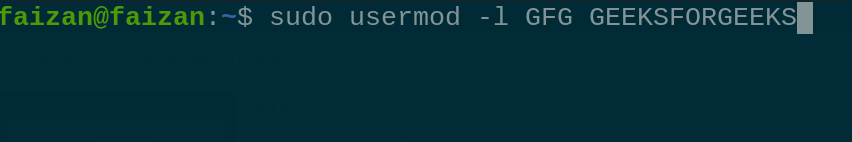
|
|
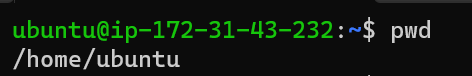
Linux fundamentals are crucial skills for a DevOps professional. Through this article, we will learn about all the required Linux commands which we will frequently use in a DevOps career. What is linux?Linux is a free and open-source software operating system , which developed by linus torvalds. It came from a unix family. it is compatibility with all major computer hardware such as x86 , ARM etc. File System in LinuxIn linux everything is represented as a file including a hardware program, the files are stored in a directory , and every directory contains a file with a tree structure. That is called file system hierarchy. Linux uses single rooted , inverted tree like structure. Root directory represents with / (forward slash). it is a top-level directory in linux. Basic command1. The `pwd` command helps you identify your location in the file system : `pwd` - Print Working Directory
 pwd 2. The `ls` command is used to list the files and directories in the current directory : `ls` - List Files and Directories
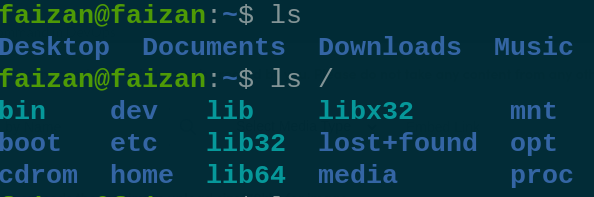 List Files and Directories 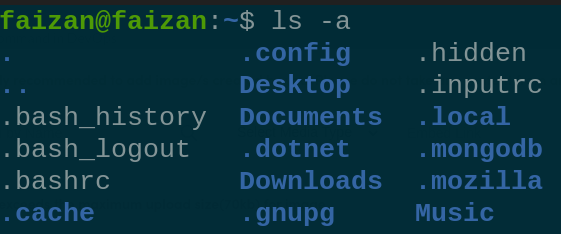 Display hidden file 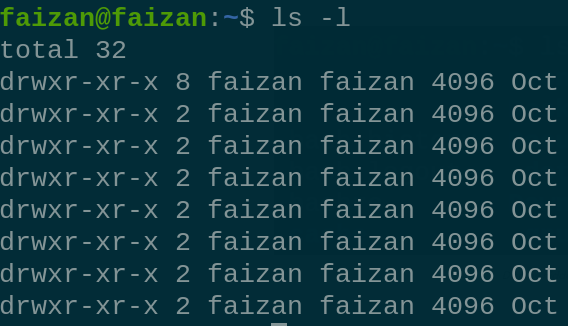 permission of all file 3. The `uname` command retrieves system information: uname - Print System Information
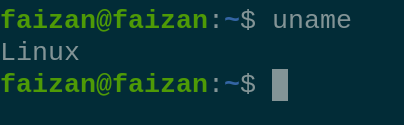 uname Note : By adding `-r ` flag to the `uname` command , you can display the kernal release version. uname -r Print Kernel Release Information
uname -r 4. The `cd` command allows you to navigate the file system by changing your current directory. cd - Change Directory
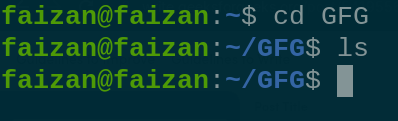 Cd 5. The `clear` command clears the terminal screen, providing a clean workspace. clear - Clear the Terminal Screen
 clear 6. `whoami` returns the username of the current user logged into the terminal. whoami - Display the Current User
whoami 7. `History` This command is used to display the history of the common that previously executed. history history
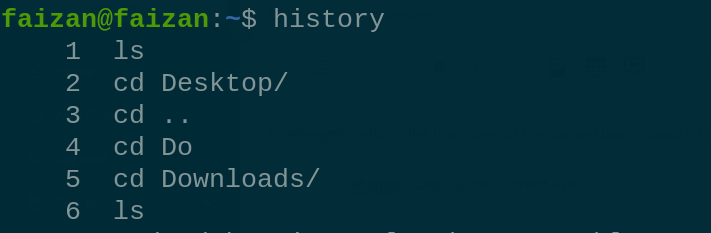 History 8. `free` This command is used to check the memory-related detail in your system. free
