|
A Rectifier is an electronic device that converts the alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) by allowing a current to flow through the device in one direction only using one or more P-N junction diodes. Many circuits use DC voltage for operation. It can easily convert AC voltage or current into DC or voltage. A P-N junction diode allows the current to flow in a forward bias condition and blocks the current in a reverse bias condition. More simply we can say that a diode allows electric current to flow in a single direction. This property of the diode allows it to act as a rectifier and the process is called rectification.
What are Rectifiers?A rectifier is an electrical device that converts Alternating Current (AC) into Direct Current (DC) by using one or more P-N junction diodes.
 Rectification When a voltage is applied on the P-N junction diode in a way that the positive terminal (+ve) of the battery is connected to the P-type semiconductor and the negative terminal(-ve) of the battery and is connected to the N-type semiconductor called forward biased. When the forward bias voltage is applied to the P-N junction diode the large number of free electrons (e-) (majority carriers) in the N-type semiconductor experiences a repulsive force from the negative terminal of batter and similarly, the large number of holes(majority carriers) in the p-type semiconductor experiences a large repulsive force from the positive terminal of the battery.
 Forward Bias As a result, the free electron in the N-type semiconductor moves from the N-side to the P-side and as such the holes in the P-type semiconductor start to move from the P to the N-side. As we know the current means flow of charges (free electrons and holes). So, the flow of the electrons from the N-side to the P-side and the holes flow from the P to the N side which conduct electric current. The maximum number of carriers produces the electric current in the forward bias. So the current produced in the forward bias is also called majority current.
When the voltage is applied to the P-N junction diode in such a manner that the positive terminal of the battery is connected to the N-type and the negative terminal of the battery is connected to the P-type then the diode is reverse biased.
So when this reverse bias voltage is applied to the P-N junction diode, the large of free electrons in the N-type experience an attractive force from the positive terminal of the battery, in the same manner, a large number of holes in the P-type experience an attractive force from the negative terminal of the battery.
-(1).webp) Reverse Bias PN Junction Diode
As a result of reverse bias the free electrons in the N-type semiconductor move away from the P-N junction and are attracted to the positive terminal of the battery. At the same, the holes in the P-type move away from the P-N junction and are attracted to the negative terminal of the battery. The electric flow does not occur across the P-N junction. The minority carrier in the P-type experiences a repulsive force from the negative terminal of the battery and as same the minority carrier in the N-type experiences a repulsive force from the positive terminal of the battery. As a result, the minority carriers free electrons in the P-type semiconductors and the minority carriers holes in the N-type start flowing in the junction. The electric current is produced by the minority carriers in very small. So the minority carrier current in the reverse bias is neglected.
The P-N junction allows the current in the forward bias and blocks the current in the reverse bias. In simple words the P-N unction allows electric current in one direction only. This unique property of the diode allows it to behave like a rectifier.
Different Types of RectifiersRectifiers are classified into two types:
- Uncontrolled Rectifier
- Controlled Rectifier
Uncontrolled Rectifiers The rectifier whose voltage is not controlled is known as an Uncontrolled rectifier.
Uncontrolled AC half-wave further divided as follows :
- Half wave rectifier
- Full wave rectifier
The rectifier that converts half cycle of the AC in the DC is called a half wave rectifier.
Similar to this a full-wave rectifier converts the positive and negative half cycle of the AC.
Half Wave RectifierThe half-wave rectifier converts the AC signal to a DC signal by passing the signal to either a negative or positive half-cycle of waveform while blocking the other half-cycle. It can easily constructed using a single diode. As we know diodes can only carry current in a single direction, they work as sample half-wave rectifiers.
The half-wave rectifier is made of 3 components:-
- Diode
- Transformer
- Resistive Load
 Half-Wave Rectifier Working of Half Wave Rectifier
Now we are deep down in understanding how a half-wave rectifier transforms AC signal to DC.
- In the defined circuit of the half-wave rectifier, a high AC voltage as an input is given to the primary side of the step-down transformer.
- The diode is in forward bias during the positive half cycle of AC voltage and it is in reverse bias during the negative half cycle.
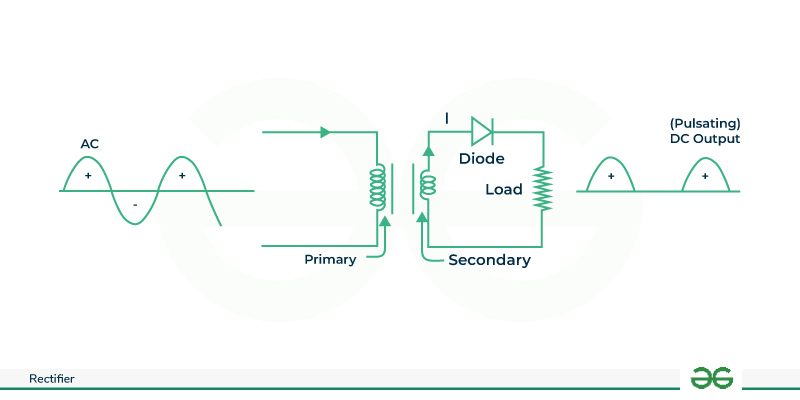 Working of Half Wave Rectifier Now we will simplify the half-wave rectifier circuit by replacing the secondary coil with a voltage source
 Voltage Source Now for the positive half side of the AC voltage source, the circuit will be
 AC Voltage Side Whenever the diode of the circuit is in forward bias it works as a closed switch but when it is in the negative half cycle the AC voltage source is equivalent to
 Open Ac Voltage Side When the diode is reverse-biased, the circuit acts as an open switch.
Half Wave Rectifier Waveform
 Half-Wave Rectifier Wave-Form Half Wave Rectifier Formula
- Ripple Factor :- It determines how half wave rectifier converts AC voltage to DC voltage. The ripple factor of the Half-wave rectifier is 1.21.

