|
|
OkHttp is pretty smart when it comes to dealing with tricky network situations. It quietly bounces back from common connection hiccups and even tries different addresses if the first attempt doesn’t work. This becomes crucial when you’re dealing with situations that use both IPv4 and IPv6 or when your services are set up in backup data centers. In this article, you are going to explore how you can use OkHttp in your Spring Boot application. Prerequisites:
What is OkHttp?OkHttp stands out as an HTTP client that prioritizes efficiency by default:
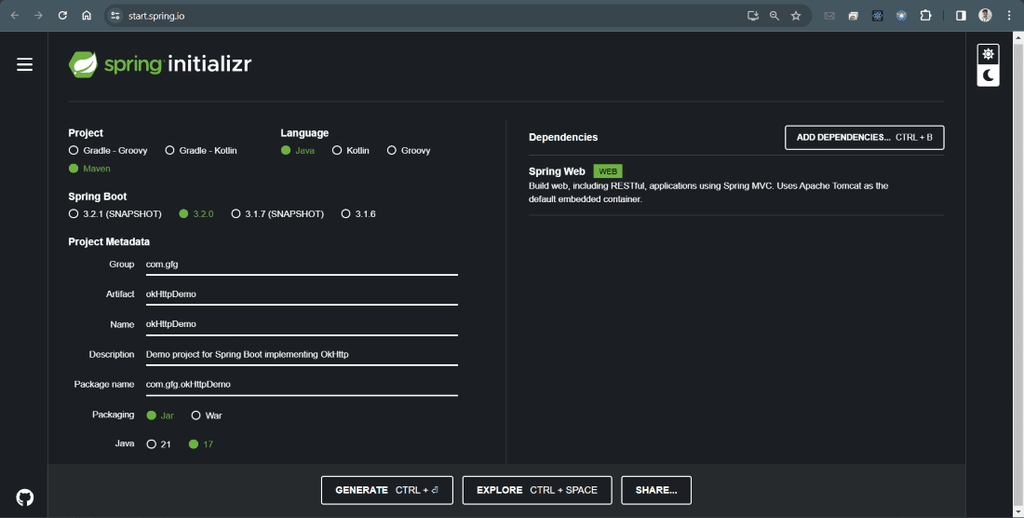
Using OkHttp is straightforward. Its request/response API employs fluent builders and immutability, facilitating ease of use. Whether you prefer synchronous blocking calls or asynchronous calls with callbacks, OkHttp accommodates both styles seamlessly. Implementation of OkHttp in an Spring Boot ApplicationLet’s get started with the implementation part to create a simple Spring Boot application that make API calls using OkHttp. Step-by-step ImplementationStep 1: Create a new Spring Boot ProjectTo create a new Spring Boot Protect, you can use Spring Initializer (https://start.spring.io/) or your preferred IDE. In the dependencies you need to select “Spring Web” dependency, as it will be useful for creating REST endpoints.
Step 2: Add OkHttp DependencyNow we need to add OkHttps dependency in the pom.xml file, paste the below code in the pom.xml or you can use the updated version from Maven website: <dependency> Now you are all set to write some code to use OkHttp in your Spring Boot Project. Step 3: Create a Service for API CallsFirstly, create a service class that will be responsible to handle API calls using OkHttp. For example, create a class named ApiService and write the below code inside the class. Java