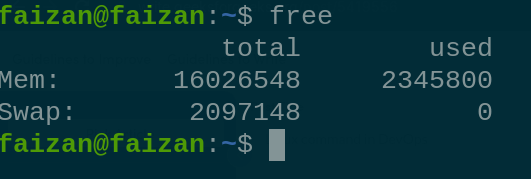 free 9. `nslookup` is used to obtain information for DNS server. it stands for Name Server Lookup. nslookup <domain name>
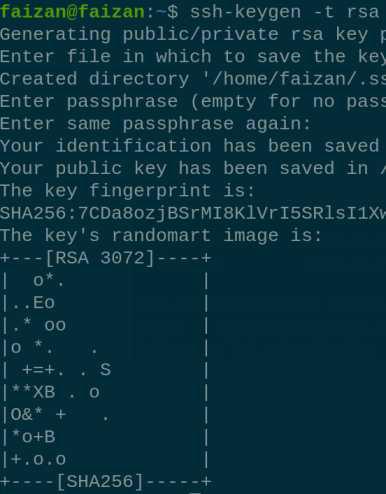
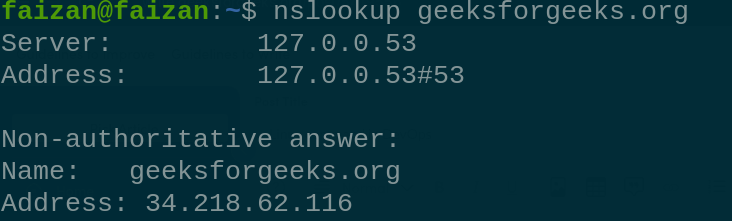 nslookup 10. `ssh-keygen` is used to establish a secure SSH connection from your host machine to any remote server. It generates a public/private key pair. ssh-keygen -t rsa
11 . `curl` is a tool which is used to fetch data and post the data over the internet. it can used various of protocol like HTTPS , SMTP and FTP. curl [options] [URL]
 curl 12 . `curl -o `flag saves the data into a file on the local machine. `curl -o [file_name] [URL...]
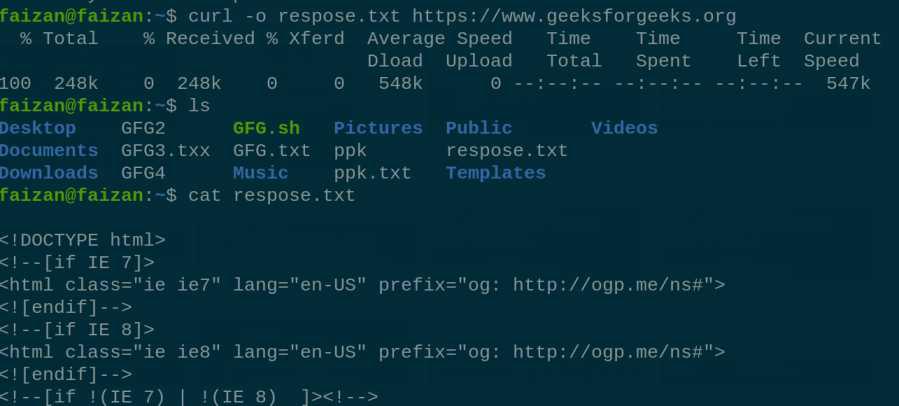 store response on local machine 13. apt-get command used to manage packages in the linux. APT stand for the Advanced Packaging Tool , and its main used of install , update , upgrade and remove the packages. apt-get [options] command
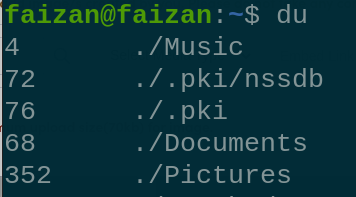
 apt 14 . `du` command is used to check disk usage space. du
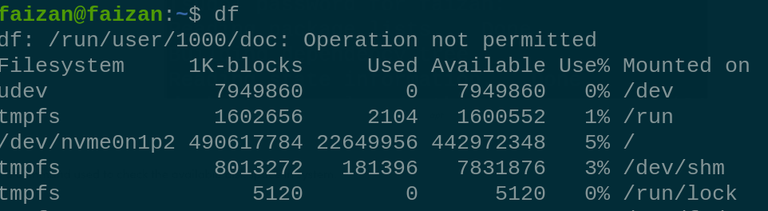
 du 15. `df` the is a command used to check the available disk space in system. df -h
 df 15. ifconfig is command is used to view the information about your network interface ifconfig [OPTIONS] [INTERFACE]
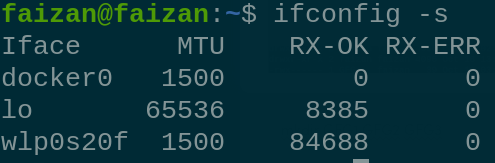 ifconfig Creating Files and Directories :In DevOps, creating and managing files and directories is a common task. Here are some essential commands : 1 . For creating a single directory: mkdir GFG
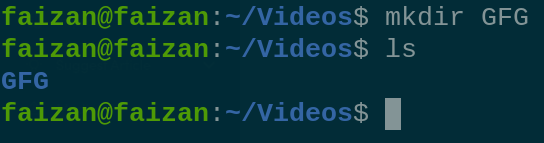 mkdir 2. For creating multiple directories: mkdir GFG1 GFG2 GFG3
mkdir gfg1 gfg2 gfg3 3. For creating directory paths (directories inside directories): mkdir -p /GFG/GFG1/GFG2
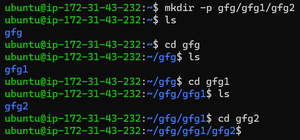 mkdir -p 4. For creating a series of numbered directories: mkdir gfg{1..3}
mkdir gfg{1..3} Copying and Pasting Files and Directories:The cp command is used for copying and pasting files or directories in Linux. Here are some commonly used options and examples: 1 . For copying a file with verbosity and force (overwrite if necessary): cp -rvf gfg1 gfg