- Efficiency:- It is the ratio of DC output to AC input

- RMS value:- RMS value of load current

- Form factor :- It is the ratio of RMS value and average value

Types of half wave rectifier:
- Positive half wave rectifier
- Negative half wave rectifier
- Positive half wave rectifier: In the positive half wave rectifier only the positive half wave cycle of the AC current allowed to flow through the circuit while the negative half wave cycle get blocked this can be achieved by using single diode in the circuit.
 Diagram of positive half wave cycle rectifier 2. Negative half wave rectifier: In the negative half wave rectifier only the negative half wave cycle of the AC current allowed to flow though the circuit while the positive half wave cycle get blocked this can be achieved by reversing the orientation of diode used in the positive half wave rectifier.
 Diagram of negative half wave cycle rectifier Full Wave Rectifier A full-wave rectifier is a circuit that converts the full cycle of AC into pulsating DC.
Circuit of Full Wave Rectifier
For full wave rectifiers, we can design the circuit in two ways.
- In first method uses a center-tapped transformer and two diodes also called center center-tapped full wave rectifier.
- In the second method we use four diodes arranged in the form of a bridge also called a bridge rectifier.
A circuit that has a step-down transformer with two diodes is connected and tapped in the center.
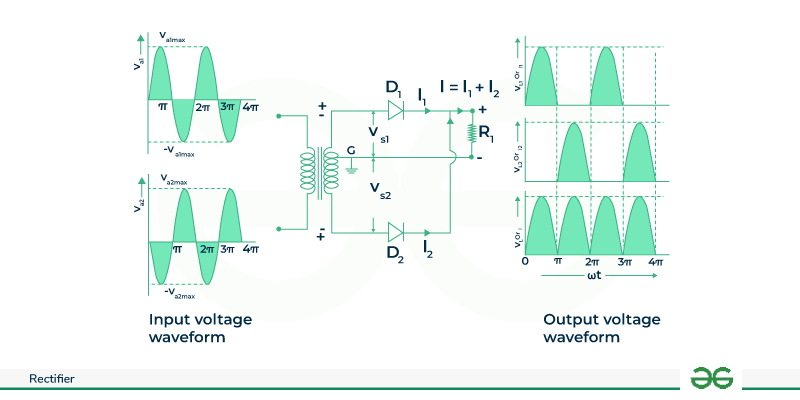 Center Tapped Rectifier Center Tap Full-wave RectifierWhen an input AC is supplied the to circuit the step-down transformer in the rectifier converts the high-voltage AC into low-voltage AC. The anode part of the circuit which is tapped in the center is connected to the transformer’s secondary winding and also same is connected to the load register. When the positive(+ve) has a cycle of the AC the upper half of the secondary winding becomes negative(-ve).
In the positive half cycle diode D1 is in a forward bias state as it is connected to the top of the secondary winding and diode D2 is in reverse bias as it is connected to the bottom part. Due to this D1 will act as a short circuit and D2 will act as an open circuit.
When the circuit is in the negative half cycle the D1 diode is reverse biased and the D2 is forward biased because the top half of the secondary circuit becomes negative and the other half becomes positive.
Full wave Rectifier Formulas:
There are some list of full wave rectifier formulas given below :
- Peak Inverse Voltage : It is the maximum voltage a diode can withstand in the reverse-biased direction before the circuit breaks. The peak inverse voltage of a full-wave rectifier is double that of a half-wave rectifier.
PIV across D1 and D2 is 2Vmax
- DC Output Voltage : The average value of DC output voltage is

