
|
|
In databases, data is stored in multiple tables and it is often necessary sometimes to combine two or more tables to fetch the required data. In MySQL, joins enable the merging of multiple tables based on the common columns. In this article, we are going to explore MySQL RIGHT JOINS which is a type of outer join in MySQL. MySQL RIGHT JOINIn MySQL, the RIGHT JOIN is a type of join operation that allows you to combine rows from two or more tables based on a related column between them. The RIGHT JOIN returns all rows from the right table (table 2) and the matched rows from the left table (table 1). If there are no matches, the result is NULL on the left table columns.
Syntax: Following is the syntax for Right join in MYSQL: SELECT columns Explanation: In the above Query, we have defined the syntax to perform RIGHT JOIN in MYSQL. Here we use the ON Clause to specify the conditions of matching columns from both tables called table1 and table2. Examples on MySQL RIGHT JOINTo understand RIGHT JOIN in a more in-depth manner we need some table on which we will perform operations or queries. we have created three tables called indian_books, indian_authors and indian_book_authors are as follow. if you don’t know How to Create Tables in MYSQLthen refer to this. Here indian_books consists of tables book_id, title, and publication_year as Columns, and here book_id of as PRIMARY KEY. After inserting some data into the indian_books table. Our table looks.  Table-Indian_books Here indian_authors consists of author_id, author_name as Columns, and author_id assigned as PRIMARY KEY. After inserting some data into the indian_books table. Our table looks.  Table-indian_authors Here indian_book_authors consists of and book_id, author_id as Columns. Here book_id, and author_id considered as FOREIGN KEY which is REFERENCES to indian_books(book_id), and indian_authors(author_id). After inserting some data into the indian_books table. Our table looks. 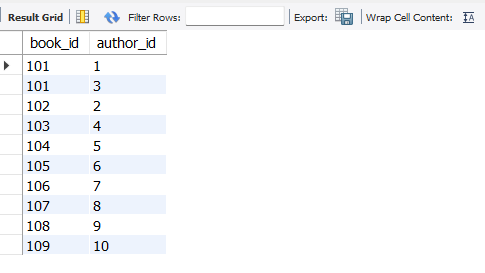 Table- indian_book_authors The relationship between all the tables is shown below. 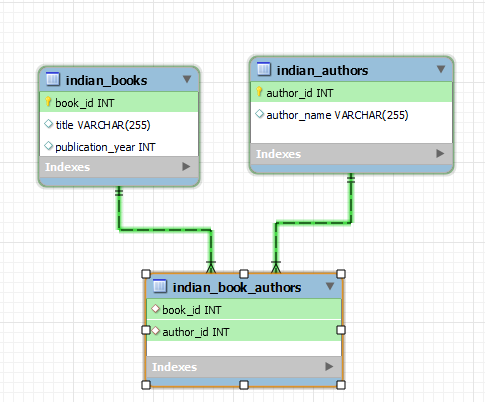 Relationship between the tables 1. Simple MySQL RIGHT JOIN with Using ClauseSELECT * Output:  Output Explanation: The query retrieves all records from indian_book_authors and matches them with corresponding records from indian_books using the USING clause, based on a common column. It lists authors’ names alongside the titles of books they authored. 2. MySQL RIGHT JOIN with GROUP BY ClauseSELECT indian_authors.author_name, COUNT(indian_books.book_id) as book_count Output:  Output Explanation: The query uses GROUP BY in MySQL to group rows with similar values, showing how many books each author has written. It employs RIGHT JOIN to combine indian_authors and indian_book_authors, then uses GROUP BY to count books per author using the aggregate function count. 3. MySQL RIGHT JOIN with WHERE ClauseSELECT indian_authors.author_name, indian_books.title  Output Explanation: The query applies a WHERE clause in MySQL to filter results based on a condition. It performs a right join between indian_authors and indian_book_authors to display author names and their books, but only for authors who published a book before 2015. 4. MySQL RIGHT JOIN on Multiple TablesSELECT * Output:  Output of the above query Explanation: This query performs a join on more than two tables. Yes, it is possible to perform join on more than two tables, you might encounter situations where you will have to join more than two tables to fetch the required data. So the above query performs a right join on all three tables and returns all the records of the indian_authors table along with the matching records of the other two indian_books and indian_book_authors tables. 5. Use of MySQL RIGHT JOIN to Get Unmatched RecordsSELECT indian_books.title Output:  Output – NULL No matched records found Explanation: This query uses a RIGHT JOIN and WHERE clause to identify records in indian_books that lack corresponding entries in indian_book_authors. The absence of any resulting rows suggests every book in our database has been attributed to at least one author. ConclusionIn this article, We have learned about RIGHT JOIN in MYSQL and explored its various concepts using a simple database of 3 tables. You can perform right join operation whenever the right table is most priority and you want to fetch the records of the right table along with the matching records of the left table. However, always ensure to use the right syntax to get the exact results you want from the query. FAQs on MySQL RIGHT JOINWhat is a RIGHT JOIN in MySQL?
When should I use RIGHT JOIN?
How is RIGHT JOIN different from INNER JOIN?
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Databases |
| Related |
|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 13 |