|
|
Postman is a powerful API development tool which offers a feature known as environment variables. These variables are used for efficient testing and development of APIs by allowing users to manage dynamic values across requests easily. Table of Content Difference between global and local variables in PostmanVariables enable you to store and reuse values in Postman. By storing a value as a variable, you can reference it throughout your collections, environments, requests, and test scripts. Variables help you work efficiently, collaborate with teammates, and set up dynamic workflows. Let’s see the difference between global and local variables in Postman
Steps to create Global VariableStep 1: After downloading and installing the Postman, open the software. Add a new Collection and give it a name like “GFG”.
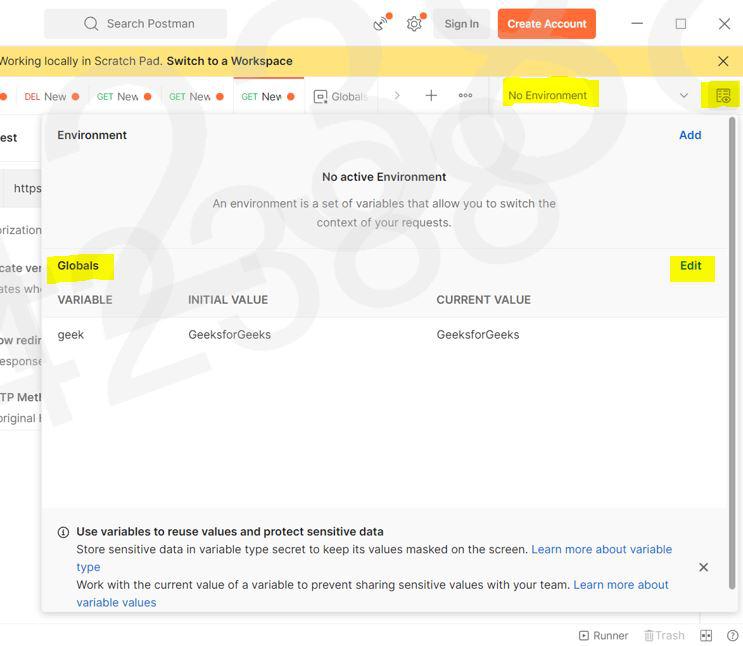
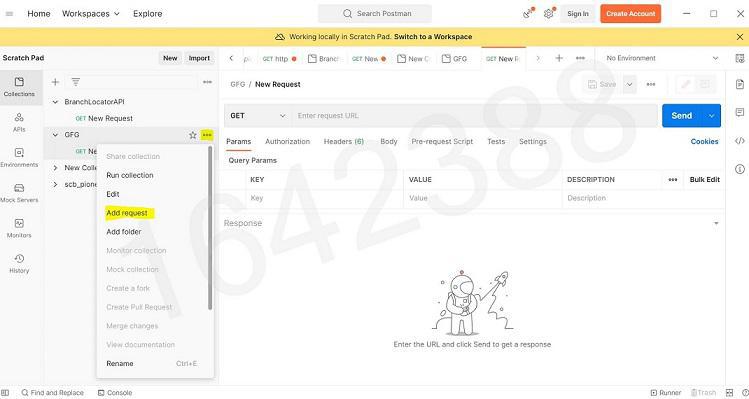
Step 2: Select the environment quick look icon Environment quick look icon in the workbench as shown. Next to Globals , select Edit (or Add if no variables have been added yet) . Step 3: Add a variable named geek and give it an initial value of GeeksforGeeks as shown below Step 5: When you hover, on the name of your collection, 3 dots will appear. Click on those 3 dots, and then click on “Add new request” Step 6: Now You can simply paste the API in the space provided and you can call the global variable by {{geek}} , then click on Send. Output will be shown in the body with the status code. Example: In this example, we will create a global variable, id with a initial value=1. We will call API like: https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/?userId={{id}}
 Ouput Steps to create Local Variable Step 1: After downloading and installing the Postman, open the software. Add a new Collection and give it a name like “GFG”.
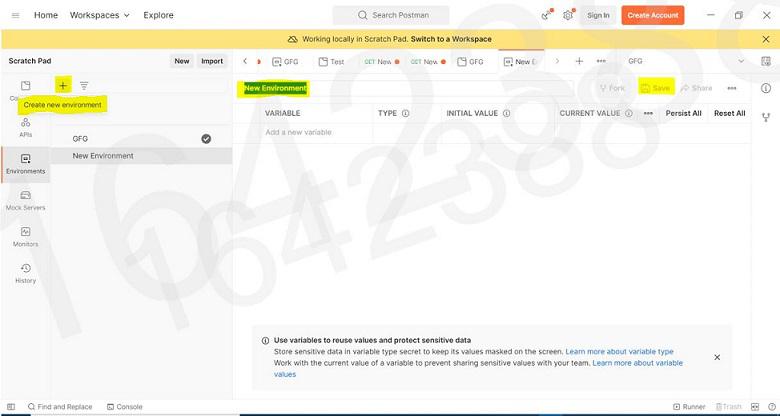
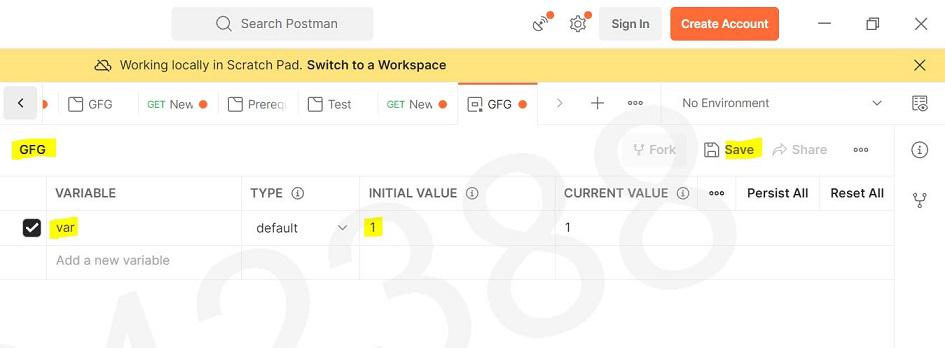
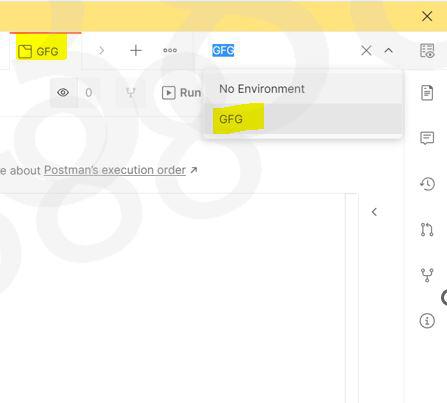
Step 2: Create a environment ; “GFG“, using the + button in Environments tab as shown below Step 3: Create a local variable ; ‘var’ and add a initial value as 1 Step 4: Go to your collection and select the environment ; “GFG” Step 5: Now You can simply paste the API in the space provided and you can call the local variable by {{var}} , then click on Send. Output will be shown in the body with the status code. API Used https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/?userId={{var}} Output:  Output |
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Geeks Premier League |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 11 |