- RMS Value : RMS value of the current is calculated as

- Form Factor :The form factor for the full wave rectifier is


- Rectification Efficiency : Efficiency of Full wave rectifier is 81.2 %

The full wave rectifier is further classified into two types :
- Bridge Rectifier
- Center Tap Rectifier
Full Wave Bridge RectifierDifferent parts of electronics require a rectified DC power supply to power various electronic basic components from the available AC main supply. Among the rectifiers, the bridges are the most efficient rectifier circuit. The bridge rectifier is a type of full wave rectifier that uses four or more diodes in a circuit to efficiently convert AC to DC.
Construction of Bridge Rectifier:
The bridge rectifier is made of four diodes let’s say D1, D2, D3, D4, and a load register RLan. All the diodes are connected with each other in a closed loop so that it can efficiently convert the AC to DC. The advantage of this configuration is the absence of an expensive center-trapped transformer.
 Bridge Construction An input signal is applied to terminals A and B, the output DC signal is obtained through the load register RL connected between terminals C and D. All 4 diodes are arranged in such a way that only 2 of the diodes conduct electricity during each occurring half cycle. The diode D12 and D4 conduct the electric current during the negative half cycle.
Working on Bridge Rectifier
When the Ac signal is supplied across the bridge rectifier, the terminal A becomes positive during half cycle and the B terminal becomes negative. This results in the D1 and D3 being in forward bias while D2 and D4 are in reverse bias.
 Working of Bridge Rectifier So, during this negative cycle, terminal B becomes positive, and terminal B becomes negative. It results in diode D2 and D4 in forward bias and D1 and D3 diodes are in reverse direction.
 Current Flow In Half-Cycle From the above discussion, we observed that the current flow in load register RL is the same in both cycles (during the positive and negative half cycle). The output DC signal polarity may be either positive or negative.
Hence a bridge rectifier allows electric current during both positive and negative half cycles of the input AC signal.
 Waveform:- AC and DC input Types of half cycles:
- Positive half cycle
- Negative half cycle
- Positive half wave cycle: Positive half wave cycle can be defined as the part of AC waveform in which the only half portion present is positive. During a positive half wave cycle voltage or current increases from zero up to its peak value then goes back to zero.
- Negative half wave cycle: The positive half wave cycle also signifies that just the positive section of the AC waveform exists; in this situation, voltage increases from zero to its negative peak before falling back to zero during a negative half wave cycle.
 Diagram of positive and negative half wave Center Tap Rectifier It is a type of rectifier which uses the center tapped transformer in order to convert AC signal to DC signals and also it uses two diodes for this. It allows the electric current to pass on in the positive and negative half cycles of the input AC signals, it uses center tapped transformer as its input. The efficiency of the circuit is high as the AC supply brings the power with the both halves of the cycle.
At the output of the center tap rectifier or the circuit, in order to make the stable DC output the ripple gets eliminated by the capacitor.
Controlled RectifierA rectifier whose voltage can be controlled means can be varied is known as a controlled rectifier. For controlling we use SCRs, MOSFET, and IGBT to make the uncontrolled rectifier into a controlled rectifier. These are proffered over the uncontrolled counterparts.
As the SCRs gets on or off at the gate signals then the complete control is established in the rectifier. The gate output is responsible for the controlling of the output voltage .The controlled rectifier is further classified into the following types:
- Half Wave Controlled rectifier
- Full Wave Controlled Rectifier
- Half-wave controlled rectifier: In a half wave controlled rectifier, input AC voltage control only one half cycle of the voltage. It is regulated by using a thyristor to control the current flow. Thyristor turned on when the input AC voltage half-cycle comes allowing current to flow hence one-cycle-half waveforms are generated at the output resulting into generation of DC waveform only on one half cycle as shown below. Therefore, half wave controlled rectifier cannot regulate output DC waveform as compared to full wave controlled rectifier.
- Full wave controlled rectifier: In full wave control rectification, both half-cycles are controlled. Thyristors are employed in to regulate currents flowing in either direction. The administering of control signals to turn ON the thyristors; which conduct during both half-cycles of the input AC voltages, results into flowing across them leading to production of DC with complete cycle waveshape output. Constructed with HTML tags. Is well as bursts than perplexing; even though the number of words has not been changed.