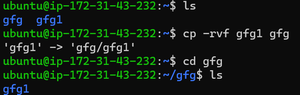 cp -rvf
|
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
sudo groupadd <groupname> |
Making a new group |
|
sudo groupdel <groupname> |
delete the group |
|
sudo usermod -g <groupname> <username> |
Adding a user to a group |
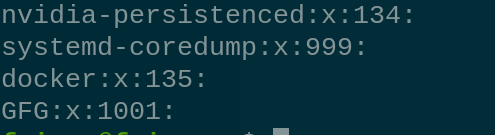
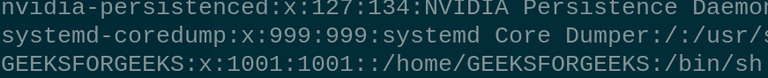
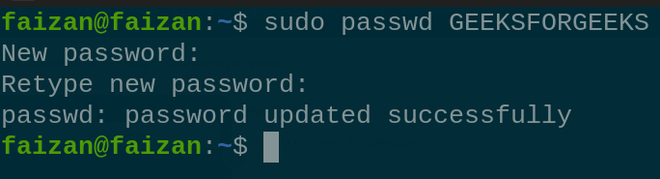
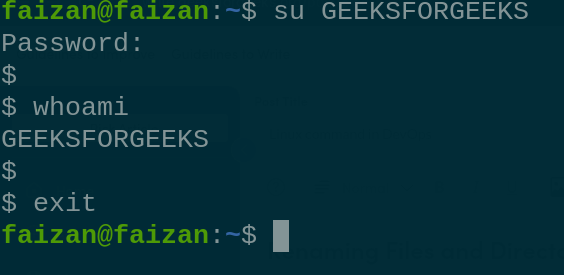
create the new Group called GFG
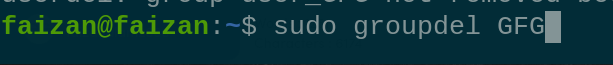
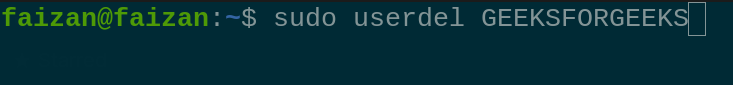
Delete the Group called GFG
Linux file system permission :
In linux , to increase the security of the file and directory. we need to used permission. There are total three type of file permission are Read , Write , Execute.
There are three type of file permission are as follow:
- user ( u ) : Permissions used for the user of the file.
- group( g ) : Permission used by the group member.
- other (o) : Permission used by all other users.
For example, suppose a file has read permissions that are allowed for the user. In this case, the user can only read that file, while the group and others will not be able to read it.
1 . `ls -ld` it is used to check the permission of directory
ls -ld
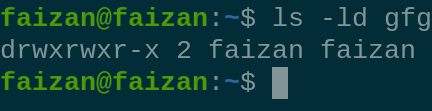
check the permission of directory
|
Permission |
Access for a file |
Access for a directory |
|---|---|---|
|
Read (r) |
display file contents and copy the file |
view contents of directory |
|
Write (w) |
modify the file contents |
modify the contents of a directory |
|
Execute (x) |
execute the file if it an executable permission |
allow use of cd command to access the directory |
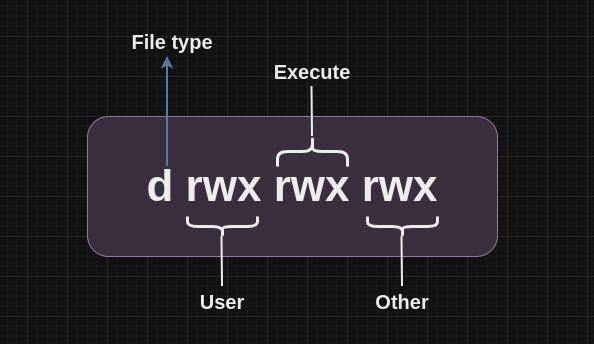
File Permission classes
Permission with numeric & symbol
|
Number |
Permission Type |
Symbol |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
No permission |
— |
|
1 |
Execute |
–x |
|
2 |
Write |
-w- |
|
3 |
Execute +Write |
-wx |
|
4 |
Read |
r– |
|
5 |
Read + Execute |
r-x |
|
6 |
Read +Write |
rw- |
|
7 |
Read + Write + Execute |
rwx |
2. chmod This command is used to change the permission of file and directory.
