phones.
- Data Security:
- Implement secure data storage practices, including encryption and regular backups, to protect users’ financial information.
Development Workflow:
- Backend Development:
- Set up a Node.js server using Express.js.
- Connect the server to a MongoDB database to store user data and financial information.
- Authentication (JWT):
- Implement user authentication using JSON Web Tokens to secure user accounts.
- API Development:
- Create RESTful APIs for managing user accounts, expenses, budgets, and other relevant functionalities.
- Frontend Development (React.js):
- Develop a responsive and dynamic user interface using React.js.
- Utilize state management libraries like Redux for efficient data handling.
- Integration:
- Connect the frontend and backend to enable seamless communication between the user interface and the server.
- Testing:
- Conduct thorough testing of both the frontend and backend to ensure the application’s reliability and functionality.
- Deployment:
- Deploy the application on hosting platforms like Heroku, AWS, or others.
- Monitoring and Maintenance:
- Implement monitoring tools and perform regular maintenance to ensure the application’s ongoing performance and security.
Project Structure:
 Project Structure Steps to Create the Expense Tracker Server:
Step 1: Set up React Project using the Command:
npm init -y
Step 2: Installing Required Dependencies.
npm install express mongoose cors
The updated dependencies in package.json file for backend:
"dependencies": {
"cors": "^2.8.5",
"express": "^4.18.2",
"mongoose": "^7.6.5",
}
Example: Below is the code of the backend server. Write the following code in server.js file.
Javascript
const express = require("express");
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
const cors = require("cors");
const app = express();
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 5000;
app.use(cors());
app.use(express.json());
mongoose.connect(
{
useNewUrlParser: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true,
}
);
const db = mongoose.connection;
db.on("error", (error) => {
console.error("MongoDB connection error:", error);
});
db.once("open", () => {
console.log("Connected to MongoDB");
});
const expenseSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
description: { type: String, required: true },
amount: { type: Number, required: true },
});
const Expense = mongoose.model("Expense", expenseSchema);
app.get("/expenses", async (req, res) => {
try {
const expenses = await Expense.find();
res.json(expenses);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error fetching expenses:", error);
res.status(500).json({ message: "Internal Server Error" });
}
});
app.post("/expenses", async (req, res) => {
const { description, amount } = req.body;
try {
if (!description || !amount) {
return res
.status(400)
.json({ message: "Description and amount are required." });
}
const newExpense = new Expense({ description, amount });
await newExpense.save();
res.json(newExpense);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error saving expense:", error);
res.status(500).json({ message: "Internal Server Error" });
}
});
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server is running on port ${PORT}`);
});
|
Steps to Create the Expense Tracker Client Side:
Step 1: Set up React Project using the Command:
npx create-react-app expense-tracker
Step 2: Navigate to the Project folder using:
cd expense-tracker
Step 3: Install Axios (for making HTTP requests):
npm install axios
The updated dependencies in package.json file for frontend:
"dependencies": {
"axios": "^1.6.2",
"react": "^18.2.0",
"react-dom": "^18.2.0",
"react-scripts": "5.0.1",
}
Example: Below is the code example of the frontend.
Javascript
import React, { useState } from 'react';
const ExpenseTracker = () => {
const [balance, setBalance] = useState(0);
const [transactions, setTransactions] = useState([]);
const [description, setDescription] = useState('');
const [amount, setAmount] = useState('');
const addExpense = () => {
const parsedAmount = parseFloat(amount);
if (isNaN(parsedAmount) || parsedAmount <= 0) {
alert('Please enter a valid amount.');
return;
}
setBalance(
(prevBalance) => prevBalance + parsedAmount);
setTransactions((prevTransactions) => [
...prevTransactions,
{ description, amount: parsedAmount },
]);
setDescription('');
setAmount('');
};
return (
<div className="container">
<h1>Expense Tracker</h1>
<div className="balance">
<h2>
Balance: $
<span id="balance">
{balance.toFixed(2)}
</span>
</h2>
</div>
<div className="transactions">
<h2>Transactions</h2>
<ul>
{
transactions
.map(
(transaction, index) => (
<li key={index}>
{
`${transaction.description}:
$${transaction.amount.toFixed(2)}`
}
</li>
))
}
</ul>
</div>
<div className="add-expense">
<h2>Add Expense</h2>
<form>
<label htmlFor="description">
Description:
</label>
<input
type="text"
id="description"
value={description}
onChange={
(e) =>
setDescription(e.target.value)
}
required
/>
<label htmlFor="amount">
Amount:
</label>
<input
type="number"
id="amount"
step="0.01"
value={amount}
onChange={
(e) =>
setAmount(e.target.value)
}
required
/>
<button type="button"
onClick={addExpense}>
Add Expense
</button>
</form>
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default ExpenseTracker;
|
CSS
body {
font-family: 'Arial', sans-serif;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
background-color: #f4f4f4;
}
.container {
max-width: 600px;
margin: 50px auto;
background-color: #fff;
padding: 20px;
box-shadow: 0 0 10px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
}
h1,
h2 {
text-align: center;
color: #333;
}
.balance {
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.balance h2 {
color: #2ecc71;
}
.transactions ul {
list-style: none;
padding: 0;
}
.transactions li {
margin-bottom: 10px;
padding: 10px;
background-color: #ecf0f1;
border-radius: 5px;
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: center;
}
.add-expense label,
.add-expense input,
.add-expense button {
margin-bottom: 10px;
display: block;
}
.add-expense button {
background-color: #3498db;
color: #fff;
padding: 10px;
border: none;
cursor: pointer;
border-radius: 5px;
}
.add-expense button:hover {
background-color: #2980b9;
}
|
Steps to start server:
npm start and node sverver
Output: Visit http://localhost:3000 in your browser to see the MERN fundraising app in action.

Output of Data saved in database:
 Data saved in the db after submission
|

