
|
|
Data protection is very crucial in today’s modern tech era. Especially for any organization that stores the personal details of their customers in their database. The main goal of SQL Data Encryption is to protect unauthorized access to data within or outside the organization. In this article, we will be going through the basics of SQL data encryption, its types, and methods to implement Data Encryption in SQL databases. What is SQL Data Encryption and How it Works?SQL data encryption involves converting the sensitive data of the database into an unreadable format using various kinds of cryptographic algorithms. Only responsible persons will be able to access the actual data through the decryption key. The SQL database supports various encryption methods, each with its unique characteristics and applications. Before deep diving into the types of SQL data encryptions let us understand how encryption works.  Workflow of Encryption Types of SQL Data EncryptionTransparent Data Encryption(TDE)
How to implement TDE?We can implement the Transparent Data Encryption using the 4 simple steps.
In order to implement the encryption we are creating the following demo table for better understanding. CREATE TABLE Student INSERT INTO Student VALUES Output Database before Encryption 1. Create database Master key using the below command you can choose password of your choice. USE dba; 2. Create Certificate using the below command USE dba; 3. Create the Encryption Key using the below command. USE dba 4. Configure the database to enable encryption using the below command ALTER DATABASE dba After Encryption we can see the data is encrypted completely.  After Encryption Column-Level Encryption
How to implement CLE?We can implement the Column level encryption using the 5 simple steps.
In order to implement the encryption we are creating the same table we used for TDE for better understanding. CREATE TABLE Student INSERT INTO Student VALUES Output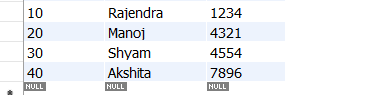 Database before encryption 1. Create the database master key using the following command. USE Student; 2. Create the self signed certificate using the following command USE Student; 3. Configure a symmetric key for column level encryption using the following command. CREATE SYMMETRIC KEY SymKey_test WITH ALGORITHM = AES_256 ENCRYPTION BY CERTIFICATE Certificate_test;
4. Select the column in which you want to encrypt the data using the following command. ALTER TABLE Student After Encryption we can see that now the data is unidentifiable.  After encryption Benefits of SQL Data EncryptionFollowing are the benefits of the SQL data encryption:
ConclusionThe data encryption is very crucial if you are an organization and you are storing the data of your customers. The choice on the type of encryption completely depends on your personal choice whether you want to encrypt the whole data or selective data. If you want to encrypt the whole data then go with TDE and if you want to encrypt the selective data then go with CLE. Ultimately we hope that this article helped you to understand about the SQl data encryption. FAQs on SQL Data EncryptionQ.1: Is SQL data encryption necessary?Answer:
Q.2: What is the role of certificate in SQL data encryption?Answer:
Q.3: What is the difference between symmetric and asymmetric encryption?Answer:
Q.4: Which encryption method should we use TDE or CLE?Answer:
|
Reffered: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org
| DBMS |
| Related |
|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Type: | Geek |
Category: | Coding |
Sub Category: | Tutorial |
Uploaded by: | Admin |
Views: | 16 |