chmod <permission of user , group , other> {filename }
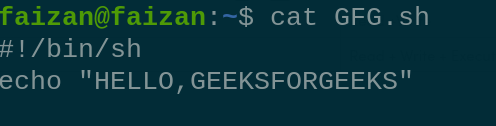
GFG file
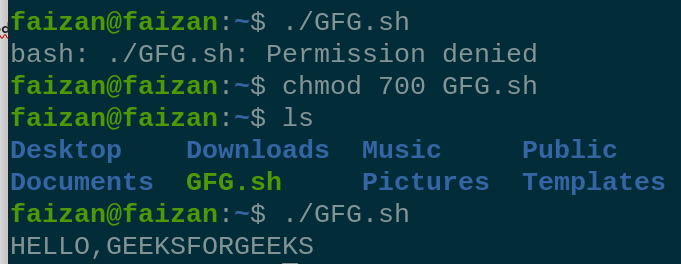
Give execution permission
3. chown : It is used to change the owner of the file and directory.
chown [owner_name] [file name]
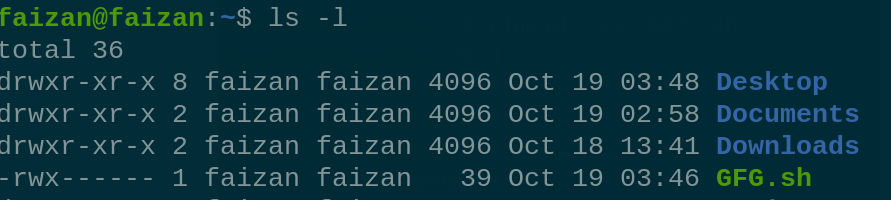
current ownership is faizan
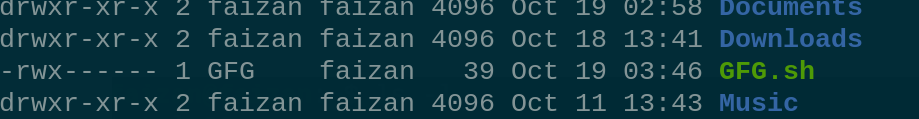
ownership change to GFG user
4. cat : it is used to read and concatenate the text inside the files. with help of this command we can displays the content inside the file.
cat <flag> {filename}
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
cat -b |
This flag adds number to the text line. |
|
cat -E |
This flag add $ at the end of each line. |
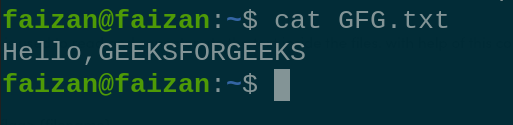
Display the contain the file GFG
5. Grep (Global Regular Expression Print) : It filter searches a file for a particular pattern of characters , and displays all lines that contain the pattern.
grep <flag or search_word> {file name}
Command |
Description |
|---|---|
|
grep -i |
Delivers results for case-insensitive strings. |
|
grep -n |
Retrieve the corresponding strings and their respective line numbers. |
|
grep -v |
Provides the output of lines that do not contain the search string. |
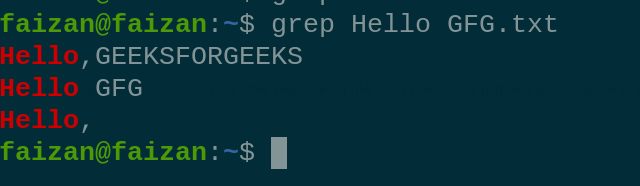
Search key word Hello from GFG.txt
Conclusion
In conclusion, this article has emphasized the vital role of Linux fundamentals in the toolkit of a DevOps professional. By providing insights into essential Linux commands and concepts, it equips individuals in the field to efficiently navigate file systems, manage users and groups, implement file permissions, and perform a variety of tasks critical for the success of DevOps operations, ultimately contributing to the security and functionality of their systems.
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| Geeks Premier League |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 10 |