This file consists of two service methods:
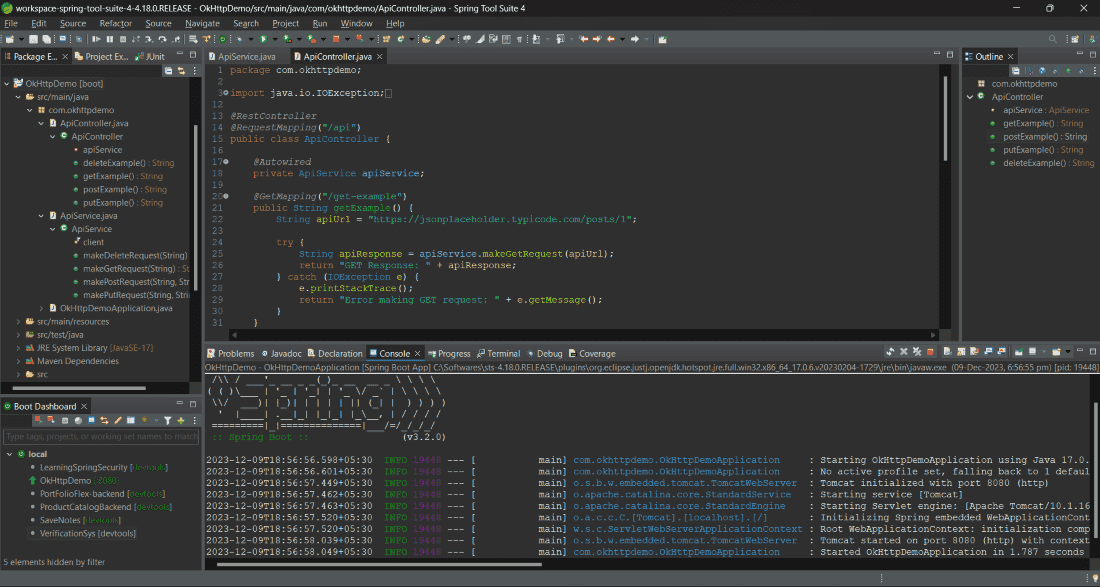
Step 4: Create a ControllerCreate a Spring MVC controller that will expose endpoints for triggering the API call. For example, create a class named ApiController. In this article, we are using https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com dummy API. Java
In the above code, you have two methods:
Step 5: Run the ApplicationTo run your Spring Boot application, you can run below Maven command in the terminal, or you can also use the IDE to run the application: mvn spring-boot:run
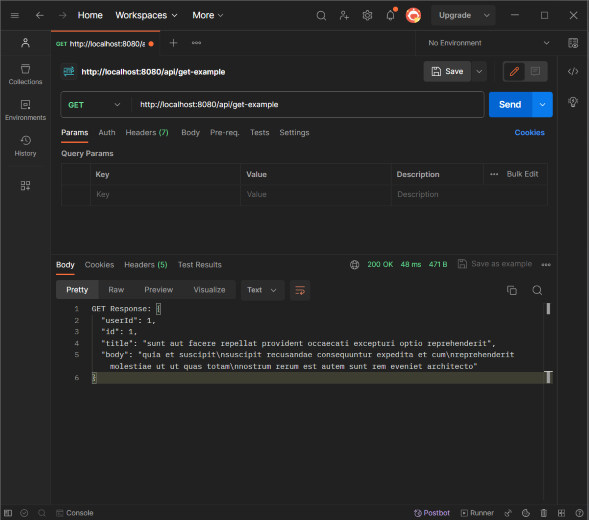
Step 6: Test the API CallFinally, to test the API call you can use your browser, a tool like cURL, or Postman to make GET/POST and other requests to the endpoints. You should see the API response or an error message. Let’s test the /api/get-example endpoint:Open Postman, then enter the URL like – http://localhost:8080/api/get-example and select GET request from left dropdown, finally click on send button, now a response will be generated.
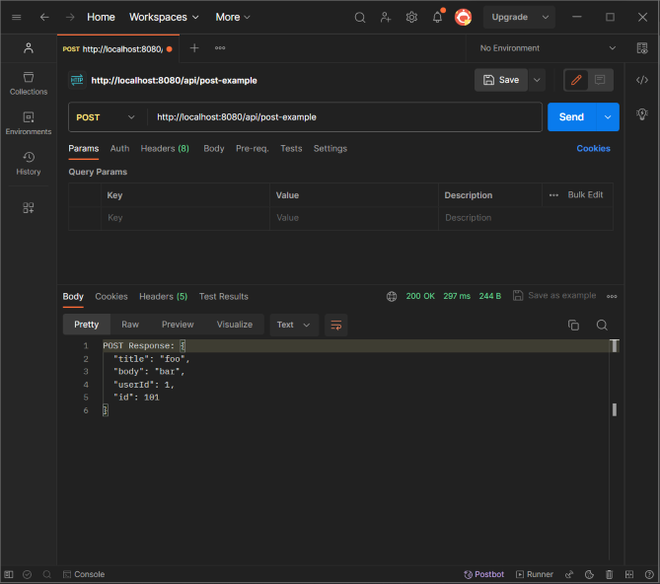
Now test the /api/post-example endpoint: Open Postman, then enter the URL like – http://localhost:8080/api/post-example and select POST request from left dropdown, finally click on send button, now a response will be generated. Remember to replace the example URLs with the actual URLs of the APIs you want to call.
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Advance Java |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 14 |