- Controlled bridge rectifier: A control bridge rectifier is a circuit that converts alternating current to direct current using four diodes in bridge configuration. It uses thyristors or similar devices to regulate the output voltage. The bridge rectifier’s output voltage and current can be regulated or adjusted as necessary by addition of these extra control components. This feature brings about a finer control of the DC output and is what makes the control bridge rectifiers appropriate for applications requiring variable DC outputs such as motor speed control, power supplies, and battery charging systems.
Benefits:
- Controlled Output: The output voltage can be precisely controlled thanks to the thyristors’ adjustable firing angle.
- Complete Utilization of AC Input: By utilizing the entire AC input, efficiency is increased.
- Versatility: Adaptable DC output allows for use in a wide range of applications.
Uses:
- DC motor drives
- DC power supply that are changeable
- Circuits for charging batteries
- Control systems for industry
Difference Between Half-Wave Rectifier and Full-Wave Rectifier
Properties
| Half-Wave Rectifier
| Full Wave Rectifier
|
|---|
| Definition
| Converts one-half of AC input into DC output
| Converts both halves of AC input into DC input
| Complexity
| Consist of a single diode
| It consists of a minimum of 2 diodes.
| Efficiency
| It utilizes only half the AC cycle.
| It utilizes the complete AC cycle.
| Voltage Regulation
| Poor
| Good
| Output Frequency
| Equal to the input frequency
| Twice the input frequency use both cycles.
| Output Voltage
| Vavg = 
| Vavg = 
| Rectification Efficiency
| 40.6% approx.
| 81.2% approx.
| Application
| Used for Low-Power application
| used in high power supply.
|
Application of RectifiersThe main application of rectifiers is to derive DC power from AC power. These are used in the power supplies of all types of electronic equipment. In power supplies, the rectifier is generally placed in series following the transformer, smoothing filter, and voltage regulator.
- Used in Powering Appliances: All electrical appliances use a DC power supply to function. By using a rectifier it helps in converting AC to DC power supply. Bridge rectifiers are used for large appliances which are capable of converting AC voltage to low DC voltage.
- Used With Transformers: With the help of a half-wave rectifier, it can help to achieve the required DC voltage by using a step-up and step-down transformer. The full wave rectifiers are used for powering the motor and LED which work on DC voltage.
- Used in soldering: A half wave rectifier is also used in soldering iron and also used in mosquito repellent to drive the lead for the fumes. In welding which is done with the help of electricity, the bridge rectifier is used to supply steady and polarized voltage.
Advantages and Disadvantages of RectifiersGiven Below are some of the Advantages and Disadvantages of Rectifiers:
Advantage- These are the simplest type of rectifier as they consist of only a few basic fundamental components.
- They are cheap and easy to use and construct.
- These rectifiers utilize both half cycles of the input AC voltage, which results in higher efficiency and less power loss.
- They produce a high amount of output voltage as compared to half-wave rectifiers.
Disadvantage
- These waste half of the energy and have a low utilization factor for transformers.
- They produce a very low output which may require other additional components for filtering.
- These rectifiers are more complex as compared to half-wave rectifiers and they also require large numbers of diodes.
- As they require a large number of components they are also expensive.
ConclusionIn conclusion, Rectifier plays an important role in converting AC to DC voltages. We have seen the working of Half-wave and full-wave rectifiers with differences between half-wave and full-wave rectifiers. We have also discussed several Applications of rectifier with their advantages and disadvantages. So basically it is a device which is used to convert AC signal to DC signal. The rectifier can take the shape of several physical forms like solid state diodes, vacuum tube diodes, mercury-arc valves, and other silicon-based semiconductor switches.
The P-N junction allows the current in the forward bias and blocks the current in the reverse bias. In simple words the P-N unction allows electric current in one direction only. This unique property of the diode allows it to behave like a rectifier.
FAQs on Types of RectifierWhat is the efficiency of the rectifiers? The efficiency of the rectifiers are defined as the ratio of output of DC power to the applied AC input power.
What is the maximum efficiency of a bridge rectifier?The maximum of the bridge rectifiers is 81.2%.
Which filter can’t be used after a half-wave rectifier? The series inductors and L filter cannot be used with half wave rectifier.
|



-(1).webp)













